Programming Projects
You may use any language: python, perl, matlab, R, C, C++, Java, etc.
Your solution should include
- Explanation of your approach, implementation, and results in well organized and grammatical text.
- source code
- instructions to install and run the code
- test data and expected results
- Answers to any specific questions
You may use existing packages/libraries to read and write sequences, but, unless otherwise instructed, generate your own code. Do not use solutions you look up on the internet.
Alignments
- DNA/protein alignment
Align a DNA sequence and a protein sequence based on the translated sequences of the DNA sequences.
Only the forward reading frames need be considered. If desired, you may use existing packages for
reading/writing sequences, scoring tables, and formatted results. Display the results in conventional pairs of
lines format showing both DNA and translated protein sequences.
- Use a local alignment algorithm
- Implement both global and local alignments
- Assume the sequences are in fasta format
- Use a scoring table such as Blosum or PAM
- Allow affine gaps within reading frames
- Allow length independent gaps between reading frames.
- allow affine gaps between reading frames
- Align two DNA sequences, same requirements as above, based on their protein translations
- Suboptimal alignment
For DNA or protein sequences, report n non-intersecting suboptimal alignments. As discussed in class, sub-optimal alignments use no pair of letters used in earlier alignments. This can be achieved by recalculating the score matrix, setting the score for all letter-pairs in previous alignments to be zero.
- allow selection of an appropriate scoring table for DNA or protein
- use a local algorithm with affine gap penalties
- display aligned sequences in conventional pairs of lines format
Simulations
- Sequence randomization
Randomize a sequence preserving its n-mer word content (i.e, 1 letter, 2-letter, 3-l;etter, …). This may be solved simply using sampling with or without replacement, but the n-mer content of the randomized sequence will not exactly match the original sequence.
- input and output in Fasta format. Your program should work for any alphanumeric letter sequence, but especially DNA and protein alphabets.
- n-mer should be selectable in range 1 to 5 (or more)
- Additional output should show original and randomized n-mer word content
- Exact solution (all n-mer counts exactly the same) using an implementation of Euler’s algorithm.
- Sequence evolution – Is a simple i.i.d. randomization a good model for proteins? Choose a random set of 50 protein sequences (from ncbi or uniprot). This problem can be combined with Simulation #1
- For the test data set, calculate the distribution of word scores using words of various length (minimum: 8, 12, 16) using a Blosum scoring table. Display as a frequency table (score vs count).
- Display as a histogram plot
- Compare to the scores distributions generated for the random sequences with different n-mer word lengths (n=1..5) preserved. Use the code in problem 1, above, or the program Ushuffle.
- Mean and standard deviation are sufficient for the comparison, although you may include more sophisticated tests.
- repeat for DNA using word lengths 4, 6, and 8.
- What n-mer model best fits the unrelated protein data?
Evolution/Trees
- Starting with a protein sequence (at least 100 residues), apply a random mutation process based on the PAM model. At random times, duplicate the sequences creating speciation events. At random times, remove some species (extinctions).
- Input parameters should include total evolution time (% true mutations), and number of leaf sequences to be generated.
- speciation and extinctions can follow simple a simple probability, i.e., probability of speciation or extinction at each step is constant.
- Implement a more sophisticated model where these events follow a distribution such as normal or gamma
- report the final set of sequences as a multiple alignment. No alignment algorithm is necessary, since the sequences are generated by random mutation, they are already aligned.
- report the tree in Newick format.
- report the true number of mutations between each pair of sequences (from the simulation history) and the observed number of differences (n x n table, where n is number of leaf nodes)
- parsimony – requires solving Evolution #1, above.
- Implement the parsimony algorithm.
- for 50 random trees with 20 leaf nodes, calculate the tree lengths and report the true tree lengths (known from the simulation), estimated tree length (from parsimony). Calculate the mean and standard deviation of the difference between the known and estimated tree lengths.
- Repeat for evolutionary distances of 50%, 100%, 200%. Are there significant differences between the known and estimated trees?
- Same as above for UPGMA trees. – requires solving Evolution #1, above.
