写一个Android输入法01——最简步骤
下一篇
文中演试用Android Studio写一个非常简单的电脑输入法。页面和互动都很简单,只求剔肉留骨,突显写一个Android电脑输入法的关键点。
- 1、开启Android Studio建立新项目,该新项目和一般APP的不同点取决于它不用加上一切Activity:
我给该电脑输入法取名为AndroidXXIME。
- 2、改动manifest文档
至始文《Android下创建一个输入法》中常说:电脑输入法是一个包括IME service的安卓软件程序流程,最先应当在程序流程的manifest中申明service。我的manifest.xml文件以下:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.binglen.androidxxime"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <service android:name=".AndroidXXIME" android:label="@string/xxime" android:permission="android.permission.BIND_INPUT_METHOD" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.view.InputMethod" /> </intent-filter> <meta-data android:name="android.view.im" android:resource="@xml/method"/> </service> </application> </manifest>
在Android Studio转化成application块的尾端加上IME service的申明。第一行粗体字申明必须BIND_INPUT_METHOD管理权限,第二行粗体字建立了一个可以配对android.view.InputMethod的intent filter,第三行粗体字界定了电脑输入法的metadata。
必须留意:service android:name务必与后边java文件中的类名保持一致。
下面建立该service中申明的資源。
- 3、method.xml
meta-data里采用了資源xml/method文档,该文件中包括了电脑输入法的subtype特性,输入法根据该特性界定它所适用的键入方式和语言表达,一个电脑输入法能够包括好几个subtype特性。在工程项目中res下建立xml文件夹,把method.xml加上到该文件夹名称下。method.xml內容以下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <input-method xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <subtype android:label="@string/subtype_en_US" android:imeSubtypeLocale="en_US" android:imeSubtypeMode="keyboard" /> </input-method>
有关subtype的特性,能够参照InputMethodSubtype:
label是该subtype的姓名
imeSubtypeLocale是该subtype适用的语言表达种类
imeSubtypeMode是它所适用的方式,能够是keyboard或是voice,当电脑输入法被唤起是,系统软件会把客户挑选的mode值发送给电脑输入法。
- 4、stings.xml
在这儿补往前文引入到的字符串数组界定:
<string name="xxime">XXIME</string> <string name="subtype_en_US">English (US)</string>
xxime在manifest中界定service的android:label时被引入到,该字符串用于显示设备“语言表达和电脑输入法”中本电脑输入法的姓名:
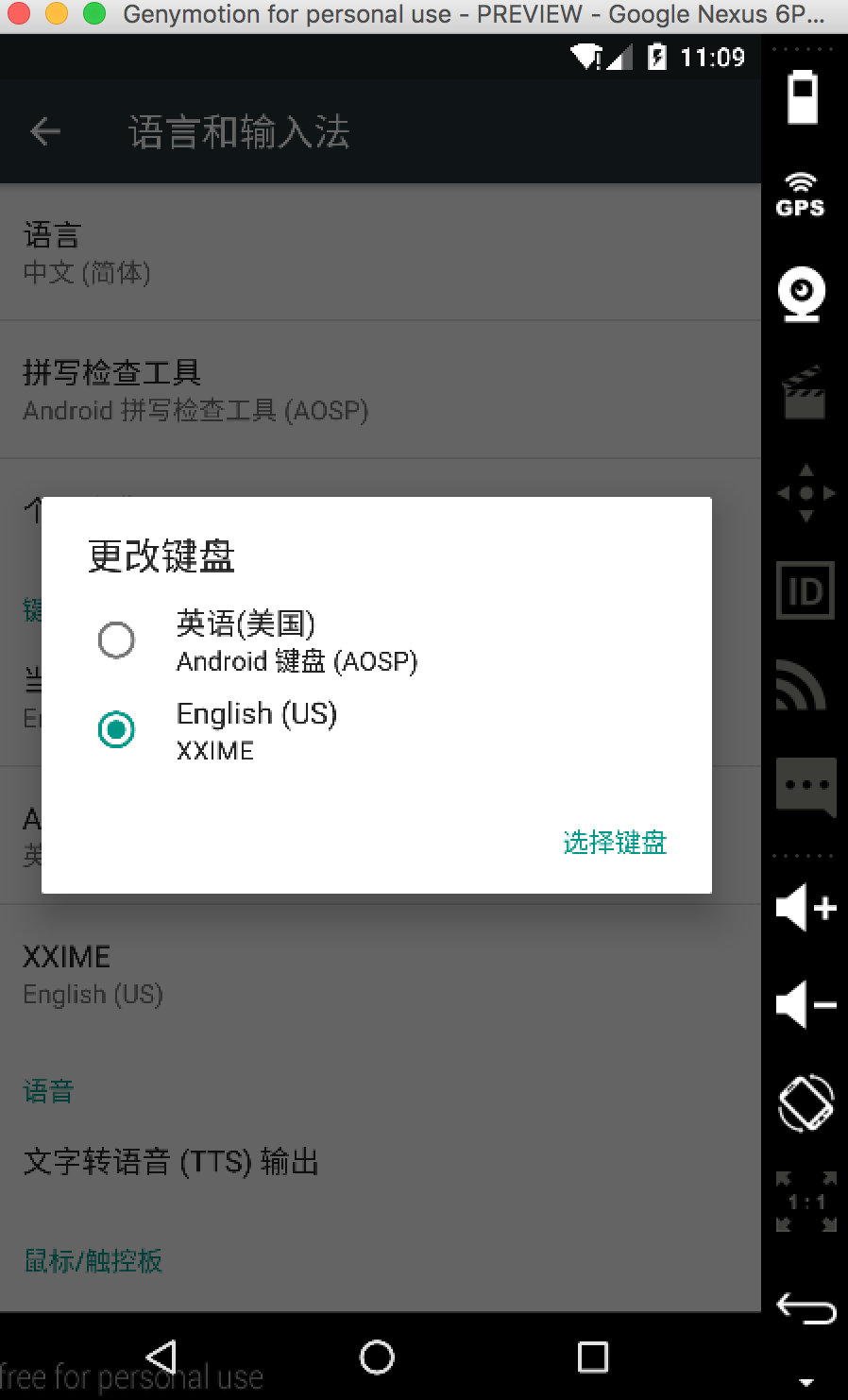
- 5、界定键盘布局
在res/layout/中加上文档keyboard.xml,界定键盘布局,內容以下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@ id/keyboard" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:keyPreviewLayout ="@layout/preview" />
