Structure of the IP header
考纲范围:
http://networkstatic.net/what-are-ethernet-ip-and-tcp-headers-in-wireshark-captures/
12-1 Computer Networks Network Layer Basics and Routing
1.The primary goal of the network layer is to transfer packets between the origin of the data and the final destination, possibly via multiple links.
2.The network layer is responsible for routing (i.e., identifying the path that a packet must take to get from the source node to the destination node) and forwarding received packets to the next node along the identified path.
3.Which of the following additional responsibilities does the network layer have?
Congestion control
Internetworking
- Every packet that the network layer of any node receives from the link layer is sent up to the transport layer of that node. FALSE
- Which of the following is not a goal of a routing algorithm? modularity
- When using shortest path routing, the shortest path is calculated and stored in a
Routing table.
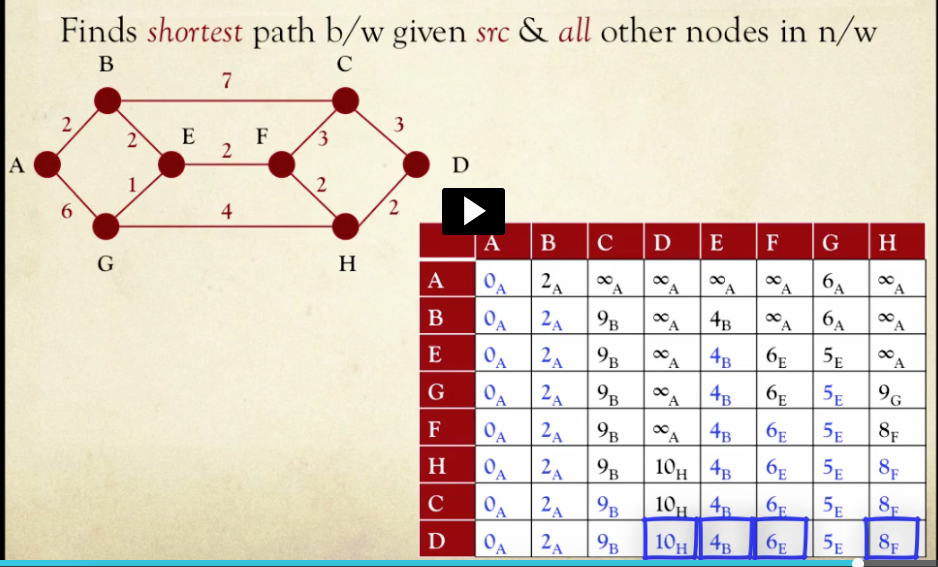
7.Dijkstra’s algorithm finds the shortest path between a given source node(s) and all destination node(s) within that network.
8.Elements written in blue font represent
nodes that have been finalized
nodes to which the shortest distance from the source node has been found
9.In any given iteration, nodes to which distances from the source node are as yet unknown are indicated using the value infinity .
10.In every iteration, the node with the shortest known distance from the source node is chosen for exploration next.
12-2 Internetworking & Congestion Control
- The common protocol in the network layer that all nodes understand is called the
Internet Protocol.
2.The Internet Protocol (IP) does not provide any reliability guarantees and so it is known as a best – effort service.
3.In Internet Protocol Version 4 protocol an IPv4 header is added to all network layer packets before sending them down to the link layer.
4.The identification field in the header provides a way recombine a packet that has been split into multiple fragments.
5.If a packet has the “do not fragment” flag set and cannot move any further because it is too large, it will be dropped.
6.IPv6 supports a larger address than IPv4 and has a simpler header than IPv4.
7.Congestion is when the network gets flooded with more packets then it can handle.
8.In traffic-aware routing, we consider the current load and direct traffic away from hotspots.
- In traffic throttling, routers track the network state and determine when congestion will occur.
10.Load shedding is when routers drop packets when congestion is too high.
13-1 IP Forwarding and Subnetting
1.Public IP addresses are guaranteed to be unique across the Internet. TRUE
2.IPv6 addresses are the future of the Internet Protocol. These addresses use
128 bits.The notation used is eight groups of four hexadecimal digits each separated by colons.
2.For the subnet represented by 171.14.0.0/18, how many least significant bits are used to identify individual hosts?
3.If the IP address range for a subnet is 145.2.12.0 to 145.2.12.255, which is the correct slash notation for this subnet? 145.2.12.0/24
4.A subnet with a shorter prefix is less specific than one with a longer prefix.