- use 50 random trees with 20 leaf nodes
- Implement UPGMA
- Use the Fitch-Margoliash method to estimate branch lengths
- Use the observed mutational distances to construct trees, compare the estimated distances from the tree to the known true distances from the simulation.
- Calculate the mean and standard deviation of the RMS difference between the known and estimated numbers of mutations.
- Repeat for evolutionary distances of 50%, 100%, 200%. Are there significant differences between the known and estimated trees?
成果展示,部分。如需需要成品,左边二维码联系我们的客服。
Simulation
1
The function seq.Rand shuffles a string sequence. The argument seq for a sequence, k for n-mer, and seed for setting set to make the result repeatable. The output will include the original one, the randamized one, and the Eulerian path.
fasta.form() function combines seq.Rand and the function for dealing with fasta format.
Codes:
# if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
# install.packages("BiocManager")
# BiocManager::install("Biostrings", version = "3.8")
# BiocManager::install("msa")
library(Biostrings)
library(msa)
library(knitr)
data("BLOSUM62")
seed <- 2018 # an example
k <- 5 # an example
seq <- "ACTGTGCAGTCGATGCTAGGTTCCGATATCTAGCTCGCTAGATC" # an example
seq.Rand <- function(seq, k, seed = NULL){
if(!is.null(seed)) set.seed(seed) # set seed, if any
if(k==1){ # if k = 1, sampling the vector without replacement
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,"")) # break a sequence to a vector, each entry only has one char
seq.v[-1] <- seq.v[sample(2:length(seq.v))] # first entry remains the same
seq.new <- Eulerian <- paste(seq.v,collapse = "")
} else{
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,"")) # break a sequence to a vector, each entry only has one char
letter.dict <- unique(seq)
len <- length(seq.v)
kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
seq.new <- Eulerian <- NULL
seq.new[1] <- Eulerian[1] <- kmer.o[1]
kmer <- kmer.o[-1]
for(i in 2:(length(kmer)+1)){ # if k>=2
# replace without relacement
temp0 <- seq.new[i-1]
overlap <- substr(temp0, 2, k)
dict.temp <- which(substr(kmer, 1, k-1) == overlap)
if (length(dict.temp) == 0) break
ind.temp <- sample(dict.temp,1)
seq.new[i] <- kmer[ind.temp]
kmer <- kmer[-ind.temp]
# print(kmer)
}
#Eulerian
kmer <- kmer.o[-1]
for(i in 2:(length(kmer)+1)){
temp0 <- Eulerian[i-1]
overlap <- substr(temp0, 2, k)
dict.temp <- which(substr(kmer, 1, k-1) == overlap)
if (length(dict.temp) == 0) { # to make sure every node is visited
dict.temp <- which(substr(kmer.o, 1, k-1) == overlap)
if (length(dict.temp) == 0) break
ind.temp <- sample(dict.temp,1)
Eulerian[i] <- kmer.o[ind.temp]
# print(kmer)
} else {
ind.temp <- sample(dict.temp,1)
Eulerian[i] <- kmer[ind.temp]
kmer <- kmer[-ind.temp]
# print(kmer)
}
}
# format the sequence
seq.new <- paste(seq.new[1],
