QM 7003 Operation Research
Midterm Exam
Operation Research期中代考 Discuss the role of models in decision making. Include the reasons for use, benefits, and potential pitfalls.
(9) 1. ESSAY Operation Research期中代考
a) Discuss the role of models in decision making. Include the reasons for use, benefits, and potential pitfalls.
(6) b) Explain the effect of degeneracy on the interpretation of LP sensitivity analysis.
(5) c) List the advantages of using a network model to solve a problem as opposed to linear programming.
(20) 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE
1) When using a quantitative decision model, the following is always true:
a.The objective is to maximize the profit.
b.The model does no more than refine raw data into more useful data.
c.The model will selectively describe the environment.
d.All of the above
2) A manager asking a “what if’ question is asking the following:
a.How sensitive is the model to changes in the objective?
b.What happens to a quantity of interest if some characteristic of the operating environment is changed in a specified way?
c.What happens if no decision variables are designated? Operation Research期中代考
d.All of the above
3) The process of building a quantitative model consists of the following three steps:
a.1) Study the environment
2) Formulate a selective representation of the problem
3)Construct a symbolic expression of the formulation
b.1) Define the variables
2) Specify the objective function
3) Determine the constraints
c.1) Study the environment
2) Specify the objective function
3)Select the appropriate solution algorithm
d.1) Collect the relevant data
2) Analyze the data for accuracy and completeness
3) Enter the data into a computer spreadsheet and pick the best answer
4) Consider the following statements:
i) A model is valuable if you make better decisions with the model than you would make without the model.
ii) Intuition is important during the problem recognition and formulation phases, but is not crucial during the implementation phase.
iii) If the recommendations generated by the model do not agree with a manager’s intuition, then the model must be wrong.
Which of these statements is/are true?
a.(i) only
b.(i) and (ii) only
c.(i), (ii) and (iii)
d.None of the above
5) Assume that an LP modeler has generated the following:
Total hours. available in Dept. A = 1000(1-e-.05MA)
where MA = Number of people scheduled to work in Dept. A.
Which of the following is true?
a.In the formal LP model, the RHS of the appropriate constraint would have to be written as: 1000 – 1000e.O3MA
b.e would be treated as a variable.
c.MA would have to be treated as a variable to make the problem linear.
d.None of the above
6) The following are true statements about the geometry of two-dimensional
graphic solutions:
a.Active constraints always pass through the optimal corner point.
b.Inactive constraints never pass through the optimal corner point.
c.Equality constraints always pass through the optimal corner point.
d.All of the above
7) Which of the following statements are true? Operation Research期中代考
i) If there is an optimal solution, there will always be at least one optimal corner point.
ii) To find the best feasible decision, one plots a single objective function contour, then displaces this contour in the optimizing direction until a corner solution is identified.
iii) ≥ constraints have surplus, ≤ constraints have slack.
a.(i) only
b.(i) and (ii) only
c.(i), (ii) and (iii)
d.None of the above
8) Suppose that sensitivity analysis reveals that a model is very sensitive to a particular parameter.
a.This would lead management to take a particular interest in the precise value of that parameter.
b.This would lead management to formulate the model in such a way that the particular parameter in question would not be involved.
c.This would weaken management’s overall confidence in the LP model.
d.All of the above
9) Changing only one of the objective function coefficients will always:
a.produce a change in the optimal objective value
b.change the slope of the objective function contours
c.result in a change for one or more decision variables
d.All of the above
10) Adding constraints to a model can:
a.impair the OV
b.leave the OV unchanged
c.Both (a) and (b)
d.Neither (a) nor (b)
11) Consider an LP with m constraints and n decision variables. At the optimal
corner, the number of variables with positive values will be less than or equal to:
a.m
b.n
c.m + n
d.m – n
12) The dual price for a given constraint:
a.is the rate of improvement in the OV as the RHS of that constraint is increased
b.may be interpreted only within the range determined by using the figures in the ALLOWABLE INCREASE and ALLOWABLE DECREASE columns for that constraint
c.will be 0 if the constraint is inactive
d.All of the above
13) For an inactive constraint in the primal problem:
a.the corresponding dual variable will be positive
b.the corresponding dual variable will be nonnegative
c.the corresponding dual variable will be 0
d.None of the above

14) The main difference between the Northwest Corner Rule and the VAM is that Operation Research期中代考
the VAM:
a.does not consider costs when allocating supplies
b.does consider costs when allocating supplies
c.assigns the minimum possible to the maximum cost cell
d.None of the above
15) The LP formulation for an assignment problem with 4 tasks to be accomplished
and 4 individuals available to do these tasks will have _______ decision variables:
a.4
b.8
c.16
d.None of the above
16) In a capacitated transshipment problem, intermediate nodes that are neither
supply points nor demand points are termed:
a.transshipment arcs
b.transshipment nodes
c.starting nodes
d.None of the above
17) If a maximal flow network has been cut, the cut capacity is:
a.equal to the sum of the arcs along the shortest path cut
b.equal to the sum of the arcs in the set with the sink
c.equal to the sum of the arcs in the set with the source
d.None of the above
18) Consider any primal problem and its corresponding dual. The following will always be true:
a.The optimal value for the primal and the dual will be the same.