点一下android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView查询有关它的XML特性,在其中keyPreviewLayout表明电脑键盘被按住时的合理布局資源。在res/layout中加上preview.xml以下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:background="#ffff00" android:textStyle="bold" android:textSize="30sp" > </TextView>
里边仅有一个TextView。
前边資源引入的根源都来源于manifest文档,却看不到哪儿引入keyboard.xml。回答在后面,AndroidXXIME.java文件中onCreateInputView()涵数中建立电脑键盘主视图和键盘布局的时候会采用,包含下边的qwerty.xml。
- 6、界定功能键信息内容
功能键信息定义在Keyboard中,其文件格式方式以下:
<Keyboard android:keyWidth="p" android:keyHeight="50px" android:horizontalGap="2px" android:verticalGap="2px" > <Row android:keyWidth="32px" > <Key android:keyLabel="A" /> ... </Row> ... </Keyboard>
这是一个嵌入构造,其下包括了Row表明一行,內部又包括Key表明一个功能键,每一个功能键有两个选填特性:
· keyLabel:功能键上表明的文本
· codes:该功能键意味着的Unicode码
大家的功能键信息内容文档在res/xml/qwerty.xml中,界定以下:
<Keyboard xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:keyWidth="10%p" android:horizontalGap="1080x" android:verticalGap="1080x" android:keyHeight="60dp" > <Row> <Key android:codes="113" android:keyLabel="q" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"/> <Key android:codes="119" android:keyLabel="w"/> <Key android:codes="101" android:keyLabel="e"/> <Key android:codes="114" android:keyLabel="r"/> <Key android:codes="116" android:keyLabel="t"/> <Key android:codes="121" android:keyLabel="y"/> <Key android:codes="117" android:keyLabel="u"/> <Key android:codes="105" android:keyLabel="i"/> <Key android:codes="111" android:keyLabel="o"/> <Key android:codes="112" android:keyLabel="p" android:keyEdgeFlags="right"/> </Row> <Row android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"> <Key android:codes="97" android:keyLabel="a" android:horizontalGap="5%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"/> <Key android:codes="115" android:keyLabel="s"/> <Key android:codes="100" android:keyLabel="d"/> <Key android:codes="102" android:keyLabel="f"/> <Key