paste(substr(seq.new[2:length(seq.new)],k-1,k),collapse = ""),
sep = "")
Eulerian <- paste(Eulerian[1],
paste(substr(Eulerian[2:length(Eulerian)],k-1,k),collapse = ""),
sep = "")
}
# output:
return(list(randseq = seq.new,
Eulerian = Eulerian,
original = seq))
}
seq.Rand(seq, k,2018)
## $randseq
## [1] "ACTGTTGGCCAAGGTTCCGGAATTAGGTAAGGACGTCAGGACCTC"
##
## $Eulerian
## [1] "ACTGTTGGCCAAGGTTCCGGAATTGGCCTTAAGGCCTGGGTTTTCCCCGGAATTAATTCTGGTTGTGGTGTTGTGGCTGTGGT"
##
## $original
## [1] "ACTGTGCAGTCGATGCTAGGTTCCGATATCTAGCTCGCTAGATC"
#fasta
fasta.form <- function(fasta, k, seed=NULL){
seq.name <- names(fasta) # deal with fasta format
seq <- paste(fasta)
result <- seq.Rand(seq, k,seed)
return(list(name = seq.name,
randseq = result$randseq,
Eulerian = result$Eulerian,
original = result$original))
}
data <- readDNAStringSet("./sequence.fasta-3.txt")
## Warning in .Call2("fasta_index", filexp_list, nrec, skip, seek.first.rec, :
## reading FASTA file ./sequence.fasta-3.txt: ignored 12146 invalid one-letter
## sequence codes
fasta.form(data[1], k,2018)
## $name
## [1] "BAG70982.1 phenylalanine ammonia-lyase [Musa balbisiana]"
##
## $randseq
## [1] "MAKAVVVVNNGGAACCKKAADDNNWWKKAAAASSTTGGSSHHDDVVKKRRMMVVRRKKVVRRGGAATTTTSSVVAAAAVVAAAAAARRAAAAVANRSSVVRRVVSSAARRDDGGVVRRAASSSASTATKHRVMWV"
##
## $Eulerian
## [1] "MAKAVVVVNNGGAACCKKAADDNNWWKKAAAASSTTGGSSHHDDVVKKRRMMVVRRKKVVRRGGAATTTTSSVVAAAAVVAAAAGSGSAARRSSVVRAAKAACCKNGNGNGVVVVVNVVVNVVVVVVAVNTATYGDGGVVRRDKVVRRGNWVVVVVVVVVNVVVVVVAVRASSNAMNSSRVVSAVTTSTVVVNAVSMRGRGRKCKACACNGNGGAAVNGGTTDSWWVARAAAGNKRAASTDDHSAGAVRSTVVAVYSAATSSGKRKGDSGTASKAASHRGGVRKAVVAVTTGGGARTTTVMMSVRGSASKAACAVSGTKVVVNVNAVASAASHHDKANGAVAKVRAAASGANGNGVNVVVVAVAATGNWDNVVVVAVCRRRCKVNNGGAGAVNVVVVVVAVSGAKTTVTDVNGGAGAAVTANATGSMKRVNAVVRMVATSYDGVRDNACAVGTWKKAACACVNVNVVVNVVVVVNVNVVVVVVVNVVVNAVVSGSATACCKGANGVVVNVVAVVNKRCKCKNGGAVVVNVNAVAAGVAATTADKAADVVAVSYTCAARAMGNTVRVNNGNGVVVVAVGRDVAANWVVAVAGGNKAKAADNGNGVNVNVVVVVNVNVNNGAVRNVTAAVNNGGAVNVVVNAVSGRVVNGSDNKAVNNGNGVNVVVVAVAGNAGGTDARAAVNNGGAVVVNVNVNAVVGGYKAKACKVVVVAVVVVNVVVNAVVGTGKGAVAADNVNNGGAACAVVGYAATTSRDSHKACKAVVVVNVNVNNGGAAVVGNNVMKVWKWKDNGAVNNGGAVVAVVGTGWKACCKKAACNGAVVGGRGDKANTNKKAWKVNVVAVVVAVVGGDGSRDTSVVVNNGNGVVVNNGNGAVVGTGRGRVAAAAAVVVVNNGVVVNVVVVVVVVAVVVVVVN"
##
## $original
## [1] "MAKAVVNGACKADNWKAASTGSHDVKRMVRKVRGATTSVAAVAAARSVRVSARDGVRASSWVMSMNKGTDSYGVTTGGATSHRRTKGGAKRNAGGSGSGNTSSAAKAAMVRVNTGYSGRAASNNGTCRGTTASGDVSYAGTGRNAKAVGDGKVGAAARASADGKGAVNGTAVGSGASMVANVAVSVSAVCVMGKTDHTHKKHHGAAAMHGSSYMKMAKKHDKKDRYARTSWGVRASTKSRNSVNDNDVSRSKAHGGNGTGVSMDNTRAVAAGKMASVNDYNNGSNSGGRNSDYGKGAAMAAYCSANVTNHVSAHNDVNSGSARKTAAVDKMSTTYVACAVDRHNKSAVKSTVSVAKRVTMGANGHARCKKVVDRHVTYVDDCSATYMKRVVAHANGDKKDAGSSKATTAKVAARAAVGGKAANRCRSYYRVRKTGTGKVRSGDKVDACGKVDCKWNGAC"
2
the distribution of word scores
Please refer to the following code and out put for the frequency tables and histgrams for the scores derived by different lengths of word.
