副标题#e#
跟着干系型数据库在某些方面的力有未逮,相识当下风行的各类数据库模式的特点和机能,无疑会给我们提供更多的选择和偏向。 neo4j是一种图形数据库,在遍历和关联查询方面具有突出的优势。空话少说,深入相识neo4j之前,先让我们实验一下奈何在措施中利用neo4j。
neo4j回收java语言开拓,假如我们要在java措施中以内嵌方法利用neo4j,只需导入neo4j的对应包即可。
首先,我们来建设一个maven项目并修改pom.xml添加对neo4j的依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>neo4j-learn</groupId>
<artifactId>neo4j-learn</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.neo4j</groupId>
<artifactId>neo4j</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
然后,我们在项目中建设一个neo4j.properties(数据库的设置文件)文件和一个java类(挪用数据库)。
neo4j.properties
# Default values for the low-level graph engine
#neostore.nodestore.db.mapped_memory=25M
#neostore.relationshipstore.db.mapped_memory=50M
#neostore.propertystore.db.mapped_memory=90M
#neostore.propertystore.db.strings.mapped_memory=130M
#neostore.propertystore.db.arrays.mapped_memory=130M
# Autoindexing
# Enable auto-indexing for nodes, default is false
#node_auto_indexing=true
# The node property keys to be auto-indexed, if enabled
#node_keys_indexable=name,age
# Enable auto-indexing for relationships, default is false
#relationship_auto_indexing=true
# The relationship property keys to be auto-indexed, if enabled
#relationship_keys_indexable=name,age
# Keep logical logs, needed for online backups to work
keep_logical_logs=true
# Enable online backups to be taken from this database.
online_backup_enabled=true
# Uncomment and specify these lines for running Neo4j in High Availability mode.
# ha.server_id is a unique integer for each instance of the Neo4j database in the cluster.
# (as opposed to the coordinator instance IDs)
# example: ha.server_id=1
#ha.server_id=
# ha.coordinators is a comma-separated list (without spaces) of the host:port of where to
# find one or more of the Neo4j coordinator servers.
# Avoid localhost due to IP resolution issues on some systems.
# example: ha.coordinators=localhost:2181,1.2.3.4:4321
#ha.coordinators=localhost:2181
# You can also, optionally, configure the ha.cluster_name. This is the name of the cluster this
# instance is supposed to join. Accepted characters are alphabetical, numerical, dot and dash.
# This configuration is useful if you have multiple Neo4j HA clusters managed by the same
# Coordinator cluster.
# Example: ha.cluster_name = my.neo4j.ha.cluster
#ha.cluster_name =
# IP and port for this instance to bind to to communicate data with the
# other neo4j instances in the cluster. This is broadcasted to the other
# cluster members, so different members can have different communication ports.
# Optional if the members are on different machines so the IP is different for every member.
#ha.server = localhost:6001
# The interval at which slaves will pull updates from the master. Comment out
# the option to disable periodic pulling of updates. Unit is seconds.
ha.pull_interval = 10
# The session timeout for the zookeeper client. Lower values make new master
# election happen closer to the master loosing connection but also more sensitive
# to zookeeper quorum hiccups. If experiencing master switches without reason
# consider increasing this value. Unit is seconds
#ha.zk_session_timeout = 5
# Amount of slaves the master will try to push a transaction to upon commit (default is 1).
# The master will optimistically continue and not fail the transaction even if it fails to
# reach the push factor. Setting this to 0 will increase write performance when writing
# through master but could potentially lead to branched data (or loss of transaction)
# if the master goes down.
#ha.tx_push_factor=1
