副标题#e#
假如思量应用措施的兼容性和可移植性,指针的长度就是一个问题,在大部门现代平台上,数据指针的长度凡是是一样的,与指针范例无关,尽量C尺度没有划定所有范例指针的长度沟通,可是凡是实际环境就是这样。可是函数指针长度大概与数据指针的长度差异。
指针的长度取决于利用的呆板和编译器,譬喻:在现代windows上,指针是32位或是64位长
测试代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stddef.h>
struct p{
int n;
float f;
};
int main()
{
struct p *sptr;
printf("sizeof *char: %d\n", sizeof(char*));
printf("sizeof *int: %d\n", sizeof(int*));
printf("sizeof *float: %d\n", sizeof(float*));
printf("sizeof *double: %d\n", sizeof(double*));
printf("sizeof *struct: %d\n", sizeof(sptr));
return 0;
}
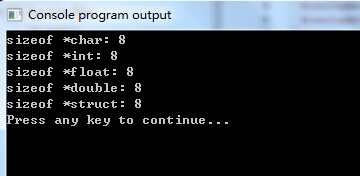
运行功效:
指针相关的预界说范例:
size_t:用于安详地暗示长度
ptrdiff_t:用于处理惩罚指针算术运算
intptr_t:用于存储指针地点
uintptr_t:用于存储指针地点
size_t范例
size_t 范例是尺度C库中界说的,应为unsigned int,在64位系统中为 long unsigned int。 C语言中,此范例位于头文件stddef.h中。它是一个与呆板相关的unsigned范例,其巨细足以担保存储内存中工具的巨细,它的目标是提供一种可移植的要领来声明与系统中可寻址的内存区域一致的长度:
因为C/C++尺度只界说一最低的位数,而不是必须的牢靠位数。并且在内存里,对数的高位对齐存储照旧低位对齐存储各系统都纷歧样。为了提高代码的可移植性,就有须要界说这样的数据范例。一般这种范例城市界说到它详细占几位内存等。虽然,有些是编译器或系统已经给界说好的。经测试发明,在32位系统中size_t是4字节的,而在64位系统中,size_t是8字节的,这样操作该范例可以加强措施的可移植性。
size_t范例用作sizeof操纵符的返回范例,同时也是许多函数的参数范例,包罗malloc和strlen
在声明譬喻字符数、可能数组索引这样的长度变量时用size_t是好的做法,它常常用于轮回计数器、数组索引,有时候还用在指针算术运算上
打印size_t范例的值要小心,这是无标记值,假如选错名目说明符,大概会获得不行靠的功效,推荐的名目说明符是%zu,在某些环境下可以思量用%u或%lu替代
#p#副标题#e#
ptrdiff_t范例
ptrdiff_t是C99尺度库中界说的一个与呆板相关的数据范例,界说在stddef.h这个文件内。ptrdiff_t范例变量凡是用来生存两个指针减法操纵的功效。
ptrdiff_t凡是被界说为long int范例,size_t 是unsigned 范例,而 ptrdiff_t 则是 signed 整型。
这两种范例的不同浮现了它们各自的用途:size_t 范例用于指明数组长度,它必需是一个正数;ptrdiff_t 范例则应担保足以存放同一数组中两个指针之间的差距,它有大概是负数。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char str[] = "Hello world!";
char *pstart = str;
char *pend = str + strlen(str);
ptrdiff_t difp = pend - pstart;
printf("%d\n", difp);
return 0;
}
intptr_t与uintptr_t范例
intptr_t与uintptr_t范例用来存放指针地点,它们提供了一种可移植且安详的要领声明指针,并且与系统中利用的指针的长度沟通,对付把指针转化为整数形式很有用。uintptr_t是intptr_t的无标记版本
关于intptr_t的范例界说如下:
/* Types for `void *' pointers. */ #if __WORDSIZE == 64 # ifndef __intptr_t_defined typedef long int intptr_t; # define __intptr_t_defined # endif typedef unsigned long int uintptr_t; #else # ifndef __intptr_t_defined typedef int intptr_t; # define __intptr_t_defined # endif typedef unsigned int uintptr_t; #endif
从界说可以看出,intptr_t在差异的平台是纷歧样的,始终与地点位数沟通,因此用来存放地点。
观念上, 尽量地点是指针, 内存打点经常利用一个无标记的整数范例更好地完成; 内核看待物理内存如同一个大数组, 而且内存地点只是一个数组索引. 进一步地, 一个指针容易解引用; 当直接处理惩罚内存存取时, 你险些从不想以这种方法解引用. 利用一个整数范例制止了这种解引用, 因此制止了 bug. 因此, 内核中凡是的内存地点经常是 unsigned long, 操作了指针和长整型一直是沟通巨细的这个事实, 至少在 Linux 今朝支持的所有平台上.C99 尺度界说了 intptr_t 和 uintptr_t 范例给一个可以持有一个指针值的整型变量
#p#分页标题#e#
测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define ID_STR_LEN 12
#define NAME_STR_LEN 10
typedef struct student
{
char id[ID_STR_LEN];
char name[NAME_STR_LEN];
uint8_t age;
}student;
student * create_student()
{
student *stu = (student *)malloc(sizeof(student));
if (stu == NULL)
return NULL;
memset(stu, 0, sizeof(student));
return stu;
}
void *free_student(student *stu)
{
if (stu)
free(stu);
return 0;
}
static void init_student(student * stu)
{
assert(stu);
const char *id = "2013112210";
const char *name = "Anker";
uint8_t age = 21;
memcpy(stu->id, id, strlen(id));
memcpy(stu->name, name, strlen(name));
stu->age = age;
}
static int handle_student(intptr_t handle)
{
if (handle == 0)
{
return -1;
}
student *stu = (student*)handle;
printf("id: %s\n", stu->id);
printf("name: %s\n", stu->name);
printf("age: %u\n", stu->age);
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
student *stu;
stu = create_student();
init_student(stu);
//将指针转换为intptr_t范例
intptr_t handle = (intptr_t)stu;
handle_student(handle);
free_student(stu);
return 0;
}
作者:archimedes
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/
