Math 307, Final
April 29, 2014 12.00-2.30pm
澳洲数学代考推荐 Showall your Answers without any explanation or without the correct accompanying work could receive no credit, even if they are correct.
Instructor: 澳洲数学代考推荐
Instructions:
- No notes, books or calculators are allowed. A MATLAB/Octave formula sheet is provided.
- Read the questions carefully and make sure you provide all the information that is asked for in the question.
- Showall your Answers without any explanation or without the correct accompanying work could receive no credit, even if they are correct.
- Answer the questions in the space provided. Continue on the back of the page if necessary.
| Question | Mark | Maximum |
| 1 | 20 | |
| 2 | 13 | |
| 3 | 16 | |
| 4 | 10 | |
| 5 | 澳洲数学代考推荐 | 14 |
| 6 | 12 | |
| 7 | 15 | |
| Total | 100 |
1.Consider the following types of matrices (all assumed to besquare): 澳洲数学代考推荐
(A)Matrices with a basis ofeigenvectors
(B)Matrices with distincteigenvalues
(C)Matrices with repeatedeigenvalues
(D)Hermitianmatrices
(E)Non-zero orthogonal projectionmatrices
(F)Matrices of the form 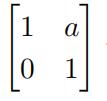 with a ≠ 0
with a ≠ 0
(a)Which types are alwaysdiagonalizable?
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(b)Which types are sometimes, but not alwaysdiagonalizable?
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(c)Whichtypes always have an orthonormal basis of eigenvectors?
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(d)Whichtypes always have an eigenvalue equal to 1?
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(e)Everymatrix of type (A) is always also of type:
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(f)Everymatrix of type (B) is always also of type: 澳洲数学代考推荐
(A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(g)Everymatrix of type (C) is always also of type:
A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(h)Everymatrix of type (D) is always also of type:
A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(i)Everymatrix of type (E) is always also of type:
A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
(j) Every matrix of type (F) is always also of type:
A) □, (B) □, (C) □ , (D) □ , (E) □ , (F) □
2.Wewish to interpolate the points (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3, y3) with x1 < x2 < x3 using a function of the form
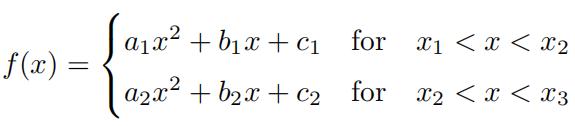
(a)Writedown the equations satisfied by a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 when f (x) is continuous and passes through the given points.
(b)Writedown the equation satisfied by a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 when f j(x) is continuous at x = x2.
(c)Write down the matrix A and the vector b in the matrix equation Aa = b satisfied by a = [a1,b1, c1, a2, b2, c2]T when the conditions of both (a) and (b) are satisfied and when x1 = 0, x2 = 1, x2 = 2, y1 = 1, y2 = 3, y3 = 2. Explain why this system of equations does not have a unique solution. 澳洲数学代考推荐
(d)Let A and b be as in (c) and assume they have been defined in MATLAB/Octave. Using that a=A\b computes a solution (even if it is not unique) and n=null(A) computes a vector in N (A), write the MATLAB/Octave code that computes and plots two different interpolating functions of the form f (x) satisfying the conditions in (a) and(b).

3.Consider theplane S defined by 2u − 3v + w = 0, and recall that the normal to this plane is the vector a = [2, −3, 1].
(a)Computethe projections of vectors [1, 0, 0] and [0, 1, 0] onto the line spanned by a.
(b)Compute the projectionsof vectors [1, 0, 0] and [0, 1, 0] onto the subspace defined by S. What is the inner product of each of these projections with [2, −3, 1]?
(c) Find a basis for the subspace of R3 defined by S. What is the dimension of thissubspace?
(d)The reflection of vector x across a subspace is (2P −I)x where I is the identity matrix and P is the matrix projecting x onto the subspace.
i.Drawa sketch to show why this definition of reflection makes sense. 澳洲数学代考推荐
ii.What is the reflection of [1, 0, 0] in planeS?
iii.What is the matrix (2P −I)2?