The mean and Variance are summarized as followings.
length of word |
Mean |
Variance |
8 |
32.31412 |
41.9872 |
12 |
47.30298 |
104.3903 |
16 |
62.61114 |
190.2871 |
The larger the length of word, the higher mean and variance since the maginitude of the scores increaase. shuffle Please refer to the following code and out put for the shuffled word, which derives the the frequency tables and histgrams for shuffled words with different n-mer. The mean and Variance of scores for different n-mer are summarized as followings.
n |
Mean |
Variance |
1 |
25.559 |
7.6516 |
2 |
25.761 |
9.493 |
3 |
25.66886 |
8.859 |
4 |
24.917 |
4.986 |
5 |
26.48 |
8.758 |
What n-mer model best fits the unrelated protein data? The 5-mer obtains larger mean, indicating 5-mer model is the best one among the above five mdoels to fit the unrelated protein data. Redo for DNA Please refer to the code and out put for DNA for details. The mean and Variance are summarized as followings.
length of word |
Mean |
Variance |
4 |
32.31412 |
41.9872 |
6 |
47.30298 |
104.3903 |
8 |
62.61114 |
190.2871 |
code and out of the score.
lengthof word: 8
data <- readDNAStringSet("./sequence.fasta-3.txt")
## Warning in .Call2("fasta_index", filexp_list, nrec, skip, seek.first.rec, :
## reading FASTA file ./sequence.fasta-3.txt: ignored 12146 invalid one-letter
## sequence codes
seq.name <- names(data)
seq <- paste(data)
data <- data.frame(seq.name, seq)
data$seq <- as.character(data$seq)
data$seq.name <- as.character(data$seq.name)
k <- 8
word.list <- NULL
for(i in 1:50){
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
}
word.list <- unique(word.list)
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# letter.dict <- unique(seq)
#
# len <- length(seq.v)
# kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
scores.list <- list()
i <- 1
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999) #set a T
socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
table(socres.8)
## socres.8
## 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
## 238 223 191 152 163 129 120 131 114 95 111 103 115 107 105 89 82 88
## 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 55 56
## 63 57 45 34 20 16 10 4 5 4 2 2 1 1
hist(socres.8)
mean(socres.8)
## [1] 32.31412
var(socres.8)
## [1] 41.9872
lengthof word: 12
# 12
k <- 12
word.list <- NULL
for(i in 1:50){
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
}
word.list <- unique(word.list)
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# letter.dict <- unique(seq)
#
# len <- length(seq.v)
# kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
scores.list <- list()
i <- 1
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.12 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.12 <- quantile(socres.12,.999)
socres.12<- socres.12[socres.12>=T.12]
table(socres.12)
## socres.12
## 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49
## 135 125 118 115 105 108 114 90 102 109 93 88 114 90 97 72 92 81
## 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67
## 97 97 73 94 87 88 90 74 86 72 81 70 75 51 50 46 25 32
## 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 77 80
## 15 11 9 4 2 1 2 3 1 1
hist(socres.12)
mean(socres.12)
## [1] 47.30298
var(socres.12)
## [1] 104.3903
lengthof word: 16
#16
k <- 16
word.list <- NULL
for(i in 1:50){
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
}
word.list <- unique(word.list)
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# letter.dict <- unique(seq)
#
# len <- length(seq.v)
# kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
scores.list <- list()
i <- 1
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
table(socres.16)
