FINAL EXAM
CS 488 Computer Networks and the Internet
计算机网络和互联网代写 Instructions No use of computers, calculators, notes, books, and no discussion with your classmates (even to ask the time, date…).
Instructions
- No use of computers, calculators, notes, books, and no discussion with your classmates (even to ask the time, date…).
- Look at your test only.
- Proctor reserve the right to re-seat the students during the exam.
- If you cannot answer a question you may want to work on the next one and return to the problem later.
- Read the questions carefully before answering.
- You can only leave the room after the first hour.
Grading policy
| Problem | Score | Maximum |
|
1 |
Multiple choice:7 points | |
|
2 |
20 (7+7+6) | |
|
3 |
20 (5+5+5+5) | |
|
4 |
13 (7+3+3+) | |
| 5 |
18(6+6+6) |
|
| 6 |
21 (7*3) |
|
| Extra-credit |
0 |
|
| TOTAL |
100 |
Multiple Choice Question (A through G) 计算机网络和互联网代写
A. Communication over the Internet is done:
- through virtual circuits
- through datagrams
- both 1 and 2
- none of the above
B. Which of the following is NOT why “Layering” is commonly used in computer networks:
- It allows widespread re-use of code and functionality.
- Encapsulation provides easy replacement of a layer.
- It provides a separation of concerns; each layer has well defined responsibilities.
- It keeps networks warm enabling them to run faster.
C. Socket programming
- makes creating network applications easier and faster
- can be done only with the use of the C programming language
- can be done only with the use of the Java programming language
- is an old technique not used any more.
D. TCP implements
- Go-Back-N
- Selective Repeat
- A hybrid between Go-Back-N and Selective Repeat
- none of the above
E. The ICMP protocol
- runs directly on top of IP
- runs on top of UDP
- runs on top of TCP
- none of the above
F. Ethernet provides which of the following services to the network layer
- flow control
- reliable data transfer
- error detection
- all of the above.
G. Which is not an objective of network security?
- Identification
- Authentication
- Access control
- Concurrency
Problem 2 计算机网络和互联网代写
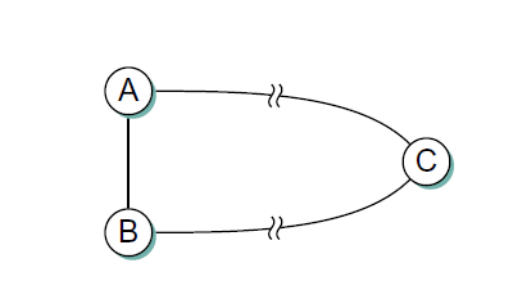
2.(a)
Give the steps as in Table 5.1 (text book) similar to in the forward search algorithm as it builds the routing database for Link-State algorithm for node A in the network shown in above figure. Show all the steps
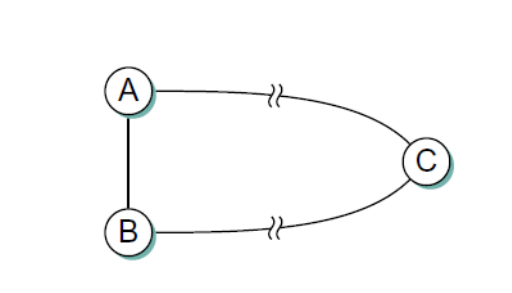
2.(b)
Give the steps as in Table 5.1 (text book) similar to in the forward search algorithm as it builds the routing database for Link-State algorithm for node A in the network shown in above figure. Show all the steps
2.(c)
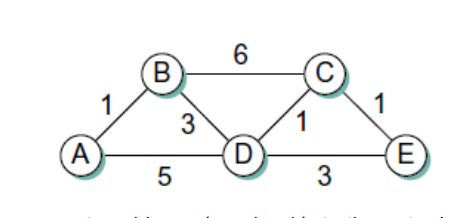
Suppose, that nodes in the network shown in Figure below, participate in link-state routing, and C receives contradictory LSPs: One from A arrives claiming the A–B link is down, but one from B arrives claiming the A–B link is up.