4.Consider the following bivariatedata:
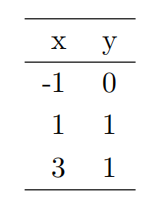
(a)Draw a sketch showing the approximate least-squares straight-line fit y = ax + b to this data.
(b) Write down the least squares (or normal) equation satisfied by 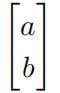
(c) What quantity is minimized by the solution to the equation in (b)?
5.Consider L2[a, b], the set of square-integrable functions on the interval x ∈ [a,b]. 澳洲数学代考推荐
(a)Why do we say that the basis functions e2πinx/(b−a)for n ∈ Z are orthogonal?
(b) Under what conditions on a and b are these functions orthonormal? Propose a set of basis functions for L2[a, b] that are orthonormal for any choice of a and b.
(c) Suppose a = 0, b = 1 and consider thefunction
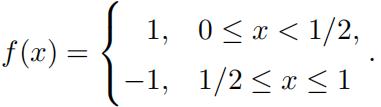
Write down (but don’t bother evaluating) the integral you’d need to do to compute the Fourier coefficients cn for f (x).
(d) Are the quantities cn − c−n purely real, purely imaginary, or neither? Why?
(e) What is the sum
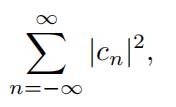
where cn are the Fourier coefficients of the function in part (c)?
6.Starting with initial values x0and x1, let xn for n = 2, 3, . . . be defined by the recursion relation
xn+1 = axn − xn−1,
where a is a real number.
(a)When this recursion relation is written in matrix form Xn+1= AXn, what are A and Xn?
(b)Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of A. What is det(A) and what does it tell you about the eigenvalues? 澳洲数学代考推荐
(c) In some applications we are interested in solutions xwhere limn→∞ xn = 0. Find non-zero initial conditions x0 and x1 that give rise to such a solution when a = 3. Solution: When a = 3 the eigenvalues are real and positive. Since λ+λ− = 1 we know the smaller one λ− must be less than
7.Thus we choose initial conditions to be the corresponding eigenvector,i.e., 澳洲数学代考推荐
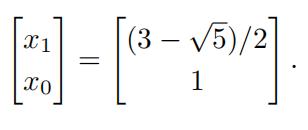
(d) For which values of a do the solutions to this recursion stay bounded, neither growing or decaying as n → ∞? (You may disregard values of a for which A has repeated eigenvalues).
8.(a) Write down the definition of a stochastic (or Markov) matrix. 澳洲数学代考推荐
(b) What can you say about the relative sizes of “Sv“1 and “v“1 for a stochastic matrix S? Explain how this implies that all the eigenvalues λ of a stochastic matrix have |λ| ≤ 1. Is it possible that all eigenvalues have |λ| < 1? Give a reason. What is “S“1 (i.e., the matrix norm when both input and output are measured with the 1-norm, also denoted “S“1,1)?
(c)What can you say about the eigenvalues of a stochastic matrix S if limn→∞Sn does not exist. Give an example of a stochastic matrix like this.
(d) Consider the following internet.
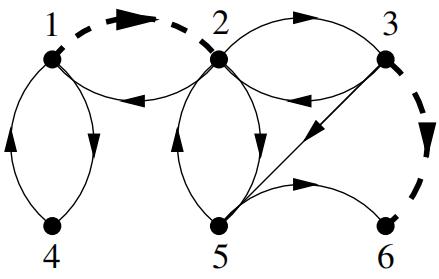
In this diagram the links depicted by dashed arrows are displayed prominently and are therefore twice as likely to be followed than the remaining links on the page. Write down (i) the stochastic matrix associated to this internet with no damping and (ii) the first column of the stochastic matrix associated to this internet with damping factor 1/2. Explain how you could use the eig command in MATLAB/Octave to compute the limiting probabilies of landing on each site.



更多代写:AI代写 参考文献格式代写 英国伦敦Finance代写 参考文献格式代写 英国论文essay代写 商业法律代写论文