b.The primal will have an optimal solution if and only if the dual has an optimal solution.
c.If the primal is infeasible, then the dual will be infeasible.
d.All of the above
19) The following are examples of interactions between the manager and the model:
a.Problem identification
b.Input data acquisition
c.Comparison of output with experience and judgment
d.All of the above
20) The application of LP to a decision problem is an example of decision making
under:
a.risk
b.uncertainty
c.certainty
d.stochastic dominance
e.None of the above
QM7003
Midterm Exam
Open Book Part Operation Research期中代考
(26) 1. The Ajax Appliance Corporation (AAC) makes both large and small appliances, and recently, they have introduced two new refrigerators. Both are small, and are for use in offices, dorm rooms, etc.
The manager of the refrigerator division at AAC has obtained demand forecasts from the marketing department for the coming quarter:
| Estimated demand in: | |||
| Product | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 |
| Standard refr. | 100 | 120 | 120 |
| Deluxe refrig. | 80 | 85 | 90 |
To make a refrigerator of either type requires 20 hours of labor, and AAC will have only 4,000 hours of labor available during each of the next three months. Because both products are new, there will be no starting inventories at the beginning of month 1. However, the manager would like to have at least one refrigerator of each type at the end of the third month (for display purposes).
Suppose that the manager bad also been able to tabulate the following:
| PRODUCT | Selling price/unit next quarter | Production cost/unit next quarter |
| Standard | $ 100 | $ 72 |
| Deluxe | $ 140 | $ 100 |
Formulate an LP model to determine a production and inventory schedule to maximize profits over the next 3 months.
(20) 2. Solve the following problem graphically. Determine exact values of the decision variables and which constraints are binding. Operation Research期中代考