# Strategy the master will use when pushing data to slaves (if the push factor is greater than 0).
# There are two options available "fixed" (default) or "round_robin". Fixed will start by
# pushing to slaves ordered by server id (highest first) improving performance since the
# slaves only have to cache up one transaction at a time.
#ha.tx_push_strategy=fixed
# Enable this to be able to upgrade a store from 1.4 -> 1.5 or 1.4 -> 1.6
#allow_store_upgrade=true
# Enable this to specify a parser other than the default one. 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 are available
#cypher_parser_version=1.6
#p#副标题#e#
#p#分页标题#e#
java文件(neo4j示例文件修改而来)
package org.easypoint;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.Direction;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.GraphDatabaseService;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.Node;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.Relationship;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.RelationshipType;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.Transaction;
import org.neo4j.graphdb.factory.GraphDatabaseFactory;
import org.neo4j.kernel.impl.util.FileUtils;
public class Learn1
{
private static final String DB_PATH = "target/neo4j-hello-db";
String greeting;
// START SNIPPET: vars
GraphDatabaseService graphDb;
Node firstNode;
Node secondNode;
Relationship relationship;
// END SNIPPET: vars
// START SNIPPET: createReltype
private static enum RelTypes implements RelationshipType
{
KNOWS
}
// END SNIPPET: createReltype
public static void main( final String[] args )
{
Learn1 hello = new Learn1();
hello.createDb();
hello.removeData();
hello.shutDown();
}
void createDb()
{
clearDb();
// START SNIPPET: startDb
graphDb = new GraphDatabaseFactory()
.newEmbeddedDatabaseBuilder( "target/database/learn1" )
.loadPropertiesFromFile(Learn1.class.getResource("/").getPath()+"neo4j.properties" )
.newGraphDatabase();
registerShutdownHook( graphDb );
// END SNIPPET: startDb
// START SNIPPET: transaction
Transaction tx = graphDb.beginTx();
try
{
// Updating operations go here
// END SNIPPET: transaction
// START SNIPPET: addData
firstNode = graphDb.createNode();
firstNode.setProperty( "message", "Hello, " );
secondNode = graphDb.createNode();
secondNode.setProperty( "message", "World!" );
relationship = firstNode.createRelationshipTo( secondNode, RelTypes.KNOWS );
relationship.setProperty( "message", "brave Neo4j " );
// END SNIPPET: addData
// START SNIPPET: readData
System.out.print( firstNode.getProperty( "message" ) );
System.out.print( relationship.getProperty( "message" ) );
System.out.print( secondNode.getProperty( "message" ) );
// END SNIPPET: readData
greeting = ( (String) firstNode.getProperty( "message" ) )
+ ( (String) relationship.getProperty( "message" ) )
+ ( (String) secondNode.getProperty( "message" ) );
// START SNIPPET: transaction
tx.success();
}
finally
{
tx.finish();
}
// END SNIPPET: transaction
}
private void clearDb()
{
try
{
FileUtils.deleteRecursively( new File( DB_PATH ) );
}
catch ( IOException e )
{
throw new RuntimeException( e );
}
}
void removeData()
{
Transaction tx = graphDb.beginTx();
try
{
// START SNIPPET: removingData
// let's remove the data
firstNode.getSingleRelationship( RelTypes.KNOWS, Direction.OUTGOING ).delete();
firstNode.delete();
secondNode.delete();
// END SNIPPET: removingData
tx.success();
}
finally
{
tx.finish();
}
}
void shutDown()
{
System.out.println();
System.out.println( "Shutting down database ..." );
// START SNIPPET: shutdownServer
graphDb.shutdown();
// END SNIPPET: shutdownServer
}
// START SNIPPET: shutdownHook
private static void registerShutdownHook( final GraphDatabaseService graphDb )
{
// Registers a shutdown hook for the Neo4j instance so that it
// shuts down nicely when the VM exits (even if you "Ctrl-C" the
// running application).
