副标题#e#
首先,我们对Collection举办说明。下面先看看Collection的一些框架类的干系图:
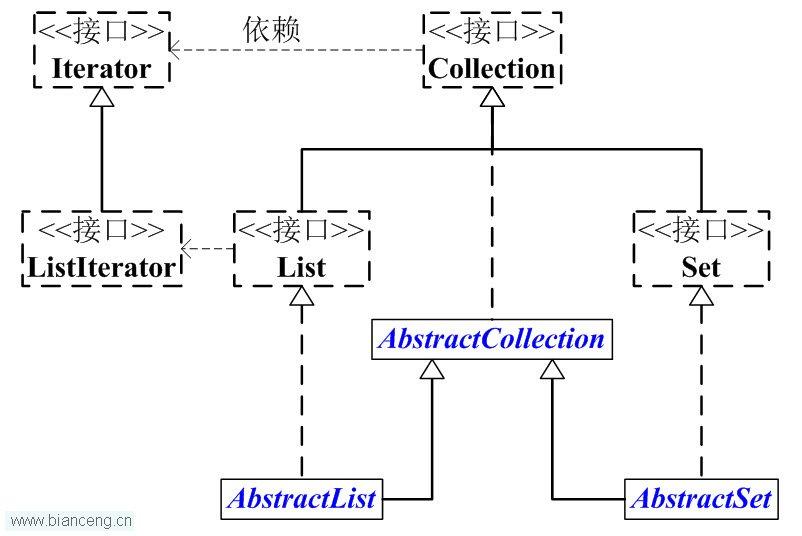
Collection是一个接口,它主要的两个分支是:List 和 Set。
List和Set都是接口,它们担任于Collection。List是有序的行列,List中可以有反复的元素;而Set是数学观念中的荟萃,Set中没有反复元素!
List和Set都有它们各自的实现类。
为了利便,我们抽象出了AbstractCollection抽象类,它实现了Collection中的绝大部门函数;这样,在Collection的实现类中,我们就可以通过担任AbstractCollection省去反复编码。AbstractList和AbstractSet都担任于AbstractCollection,详细的List实现类担任于AbstractList,而Set的实现类则担任于AbstractSet。
别的,Collection中有一个iterator()函数,它的浸染是返回一个Iterator接口。凡是,我们通过Iterator迭代器来遍历荟萃。ListIterator是List接口所特有的,在List接口中,通过ListIterator()返回一个ListIterator工具。
接下来,我们看看各个接口和抽象类的先容;然后,再对实现类举办具体的相识。
1 Collection简介
Collection的界说如下:
interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {}
它是一个接口,是高度抽象出来的荟萃,它包括了荟萃的根基操纵:添加、删除、清空、遍历(读取)、是否为空、获取巨细、是否掩护某元素等等。
Collection接口的所有子类(直接子类和间接子类)都必需实现2种结构函数:不带参数的结构函数 和 参数为Collection的结构函数。带参数的结构函数,可以用来转换Collection的范例。
// Collection的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray()
2 List简介
List的界说如下:
interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {}
List是一个担任于Collection的接口,即List是荟萃中的一种。List是有序的行列,List中的每一个元素都有一个索引;第一个元素的索引值是0,往后的元素的索引值依次+1。和Set差异,List中答允有反复的元素。
List的官方先容如下:
A List is a collection which maintains an ordering for its elements. Every element in the List has an index. Each element can thus be accessed by its index, with the first index being zero. Normally, Lists allow duplicate elements, as compared to Sets, where elements have to be unique.
#p#副标题#e#
关于API方面。既然List是担任于Collection接口,它自然就包括了Collection中的全部函数接口;由于List是有序行列,它也特另外有本身的API接口。主要有“添加、删除、获取、修改指定位置的元素”、“获取List中的子行列”等。
// Collection的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray() // 对比与Collection,List新增的API: abstract void add(int location, E object) abstract boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract E get(int location) abstract int indexOf(Object object) abstract int lastIndexOf(Object object) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator() abstract E remove(int location) abstract E set(int location, E object) abstract List<E> subList(int start, int end)
3 Set简介
Set的界说如下:
interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> {}
#p#分页标题#e#
Set是一个担任于Collection的接口,即Set也是荟萃中的一种。Set是没有反复元素的荟萃。
关于API方面。Set的API和Collection完全一样。
// Set的API abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray()
4 AbstractCollection
AbstractCollection的界说如下:
abstractclass AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> {}
AbstractCollection是一个抽象类,它实现了Collection中除iterator()和size()之外的函数。
AbstractCollection的主要浸染:它实现了Collection接口中的大部门函数。从而利便其它类实现Collection,好比ArrayList、LinkedList等,它们这些类想要实现Collection接口,通过担任AbstractCollection就已经实现了大部门的接口了。
5 AbstractList
AbstractList的界说如下:
abstractclass AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {}
AbstractList是一个担任于AbstractCollection,而且实现List接口的抽象类。它实现了List中除size()、get(int location)之外的函数。
AbstractList的主要浸染:它实现了List接口中的大部门函数。从而利便其它类担任List。
别的,和AbstractCollection对比,AbstractList抽象类中,实现了iterator()接口。
6 AbstractSet
AbstractSet的界说如下:
abstractclass AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> {}
AbstractSet是一个担任于AbstractCollection,而且实现Set接口的抽象类。由于Set接口和Collection接口中的API完全一样,Set也就没有本身单独的API。和AbstractCollection一样,它实现了List中除iterator()和size()之外的函数。
AbstractSet的主要浸染:它实现了Set接口中的大部门函数。从而利便其它类实现Set接口。
7 Iterator
查察本栏目
Iterator的界说如下:
interface Iterator<E> {}
Iterator是一个接口,它是荟萃的迭代器。荟萃可以通过Iterator去遍历荟萃中的元素。Iterator提供的API接口,包罗:是否存在下一个元素、获取下一个元素、删除当前元素。
留意:Iterator遍历Collection时,是fail-fast机制的。即,当某一个线程A通过iterator去遍历某荟萃的进程中,若该荟萃的内容被其他线程所改变了;那么线程A会见集适时,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,发生fail-fast事件。关于fail-fast的具体内容,我们会在后头专门举办说明。TODO
// Iterator的APIabstractboolean hasNext()abstract E next()abstractvoid remove()
8 ListIterator
ListIterator的界说如下:
interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {}
ListIterator是一个担任于Iterator的接口,它是行列迭代器。专门用于便利List,能提供向前/向后遍历。对比于Iterator,它新增了添加、是否存在上一个元素、获取上一个元素等等API接口。
// ListIterator的API // 担任于Iterator的接口 abstract boolean hasNext() abstract E next() abstract void remove() // 新增API接口 abstract void add(E object) abstract boolean hasPrevious() abstract int nextIndex() abstract E previous() abstract int previousIndex() abstract void set(E object)