Given the following LP problem where the objective function is a profit expression:
Let x1, x2 = number of units of products 1 and 2 to produce, respectively
(28) 3. Consider the following LP and solution:
Let T, C = # of tables and chairs to produce next month
MAX the PROFIT: MAX 40T + 18C
s.t. 8T + 5C < 160,000 (bd-ft lumber)
5T + 6C < 150,000 (hrs labor)
T < 9,000 (table leg avail)
T > 4,000 (table contract)
C > 5,000 (chair contract)
T>0 C>0
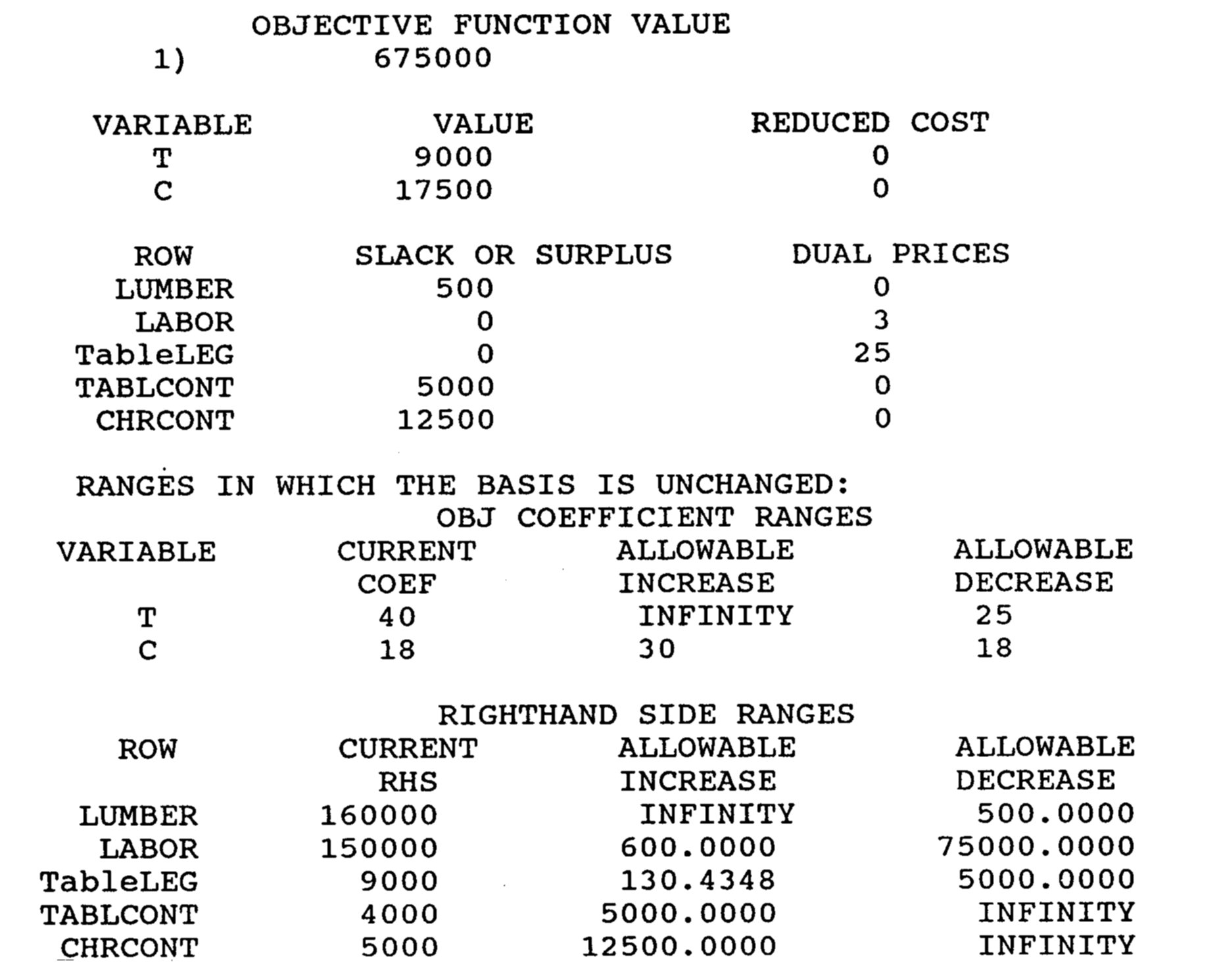
a.What is the optimal solution and associated profit?
b.Which constraints are binding?
c.Will any of the three resources be unused? If so, which one(s), and how many units will not be required?
d.Suppose that the manager of the firm could get more labor hours, but would have to pay overtime rates if he did so. This would increase the cost by $2 per additional hour. Should he get more labor? If so, how many additional hours?
e.Suppose that the marketing department informed the manager of increased competition and recommended that the selling price per table be reduced by $10. If no other revenue or cost data changed, what would happen to the optimal product mix of tables and chairs if this reduction were implemented?
f.Is the solution degenerate? Why or why not? Operation Research期中代考
g.Suppose that the manager was informed that he would have 400 less board feet of lumber next month and 15,000 fewer labor hours. What would this do to the optimal basis? optimal solution? optimal profit?
h.The marketing department would like to offer a new TV stand that would use 14 board feet of lumber and 4 hours of labor. The marketing department has priced the next product so that its profit contribution would be $16. Should they produce it?
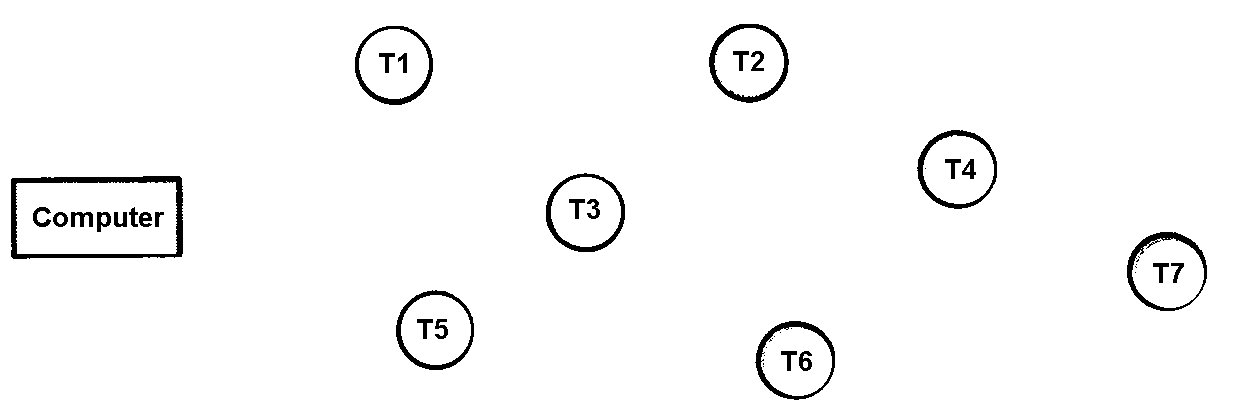
(18) 4. Your company plans to install an information system composed of a mainframe computer and seven terminals.