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook( new Thread()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
graphDb.shutdown();
}
} );
}
// END SNIPPET: shutdownHook
}
#p#分页标题#e#
运行java文件,可以看到在target/database/下建设了一个learn1的数据库。
[easy@easy learn1]$ pwd /home/easy/workspace/neo4j-learn/target/database/learn1 [easy@easy learn1]$ ls active_tx_log index messages.log neostore neostore.id neostore.nodestore.db neostore.nodestore.db.id neostore.propertystore.db neostore.propertystore.db.arrays neostore.propertystore.db.arrays.id neostore.propertystore.db.id neostore.propertystore.db.index neostore.propertystore.db.index.id neostore.propertystore.db.index.keys neostore.propertystore.db.index.keys.id neostore.propertystore.db.strings neostore.propertystore.db.strings.id neostore.relationshipstore.db neostore.relationshipstore.db.id neostore.relationshiptypestore.db neostore.relationshiptypestore.db.id neostore.relationshiptypestore.db.names neostore.relationshiptypestore.db.names.id nioneo_logical.log.active nioneo_logical.log.v0 store_lock tm_tx_log.1 [easy@easy learn1]$
我们已经简朴的将neo4j在j嵌入在ava措施中,并且从java代码我们也可以看出,neo4j数据库主要依靠node,relationship和property来存储数据,操作relationship将各个node链接起来。
除了以内嵌的方法利用NEO4J,我们也可以将NEO4J作为处事来利用。
首先,在neo4j官网下载neo4j数据库,将其解压后,在bin目次下运行 neo4j start,启动数据处事。此时,可以在http://localhost:7474/webadmin/ 视察处事的运行状态。
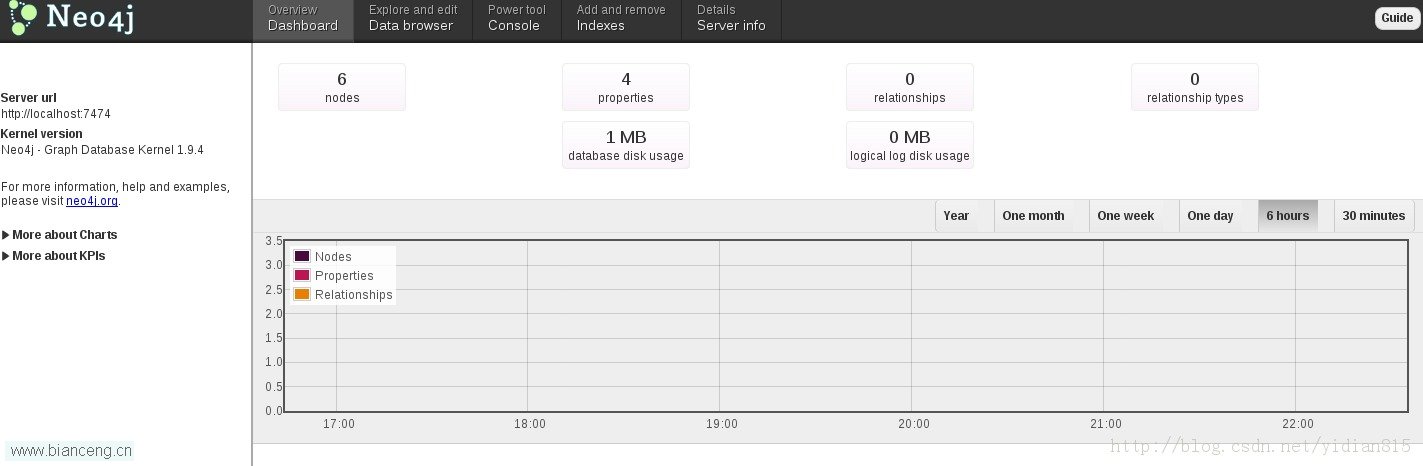
查察本栏目
neo4j为我们提供了REST方法来会见数据库处事,这里我们利用JERSEY作为REST 客户端。设置MAVEN依赖如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-project</artifactId>
<version>1.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-server</artifactId>
<version>1.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-client</artifactId>
<version>1.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-core</artifactId>
<version>1.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-json</artifactId>
<version>1.17</version>
</dependency>
新建java类Learn1Rest