android:codes="103" android:keyLabel="g"/> <Key android:codes="104" android:keyLabel="h"/> <Key android:codes="106" android:keyLabel="j"/> <Key android:codes="107" android:keyLabel="k"/> <Key android:codes="108" android:keyLabel="l" android:keyEdgeFlags="right"/> </Row> <Row> <Key android:codes="39" android:keyLabel="'" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"/> <Key android:codes="122" android:keyLabel="z"/> <Key android:codes="120" android:keyLabel="x"/> <Key android:codes="99" android:keyLabel="c"/> <Key android:codes="118" android:keyLabel="v"/> <Key android:codes="98" android:keyLabel="b"/> <Key android:codes="110" android:keyLabel="n"/> <Key android:codes="109" android:keyLabel="m"/> <Key android:codes="44" android:keyLabel=","/> <Key android:codes="46" android:keyLabel="." android:keyEdgeFlags="right"/> </Row> <Row android:rowEdgeFlags="bottom"> <Key android:codes="63" android:keyLabel="\?" android:keyWidth="10%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"/> <Key android:codes="47" android:keyLabel="/" android:keyWidth="10%p" /> <Key android:codes="32" android:keyLabel=" " android:keyWidth="40%p" android:isRepeatable="true"/> <Key android:codes="-5" android:keyLabel="DEL" android:keyWidth="20%p" android:isRepeatable="true"/> <Key android:codes="-4" android:keyLabel="DONE" android:keyWidth="20%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="right"/> </Row> </Keyboard>
在其中有一些负数是界定在Keyboard类中的变量定义。
在字母a键的界定中有:android:horizontalGap=”5%p”,官方网文本文档表述android:horizontalGap用于界定功能键中间的间隔,实际上是与上一个功能键中间的间距,如果是左侧开头的的功能键,则是与左边沿中间的间距。%p表明在父部件中的规格占有率。
- 6、建立服务项目
下面就必须为电脑输入法建立service和listener了。能够在一个类里进行这两个人物角色,AndroidXXIME类拓展了InputMethodService,并完成了KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener插口。此类的界定以下:
