LUBS5006M
International Business Finance
国际商业代写 Question 1. Explain the basic differences between the operation of a currency forward market and a futures market.
FUTURES AND OPTIONS ON FOREIGN EXCHANGE 国际商业代写
Question 1. Explain the basic differences between the operation of a currency forward market and a futures market.
Question 2. In order for a derivatives market to function most efficiently, two types of economic agents are needed: hedgers and speculators. Explain.
Question 3. Why are most futures positions closed out through a reversing trade rather than held to delivery?
Question 4. What is the major difference in the obligation of one with a long position in a futures (or forward) contract in comparison to an options contract?
Question 5. What is meant by the terminology that an option is in-, at-, or out-of-the-money?
Question 6. 国际商业代写
Assume today’s settlement price on a CME EUR futures contract is $1.3140/EUR. You have a short position in one contract. Your performance bond account currently has a balance of $1,700. The next three days’ settlement prices are $1.3126, $1.3133, and $1.3049. The contract size of one EUR contract is EUR125,000. Calculate the changes in the performance bond account from daily marking-to-market and the balance of the performance bond account after the third day.
Question 7. Do problem 6 again assuming you have a long position in the futures contract.
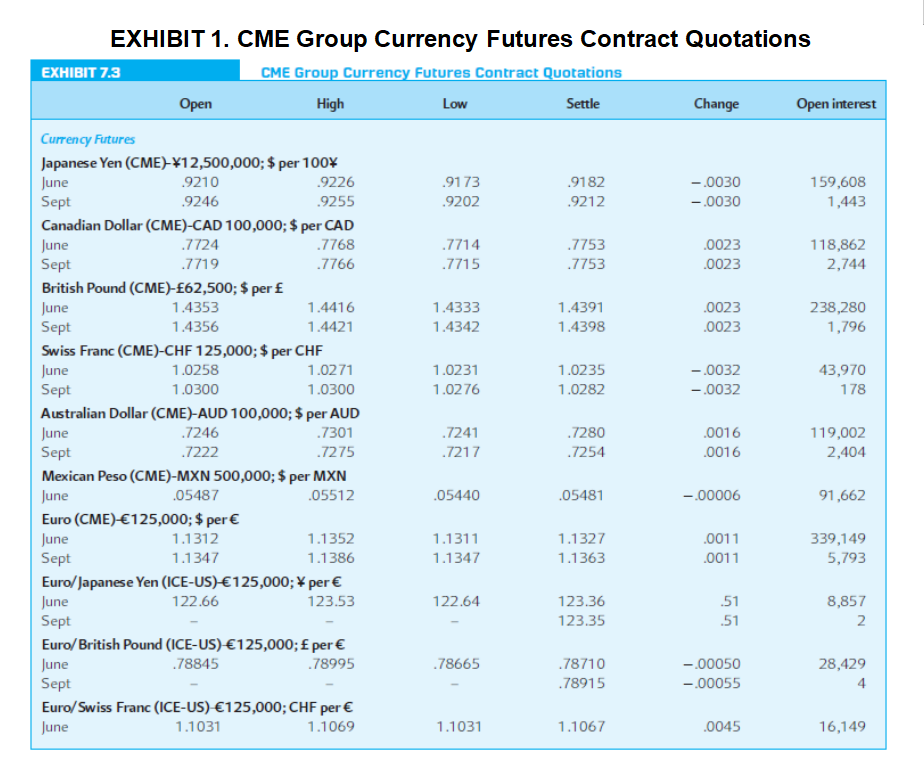
Question 8. Using the quotations in Exhibit 1 (on next page), note that the September 2016 Mexican peso futures contract has a price of $0.05481 per MXN. You believe the spot price in September will be $0.06133 per MXN.
What speculative position would you enter into to attempt to profit from your beliefs?
Calculate your anticipated profits, assuming you take a position in three contracts.
What is the size of your profit (loss) if the futures price is indeed an unbiased predictor of the future spot price and this price materializes?
Question 9.
Do problem 8 again assuming you believe the September 2016 spot price will be $0.04829 per MXN.
Question 10. Assume that the Japanese yen is trading at a spot price of 92.04 cents per 100 yen. Further assume that the premium of an American call (put) option with a striking price of 93 is 2.10 (2.20) cents per 100 yen. Calculate the intrinsic value and the time value of the call and put options.