## socres.16
## 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59
## 131 113 91 100 99 85 93 100 90 99 73 75 74 75 77 86 72 72
## 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77
## 62 72 64 60 66 70 56 67 66 60 71 75 72 75 61 92 71 72
## 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 94 95 96
## 67 88 71 63 57 52 51 49 44 28 25 13 5 15 6 2 3 2
## 97 98 99
## 2 1 1
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 62.61114
var(socres.16)
## [1] 190.2871
code and out put for shuffle
## shuffle
shuffle.1 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],1,2018)$randseq
shuffle.2 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],2,2018)$randseq
shuffle.3 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],3,2018)$randseq
shuffle.4 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],4,2018)$randseq
shuffle.5 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],5,2018)$randseq
# 1mer
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.1,""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 25.559
var(socres.16)
## [1] 7.651598
kable(table(socres.16))
socres.16 |
Freq |
23 |
965 |
24 |
724 |
25 |
564 |
26 |
420 |
27 |
322 |
28 |
237 |
29 |
149 |
30 |
103 |
31 |
61 |
32 |
53 |
33 |
49 |
34 |
26 |
35 |
11 |
36 |
8 |
37 |
8 |
38 |
2 |
39 |
2 |
40 |
1 |
41 |
4 |
42 |
1 |
43 |
2 |
# 2mer
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.2,""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 25.76066
var(socres.16)
## [1] 9.493101
kable(table(socres.16))
socres.16 |
Freq |
23 |
2026 |
24 |
1541 |
25 |
1055 |
26 |
843 |
27 |
648 |
28 |
467 |
29 |
363 |
30 |
251 |
31 |
184 |
32 |
134 |
33 |
86 |
34 |
89 |
35 |
49 |
36 |
32 |
37 |
19 |
38 |
10 |
39 |
9 |
40 |
4 |
41 |
4 |
42 |
5 |
43 |
3 |
44 |
2 |
45 |
3 |
51 |
1 |
54 |
2 |
# 3mer
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.3,""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 25.66886
var(socres.16)
## [1] 8.858734
kable(table(socres.16))
socres.16 |
Freq |
23 |
930 |
24 |
732 |
25 |
553 |
26 |
378 |
27 |
288 |
28 |
220 |
29 |
168 |
30 |
118 |
31 |
77 |
32 |
56 |
33 |
34 |
34 |
21 |
35 |
19 |
36 |
10 |
37 |
12 |
38 |
6 |
39 |
8 |
40 |
4 |
41 |
2 |
42 |
1 |
43 |
2 |
44 |
2 |
45 |
1 |
# 4mer
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.4,""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 24.91729
var(socres.16)
## [1] 4.985532
kable(table(socres.16))
socres.16 |
Freq |
23 |
48 |
24 |
25 |
25 |
19 |
26 |
15 |
27 |
9 |
28 |
7 |
29 |
2 |
30 |
3 |
31 |
3 |
32 |
1 |
33 |
1 |
# 5mer
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.5,""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.16 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.16 <- quantile(socres.16,.999)
socres.16 <- socres.16[socres.16>=T.16]
#table(socres.16)
hist(socres.16)
mean(socres.16)
## [1] 26.48
var(socres.16)
## [1] 8.757766
kable(table(socres.16))
socres.16 |
Freq |
24 |
262 |
25 |
204 |
26 |
144 |
27 |
98 |
28 |
79 |
29 |
39 |
30 |
32 |
31 |
28 |
32 |
20 |
33 |
14 |
34 |
9 |
35 |
4 |
36 |
4 |
37 |
4 |
38 |
3 |
39 |
2 |
40 |
2 |
44 |
1 |
51 |
1 |
For DNA data:
lengthof word: 4
data <- readDNAStringSet("./sequence.dna.txt")
seq.name <- names(data)
seq <- paste(data)
seq <- seq[1:50]
k <- 4
word.list <- NULL
for(i in 1:50){
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
}
word.list <- unique(word.list)
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# letter.dict <- unique(seq)
#
# len <- length(seq.v)
# kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
scores.list <- list()
i <- 1
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
socres.4 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.4 <- quantile(socres.4,.999) #set a T
socres.4 <- socres.4[socres.4>=T.4]
table(socres.4)
## socres.4
## 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 36
## 71 65 59 30 7 3 9 6 1
hist(socres.4)
mean(socres.4)
## [1] 27.68127
var(socres.4)
## [1] 3.066008
lengthof word: 6
# 12
k <- 6
word.list <- NULL