public class AndroidXXIME extends InputMethodService implements KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener { private KeyboardView keyboardView; // 相匹配keyboard.xml中界定的KeyboardView private Keyboard keyboard; // 相匹配qwerty.xml中界定的Keyboard @Override public void onPress(int primaryCode) { } @Override public void onRelease(int primaryCode) { } @Override public void onText(CharSequence text) { } @Override public void swipeDown() { } @Override public void swipeLeft() { } @Override public void swipeRight() { } @Override public void swipeUp() { } @Override public View onCreateInputView() { // keyboard被建立后,将启用onCreateInputView涵数 keyboardView = (KeyboardView)getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.keyboard, null); // 这里应用了keyboard.xml keyboard = new Keyboard(this, R.xml.qwerty); // 这里应用了qwerty.xml keyboardView.setKeyboard(keyboard); keyboardView.setOnKeyboardActionListener(this); return keyboardView; } private void playClick(int keyCode){ // 点一下功能键时播放视频响声,在onKey涵数中被启用 AudioManager am = (AudioManager)getSystemService(AUDIO_SERVICE); switch(keyCode){ case 32: am.playSoundEffect(AudioManager.FX_KEYPRESS_SPACEBAR); break; case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DONE: case 10: am.playSoundEffect(AudioManager.FX_KEYPRESS_RETURN); break; case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DELETE: am.playSoundEffect(AudioManager.FX_KEYPRESS_DELETE); break; default: am.playSoundEffect(AudioManager.FX_KEYPRESS_STANDARD); } } @Override public void onKey(int primaryCode, int[] keyCodes) { InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection(); playClick(primaryCode); switch(primaryCode){ case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DELETE : ic.deleteSurroundingText(1, 0); break; case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DONE: ic.sendKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER)); break; default: char code = (char)primaryCode; ic.commitText(String.valueOf(code), 1); } } }
- 7、运作。具体做法参照《SoftKeyboard在AndroidStudio下的配置和运行》,页面以下:
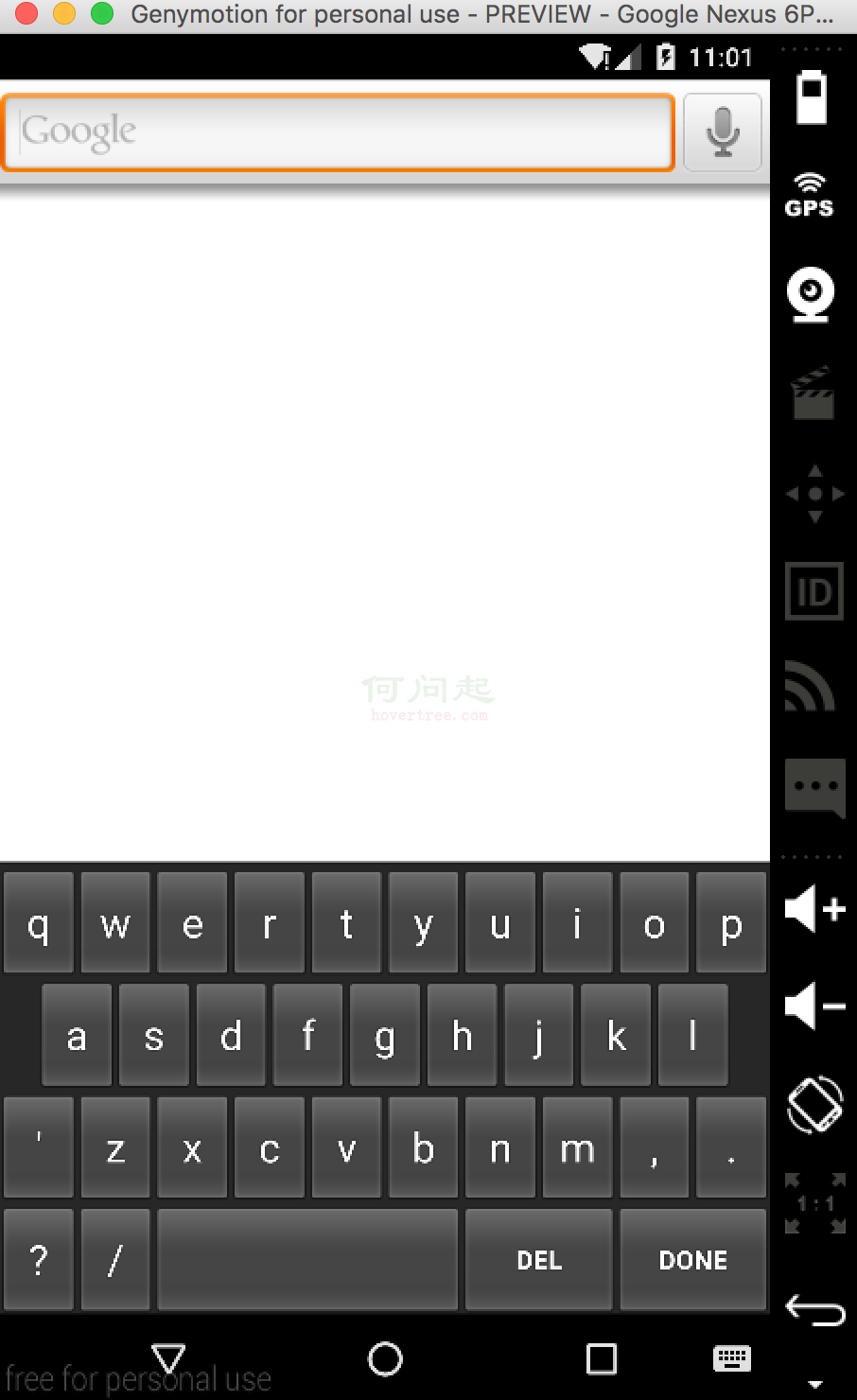
该方法编码可参照https://github.com/palanceli/AndroidXXIME/tree/v1