The computer may be connected directly to a terminal or a terminal may be connected to another terminal that is connected to the computer. The matrix of distances is given below (an x means no direct connection is possible), as well as the map of terminals and computer locations. Find the optimal installation plan.
| Terminal Number | ||||||||
| Computer | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | |
| Terminal | — | 20 | 48 | 25 | 61 | 21 | 37 | 60 |
| T1 | 20 | — | 30 | 32 | 60 | 50 | 65 | 85 |
| T2 | 48 | 30 | — | 22 | 33 | 40 | x | 73 |
| T3 | 25 | 32 | 22 | — | 36 | 18 | x | x |
| T4 | 61 | 60 | 33 | 36 | — | 67 | 52 | 40 |
| T5 | 21 | 50 | 40 | 18 | 67 | — | x | x |
| T6 | 37 | 65 | x | x | 52 | x | — | x |
| T7 | 60 | 85 | 73 | x | 40 | x | x | — |
(18) 5. The network in Figure 6-10 shows the routes for shipping cars from three plants (nodes 1, 2, and 3) to five dealers (nodes 6 through 10) by way of two distribution centers (nodes 4 and 5). Assume that the unit shipping cost from node i node j is cij. Answer the following:
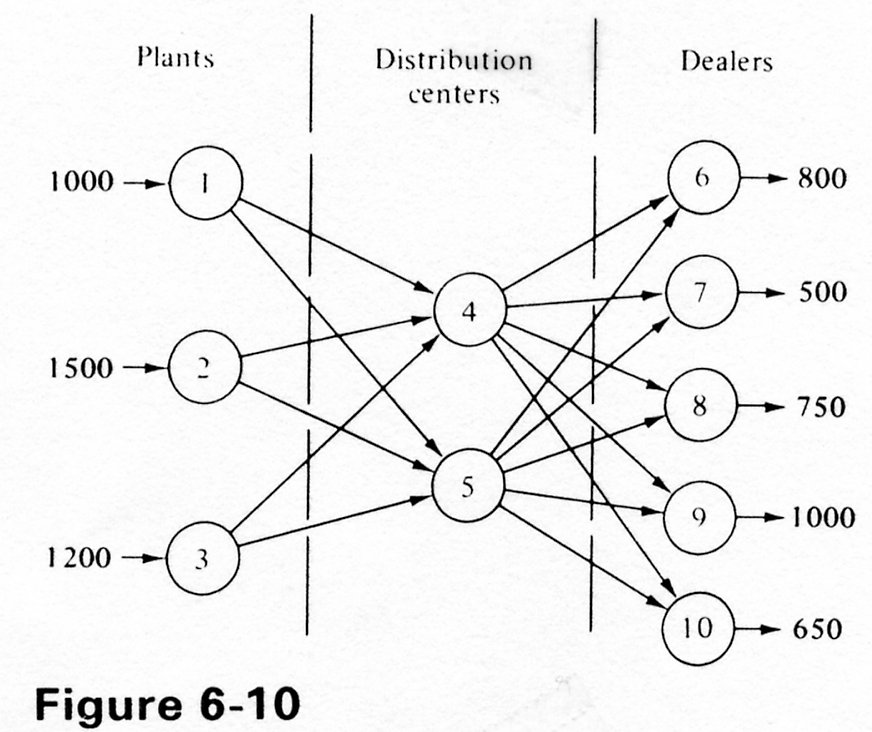
Graphically reformulate the network model so that transshipping is allowed among the dealers and ensure that distribution center 4 will ship 240 cars directly to customers.