(a) How could this happen? (explain)
(b) What should C do? What can C expect? (explain)
Do not assume that the LSPs contain any synchronized timestamp.
Problem 3 计算机网络和互联网代写
3.(a)
Suppose there are three routers between a source host and a destination host. Ignoring fragmentation, an IP datagram sent from the source host to the destination host will travel over how many interfaces? How many forwarding tables will be indexed to move the datagram from the source to the destination? Explain!
3.(b)
Suppose an application generates chunks of 40 bytes of data every 20 msec, and each chunk gets encapsulated in a TCP segment and then an IP datagram. What percentage of each datagram will be overhead, and what percentage will be application data? (explain)
3.(c)
Describe how packet loss can occur at output ports. Can this loss be prevented by increasing the switch fabric speed? (explain)
3.(d)
Describe how packet loss can occur at input ports. Describe how packet loss at input ports can be eliminated (without using inline buffers)
Problem 4 计算机网络和互联网代写
4.(a)
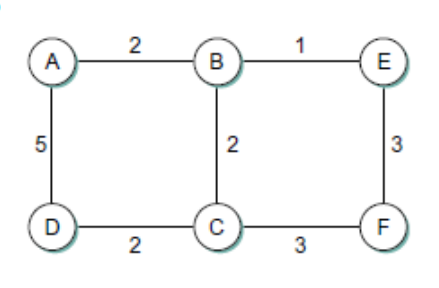
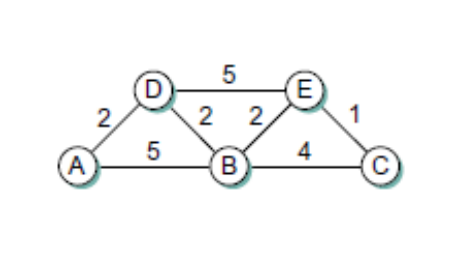
For the network given in Figure above, give global distance–vector tables like those of figure 5.6 (textbook) when
(a) Each node knows only the distances to its immediate neighbors.
(b) Each node has reported the information it had in the preceding step to its immediate neighbors.
(c) Step (b) happens a second time.
4.(b)
Describe how loops in paths can be detected in BGP.
4.(c)
Will a BGP router always choose the loop-free route with the shortest ASpath length? Justify your answer
Problem 5 计算机网络和互联网代写
5.(a)
The sequence number field in the TCP header is 32 bits long, which is big enough to cover over 4 billion bytes of data. Even if this many bytes were never transferred over a single connection, why might the sequence number still wrap around from 232 −1 to 0?
5.(b)
Suppose a host wants to establish the reliability of a link by sending packets and measuring the percentage that is received; routers, for example, do this. Explain the difficulty doing this over a TCP connection.
5.(c)
From a service perspective, what is an important difference between a symmetric-key system and a public key system?
Suppose that an intruder has an encrypted message as well as the decrypted version of the message. Can the intruder mount a ciphertext-only attack, a known-plaintext attack, or a chosen-plaintext attack? Explain.
Problem 6 计算机网络和互联网代写
6.(a).
A fundamental cryptographic principle states that all messages must have redundancy. But we also know that redundancy helps an intruder tell if a guessed key is correct. Consider two forms of redundancy. First, the initial n bits of plaintext contain a known pattern. Second, the final n bits of the message contain a hash over the message. From a security point of view, are these equivalent? Discuss your answer.
6.(b)
Consider a banking system that uses the following format for transaction messages: tow bytes for the sender ID, two bytes for the receiver ID, and four bytes for the amount to be transferred. Transactions are encrypted before sending. What could you add to these messages to make them adhere to the two cryptographic principles discussed in this chapter 8.
6.(c)
What are the differences between message confidentiality and message integrity? Can you have confidentiality without integrity? Can you have integrity without confidentiality? Justify your answer.

更多代写:计算机Project网课代管 雅思代考 英国PSY心理学网课作业代写 澳洲代写范文 research写作 国外书评代写