副标题#e#
方针:
这次进修的方针是答复下面的几个问题:
1 图片像素是如何被扫描的?
2OpenCV 矩阵值如何被存储?
3如何权衡算法的机能?
4什么是查找表和为什么要用他们?
看完这篇,但愿可以或许办理上面的这些问题。
正文:
首先我们思量一下简朴的色彩低落要领(color reduction method,翻译的欠好请指正),假如利用的是c或c++无标记的char(八字节巨细的空间),一个信道(channel)有256个差异的值(2^8=256),可是假如利用的是GRB方案,三个channel的话,颜色的数量就会变为256*256*256,或许是16个million这么多,这么多的颜色数量,对付计较机来说仍然是一个承担,所以可以想一些要领来低落这些色彩数量。
可以利用简朴的要领来低落图像色彩空间,好比,将0-9的数字都统一用0来取代,10-19的数字都统一用10取代。这种转换方案可以用下面的公式暗示
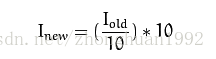
通过上面的公式,把所有像素点的值更新一下。可是,上面的公式中有除法,这里要表达一个是,计较劲较量多的环境下,不消乘除,就不要用,最好把他们转换为加减。我们知道,在转换前像素点的值只有256个,所以我们可以用查找表的方法,我们事先把所有的计较功效都生存在一个数组里,每次要执行上面的公式计较的时候,功效直接从数组里取出来就ok了。好比32对应30,表table[32]=30是早计较出来的,直接会见table[32]就OK了。
图片矩阵如安在内存中存储的:
灰度图片的矩阵存储方法:
灰度图片的每一个像素点,只由一个值来暗示,所以,就是一个普通的二维矩阵。

彩色图片的矩阵存储方法:
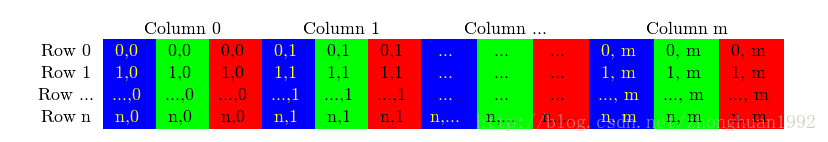
彩色图片的存储方法和灰度图片纷歧样,这里展示的是RGB名目标,可以看到,每一个像素,由三个值,代表蓝色,绿色,赤色的三个数值暗示,存储方法不是三维的,而是二维,不外列向量放大了三倍。从图片中可以清楚的看到。
#p#副标题#e#
效率:
较量像素数量低落方法效率的代码,在本文的最后头,代码看上去许多,其实布局较量简朴,看一会儿就大白了。附上一张功效图:
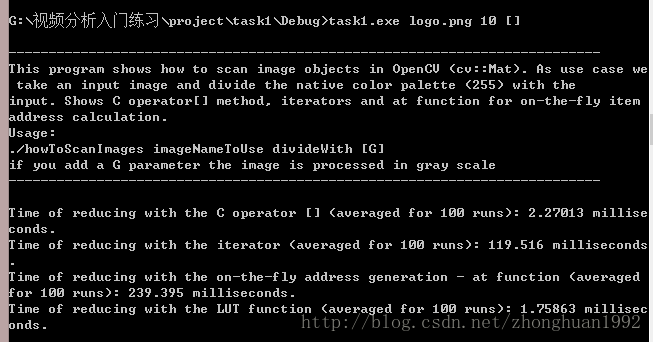
最快的OpenCV内的LUT函数。关于LUT,看这里
可以大致的看一下代码,代码不难,很容易懂:
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void help()
{
//这里提示输入有三个参数,第一个是图像的名字,第二个是参数是公式中的低落颜色数的数字,这里是10,第三个参数,假如是[G]代表是灰度图片,不然不是。
cout
<< "\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< "This program shows how to scan image objects in OpenCV (cv::Mat). As use case"
<< " we take an input image and divide the native color palette (255) with the " << endl
<< "input. Shows C operator[] method, iterators and at function for on-the-fly item address calculation."<< endl
<< "Usage:" << endl
<< "./howToScanImages imageNameToUse divideWith [G]" << endl
<< "if you add a G parameter the image is processed in gray scale" << endl
<< "--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< endl;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I, const uchar* table);
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I, const uchar* table);
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar * table);
/*
措施主要是看差异的color reduction方法对付措施运行速度的影响。
利用getTickCount()函数来获取当前时间,操作当前时间-上次获取的时间,来获得运行时间
*/
int main( int argc, char* argv[])
{
help();
if (argc < 3)
{
cout << "Not enough parameters" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat I, J;
if( argc == 4 && !strcmp(argv[3],"G") )
I = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
else
I = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
if (!I.data)
{
cout << "The image" << argv[1] << " could not be loaded." << endl;
return -1;
}
int divideWith = 0; // convert our input string to number - C++ style
stringstream s; //利用stringstream来认真将参数转换为数字
s << argv[2];
s >> divideWith;
if (!s || !divideWith)
{
cout << "Invalid number entered for dividing. " << endl;
return -1;
}
uchar table[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
table[i] = (uchar)(divideWith * (i/divideWith));
const int times = 100;
double t;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
J = ScanImageAndReduceC(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the C operator [] (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
J = ScanImageAndReduceIterator(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the iterator (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the on-the-fly address generation - at function (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U);
uchar* p = lookUpTable.data;
for( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
p[i] = table[i];
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
LUT(I, lookUpTable, J);
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the LUT function (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
return 0;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols * channels;
if (I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i,j;
uchar* p;
for( i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for ( j = 0; j < nCols; ++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<uchar>(), end = I.end<uchar>(); it != end; ++it)
*it = table[*it];
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<Vec3b>(), end = I.end<Vec3b>(); it != end; ++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
}
}
return I;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
I.at<uchar>(i,j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i,j)];
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
{
_I(i,j)[0] = table[_I(i,j)[0]];
_I(i,j)[1] = table[_I(i,j)[1]];
_I(i,j)[2] = table[_I(i,j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}
作者:csdn博客 钟桓