Question 11. A speculator is considering the purchase of five three-month Japanese yen call options with a striking price of 96 cents per 100 yen. The premium is 1.35 cents per 100 yen. The spot price is 95.28 cents per 100 yen and the 90-day forward rate is 95.71 cents. The speculator believes the yen will appreciate to $1.00 per 100 yen over the next three months. As the speculator’s assistant, you have been asked to prepare the following:
1. Graph the call option cash flow schedule.
2. Determine the speculator’s profit if the yen appreciates to $1.00/100 yen.
3. Determine the speculator’s profit if the yen only appreciates to the forward rate.
4. Determine the future spot price at which the speculator will only break even.
The Market For Foreign Exchange 国际商业代写
Question 1. What is meant by a currency trading at a discount or at a premium in the forward market?
Question 2. A CAD/$ bank trader is currently quoting a small figure bid-ask of 35-40, when the rest of the market is trading at CAD1.3436-CAD1.3441. What is implied about the trader’s beliefs by his prices?
Question 3. What is triangular arbitrage? What is a condition that will give rise to a triangular arbitrage opportunity?
Question 4. Over the past five years, the exchange rate between British pound and U.S. dollar, $/£, has changed from about 1.90 to about 1.45. Would you agree that over this five-year period that British goods have become cheaper for buyers in the United States?
Question 5. 国际商业代写
A foreign exchange trader with a U.S. bank took a short position of £5,000,000 when the $/£ exchange rate was 1.55. Subsequently, the exchange rate has changed to 1.61. Is this movement in the exchange rate good from the point of view of the position taken by the trader? By how much has the bank’s liability changed because of the change in the exchange rate?
Question 6. Given the following information, what are the NZD/SGD currency against currency bid-ask quotations?
American Terms European Terms
Bank Quotations Bid Ask Bid Ask
New Zealand dollar .7265 .7272 1.3751 1.3765
Singapore dollar .6135 .6140 1.6287 1.6300
Question 7. Doug Bernard specializes in cross-rate arbitrage. He notices the following quotes:
Swiss franc/dollar = SFr1.5971/$
Australian dollar/U.S. dollar = A$1.8215/$
Australian dollar/Swiss franc = A$1.1440/SFr
Ignoring transaction costs, does Doug Bernard have an arbitrage opportunity based on these quotes? If there is an arbitrage opportunity, what steps would he take to make an arbitrage profit, and how would he profit if he has $1,000,000 available for this purpose.
Question 8. 国际商业代写
The current spot exchange rate is $1.95/£ and the three-month forward rate is $1.90/£. Based on your analysis of the exchange rate, you are pretty confident that the spot exchange rate will be $1.92/£ in three months. Assume that you would like to buy or sell £1,000,000.
a. What actions do you need to take to speculate in the forward market? What is the expected dollar profit from speculation?
b. What would be your speculative profit in dollar terms if the spot exchange rate actually turns out to be $1.86/£.
Question 9. Omni Advisors, an international pension fund manager, plans to sell equities denominated in Swiss Francs (CHF) and purchase an equivalent amount of equities denominated in South African rands (ZAR). Omni will realize net proceeds of 3 million CHF at the end of 30 days and wants to eliminate the risk that the ZAR will appreciate relative to the CHF during this 30-day period. The following exhibit shows current exchange rates between the ZAR, CHF, and the U.S. dollar (USD).
Currency Exchange Rates
| ZAR/USD | ZAR/USD | CHF/USD | CHF/USD | |
| Maturity | Bid | Ask | Bid | Ask |
| Spot | 6.2681 | 6.2789 | 1.5282 | 1.5343 |
| 30-day | 6.2538 | 6.2641 | 1.5226 | 1.5285 |
| 90-day | 6.2104 | 6.2200 | 1.5058 | 1.5115 |
a. Describe the currency transaction that Omni should undertake to eliminate currency risk over the 30-day period.
b. Calculate the following:
- The CHF/ZAR cross-currency rate Omni would use in valuing the Swiss equity portfolio.
- The current value of Omni’s Swiss equity portfolio in ZAR.
- The annualized forward premium or discount at which the ZAR is trading versus the CHF.

更多代写:北美CS quiz代考价格 美国gre代考 英国宏观经济代考 北美final论文代写 北美法律论文代写 人工代写
