OPT13 – Information Theory
TP2: Compression, Prediction, Generation Text Entropy
信息论作业代写 Given a text of length n, a sequence of symbols is just a vector (x1, . . . , xn) where each xi is a symbol i.e. xi = a, b, c, ….
In this TP we are interested in compressing and generating texts written in natural languages.
Given a text of length n, a sequence of symbols is just a vector (x1, . . . , xn) where each xi is a symbol i.e. xi = a, b, c, …. 信息论作业代写
In order to model the sequence of symbols we need a joint probability distri- bution for each symbol in the sequence, namely p(X1 = x1, X2 = x2, . . . , Xn = xn). If our alphabet had M symbols, for modelling a sequence of length n we would need M n probabilities. Thus some assumptions are required in order to reduce this dimensionality. In this case we will use two different models for p, the IID and the Markov Chain model.

IID Model
The first model assumes:
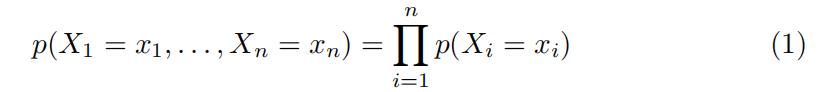
i.e.that the symbols in a sequence are independent and identically distributed. In this can we need now only M probabilities, one for each symbol. One can generalize and use symbols not of a single character but of multiples ones. For example using 3 characters per symbol, the symbols would be of the form aaa,aab,…,zzz. When using k characters per symbols in an alphabet of M characters, the needed probabilities would be Mk.
Markov Chain Model 信息论作业代写
The Markov Chain model assume a limited range of dependence of the symbols. Indeed for an order k Markov Chain:
p(Xi|Xi−1, . . . , X1) = p(Xi|Xi−1, . . . , Xi−k) (2)
* https://www.lri.fr/ gcharpia/informationtheory/
The meaning of the above structure is that the i-th symbol in the sequence depends only on the previous k symbols. We add the time invariant assumption, meaning that the conditional probabilities do not depend on the time index i i.e. p(Xi Xi−1, . . . , Xi−k) = p(Xk+1 Xk, . . . , X1). The most common and widely used Markov Chain is the Markov Chain of order 1:
p(Xi|Xi−1, . . . , X1) = p(Xi|Xi−1) (3)
In this case the conditional probability p(Xi Xi−1) can be expressed using M 2 numbers.
Questions 信息论作业代写
- Interpret the time invariant assumption associated to our Markov chains.
- How can we rewrite a Markov chain of higher order as a Markov chain of order1?
- Givena probability distribution over symbols, how to use it for generating sentences?
In order to construct our IID and Markov Chain models we need some text. Our source will be a set of classical novels available here. We will use the symbols in each text to learn the probabilities of each model. 信息论作业代写
Practical For both models, perform the following steps:
- For different orders of dependencies, train the model on a novel andcom- pute the associated What do you observe as the order increases? Explain your observations.
- Use the other novels as test sets and compute the cross-entropy for each model trained previously. How to handle symbols (or sequences of sym- bols) not seen in the trainingset? 信息论作业代写
- For each order of dependencies, compare the cross-entropy with the en- Explain and interpret thedifferences.
- Choose the order of dependencies with the lowest cross-entropy andgen- erate some
- Train one model per novel and use the KL divergence in order to cluster the novels.
Implementation hints 信息论作业代写
- It is possible to implement efficiently the two models with dictionariesin Python. For the IID model, a key of the dictionary is simply a symbol and the value is the number of occurrences of the symbol in the text. For a Markov chain, a key of the dictionary is also a symbol, but the value is a vector that contains the number of occurrences of each character of the alphabet. Notice that a symbol may consist of one or several characters. Note also that there is no need to explicitly consider all possible symbols; the ones that are observed in the training set are sufficient.
- Alow probability can be assigned to symbols not observed in the training set. How to choose this probability?

更多代写:cs作业代写 online quiz代考推荐 英国作业代写案例 课程论文作业代写 英国医学代写 英国项目管理论文代写