- Routing tables contain one entry for every possible destination IP on the internet. FALSE
6.How do routers extract the prefix bits from an IP address? They perform a binary AND operation between the IP and the subnet mask.
7.If there are multiple matching entries in the routing table, the match with the most specific prefix is chosen. TRUE
14-1 Transport Layer Basics, UDP
1.The transport layer provides logical end-to-end communication between hosts and is entirely run on host computers.
2.Transport layer data is not examined by nodes in between the source and destination computers.
3.Transport layer protocols support concurrent network usage by multiple application processes on the host.
4.Which of the following features may be provided by transport layer protocols?
Flow control
Congestion control
5.A host identifier (i.e., IP address) is also known as a network Service Access Point and a process identifier within a host (i.e., port number) is also known as a transport Service Access Point. The combination of the two identifiers forms a socket.
6.User Datagram Protocol (i.e., UDP) is an unreliable connectionless protocol.
7.UDP provides limited flow control FALSE
8.The length of the UDP header is fixed .
9.The IPv4 pseudo-header contents are not part of the UDP header and are only used in the UDP checksum calculation. True
The reason the UDP length is different in both UDP frames is because the data being sent is of different sizes. We can predict the UDP length by taking the number of characters in the string being sent and then adding 8, which is length of the next header. For example, the number of characters in “hello” is 5, and if we add 8 we have 13, which is the Wireshark header value. Similarly, the number of characters (including spaces) in “This is a longer message” is 24, and if we add 8, we have 32, which is the Wireshark header value.
15-1 Computer Networks TCP
1.Transmission Control Protocol or TCP provides a stream service, which is a reliable connection-oriented service.
2.A host must be in a listen or passive open state in order to receive incoming TCP connection requests.
3.TCP uses a mechanism called sequence number through which the destination/receiver can specify which segment it is acknowledging and through which the destination node can reconstruct the original stream of data if needed.
4.If the SYN flag is set to 1 in a segment sent by host A to host B, the sequence number field indicates the initial sequence number that host Awill use in segments that it sends to host B .
If the SYN flag is set to 0 in a segment sent by host A to host B, the sequence number field indicates the sequence number of the first data byte in the segment.
5.Connection establishment in TCP requires a 3 -way handshake between the two host involved.
6.Which of the following flags are used during the connection establishment phase of TCP?
SYN
ACK
7.TCP uses a mechanism called the sliding window protocol for flow control.
8.Congestion control is achieved in TCP by adjusting the transmission rate on the sender/source node.
15-2 Application Layer Basics and DNS
1.The fundamental responsibility of the Application layer is to provide networking services to users.
2.Domain Name System (DNS) is a service that resolves Human-readable names into IP addresses .
3.DNS uses name servers to maintain the mappings it needs.
4.Name resolution performed by DNS is a single step process FALSE
5.A DNS cache is a temporary database that contains a record of recent and attempted
visits to websites or other internet domains.
6.A DNS cache becomes poisoned when unauthorized domain names or IP addresses are inserted into it.
16-1 Application Layer: WWW, HTTP & SSH
1.The world wide web is a vast collection of pages, which are named with a uniform resource locator.
2.The viewing of a webpage on a browser is the result of a conversation between the browser (which acts as a client ) and the server .
4.Secure Shell or SSH is a network protocol for securing data that flows between a client and a server.
- FTP and Telnet, two other protocols that send data across a network, are different from SSH in that they send unencrypted data. SSH on the other hand, sends encrypted data using a set of cryptographic keys.
6.Select ALL that apply. What are some things that you can do securely with SSH?
Transfer files across a network
Execute system commands from a remote location
Perform port forwarding.
7.Port forwarding allows traffic flowing from an SSH client to an SSH server to be
Multiplexed into port 22 and then sent across the network in an encrypted tunnel.
https://www.sojson.com/convert/subnetmask.html
http://www.moserware.com/2009/09/stick-figure-guide-to-advanced.html
http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_DNSMessageHeaderandQuestionSectionFormat.htm
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B2pK0GpUEQ4hdXN1dmUzb0ZVVXM/view
D to b https://www.rapidtables.com/convert/number/decimal-to-binary.html
B to d https://www.rapidtables.com/convert/number/binary-to-decimal.html