for(i in 1:50){
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
}
word.list <- unique(word.list)
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# letter.dict <- unique(seq)
#
# len <- length(seq.v)
# kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
scores.list <- list()
i <- 1
seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
len <- length(seq.v)
scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
}
scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
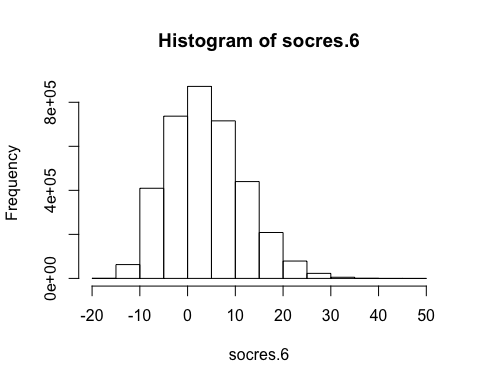
socres.6 <- unlist(scores.list)
T.6 <- quantile(socres.6,.999)
socres.6<- socres.6[socres.12>=T.6]
table(socres.6)
## socres.6
## -18 -17 -16 -15 -14 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9
## 1 19 122 502 1616 4148 9135 17839 30029 46708
## -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1
## 65803 82215 101207 113498 121924 137414 146644 158432 172517 178802
## 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
## 179153 177808 173615 162771 163037 151507 145695 133913 121480 109037
## 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
## 98724 88369 76383 67296 55174 49082 42024 34643 27584 22694
## 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
## 18865 15985 12269 9021 6915 5965 4384 3356 2229 1766
## 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
## 1335 1054 637 405 278 238 173 94 47 37
## 42 43 44 45 46 47 48
## 38 13 3 2 6 4 1
hist(socres.6)
mean(socres.6)
## [1] 4.324427
var(socres.6)
## [1] 62.15408
lengthof word: 8
#
# #16
# k <- 8
# word.list <- NULL
# for(i in 1:50){
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# word.list <- c(word.list, sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")}))
# }
#
# word.list <- unique(word.list)
#
# # seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq,""))
# # letter.dict <- unique(seq)
# #
# # len <- length(seq.v)
# # kmer.o <- sapply(1:(len-k+1), function(x){paste(seq.v[x:(x+k-1)],collapse="")})
#
# scores.list <- list()
# i <- 1
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(seq[i],""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.16 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# table(socres.8)
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
shuffle
# ## shuffle
# shuffle.1 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],1,2018)$randseq
# shuffle.2 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],2,2018)$randseq
# shuffle.3 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],3,2018)$randseq
# shuffle.4 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],4,2018)$randseq
# shuffle.5 <- seq.Rand(seq[1],5,2018)$randseq
#
# # 1mer
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.1,""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
# kable(table(socres.8))
#
# # 2mer
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.2,""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
# kable(table(socres.8))
#
# # 3mer
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.3,""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
# kable(table(socres.8))
#
# # 4mer
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.4,""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
# kable(table(socres.8))
#
# # 5mer
# seq.v <- unlist(strsplit(shuffle.5,""))
# len <- length(seq.v)
# scores.temp <- matrix(rep(0,length(word.list)*(len+1-k)),length(word.list))
# for(j in 1:length(word.list)){
# scores.temp[j, ] <- sapply(1:(len+1-k),function(x){sum(diag(BLOSUM62[unlist(strsplit(word.list[j],"")), seq.v[x:(x+k-1)]]))})
# }
# scores.temp <- as.vector(scores.temp)
# scores.list[[i]] <- scores.temp
#
# socres.8 <- unlist(scores.list)
# T.8 <- quantile(socres.8,.999)
# socres.8 <- socres.8[socres.8>=T.8]
# #table(socres.8)
# hist(socres.8)
# mean(socres.8)
# var(socres.8)
# kable(table(socres.8))