package org.easypoint;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientResponse;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.WebResource;
import com.sun.jersey.api.client.Client;
import java.net.URI;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: easy
* Date: 13-10-20
* Time: 下午9:39
* To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
*/
public class Learn1Rest {
public static void main(String args[]){
Learn1Rest lr = new Learn1Rest();
URI firstNode = lr.createNode();
lr.addProperty( firstNode, "name", "Joe Strummer" );
URI secondNode = lr.createNode();
lr.addProperty( secondNode, "band", "The Clash" );
}
public URI createNode(){
String SERVER_ROOT_URI = "http://localhost:7474/db/data/";
final String nodeEntryPointUri = SERVER_ROOT_URI + "node";
WebResource resource = Client.create().resource(nodeEntryPointUri);
ClientResponse response = resource.accept( MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON )
.type(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.entity("{}")
.post(ClientResponse.class);
final URI location = response.getLocation();
System.out.println( String.format("POST to [%s], status code [%d], location header [%s]",
nodeEntryPointUri, response.getStatus(), location.toString() ) );
response.close();
return location;
}
public void addProperty(URI nodeUri,String propertyName, String propertyValue){
String propertyUri = nodeUri.toString() + "/properties/" + propertyName;
WebResource resource = Client.create()
.resource( propertyUri );
ClientResponse response = resource.accept( MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON )
.type( MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON )
.entity( "\"" + propertyValue + "\"" )
.put( ClientResponse.class );
System.out.println( String.format( "PUT to [%s], status code [%d]",
propertyUri, response.getStatus() ) );
response.close();
}
}
运行main要领,再次查察http://localhost:7474/webadmin/
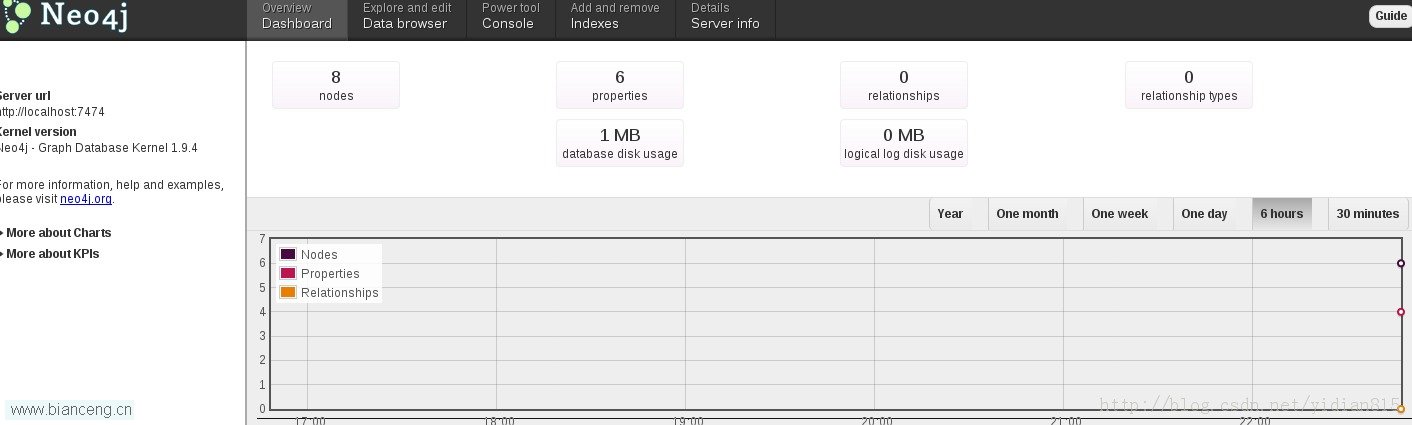
节点数量增加,会见乐成。
