副标题#e#
这一章,我们对HashSet举办进修。
我们先对HashSet有个整体认识,然后再进修它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会利用HashSet。
第1部门 HashSet先容
HashSet 简介
HashSet 是一个没有反复元素的荟萃。
它是由HashMap实现的,不担保元素的顺序,并且HashSet答允利用 null 元素。
HashSet长短同步的。假如多个线程同时会见一个哈希 set,而个中至少一个线程修改了该 set,那么它必需 保持外部同步。这凡是是通过对自然封装该 set 的工具执行同步操纵来完成的。假如不存在这样的工具,则应该利用 Collections.synchronizedSet 要领来“包装” set。最亏得建设时完成这一操纵,以防备对该 set 举办意外的差异步会见:
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(…));
HashSet通过iterator()返回的迭代器是fail-fast的。
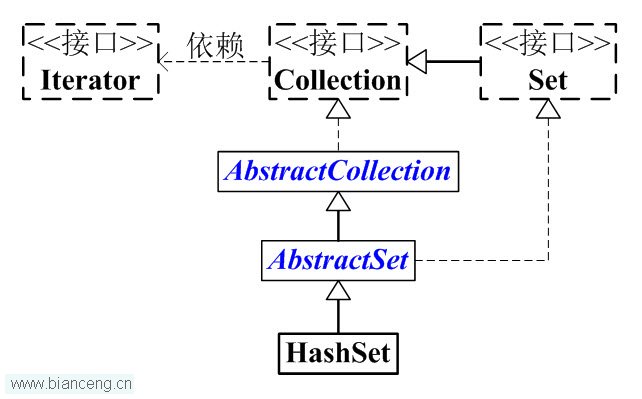
HashSet的担任干系如下:
java.lang.Object
java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
java.util.AbstractSet<E>
java.util.HashSet<E>
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { }
HashSet与Map干系如下图:
查察本栏目
HashSet的结构函数
// 默认结构函数
public HashSet()
// 带荟萃的结构函数
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c)
// 指定HashSet初始容量和加载因子的结构函数
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
// 指定HashSet初始容量的结构函数
public HashSet(int initialCapacity)
// 指定HashSet初始容量和加载因子的结构函数,dummy没有任何浸染
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy)
HashSet的主要API
boolean add(E object) void clear() Object clone() boolean contains(Object object) boolean isEmpty() Iterator<E> iterator() boolean remove(Object object) int size()
第2部门 HashSet源码理会
为了更相识HashSet的道理,下面临HashSet源码代码作出阐明。
package java.util;
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;
// HashSet是通过map(HashMap工具)生存内容的
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// PRESENT是向map中插入key-value对应的value
// 因为HashSet中只需要用到key,而HashMap是key-value键值对;
// 所以,向map中添加键值对时,键值对的值牢靠是PRESENT
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
// 默认结构函数
public HashSet() {
// 挪用HashMap的默认结构函数,建设map
map = new HashMap<E,Object>();
}
// 带荟萃的结构函数
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 建设map。
// 为什么要挪用Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16),从 (c.size()/.75f) + 1 和 16 中选择一个较量大的树呢?
// 首先,说明(c.size()/.75f) + 1
// 因为从HashMap的效率(时间本钱和空间本钱)思量,HashMap的加载因子是0.75。
// 当HashMap的“阈值”(阈值=HashMap总的巨细*加载因子) < “HashMap实际巨细”时,
// 就需要将HashMap的容量翻倍。
// 所以,(c.size()/.75f) + 1 计较出来的正好是总的空间巨细。
// 接下来,说明为什么是 16 。
// HashMap的总的巨细,必需是2的指数倍。若建设HashMap时,指定的巨细不是2的指数倍;
// HashMap的结构函数中也会从头计较,找出比“指定巨细”大的最小的2的指数倍的数。
// 所以,这里指定为16是从机能思量。制止反复计较。
map = new HashMap<E,Object>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
// 将荟萃(c)中的全部元素添加到HashSet中
addAll(c);
}
// 指定HashSet初始容量和加载因子的结构函数
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<E,Object>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
// 指定HashSet初始容量的结构函数
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<E,Object>(initialCapacity);
}
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
// 返回HashSet的迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
// 实际上返回的是HashMap的“key荟萃的迭代器”
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
// 将元素(e)添加到HashSet中
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
// 删除HashSet中的元素(o)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
// 克隆一个HashSet,并返回Object工具
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError();
}
}
// java.io.Serializable的写入函数
// 将HashSet的“总的容量,加载因子,实际容量,所有的元素”都写入到输出流中
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out HashMap capacity and load factor
s.writeInt(map.capacity());
s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor());
// Write out size
s.writeInt(map.size());
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Iterator i=map.keySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); )
s.writeObject(i.next());
}
// java.io.Serializable的读取函数
// 将HashSet的“总的容量,加载因子,实际容量,所有的元素”依次读出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in HashMap capacity and load factor and create backing HashMap
int capacity = s.readInt();
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
map = (((HashSet)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor));
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
}
}
说明:
#p#副标题#e#
#p#分页标题#e#
HashSet的代码实际上很是简朴,通过上面的注释应该很可以或许看懂。它是通过HashMap实现的,若对HashSet的领略有坚苦,发起先进修以下HashMap;学完HashMap之后,在进修HashSet就很是容易了。
第3部门 HashSet遍历方法
3.1 通过Iterator遍历HashSet
第一步:按照iterator()获取HashSet的迭代器。
第二步:遍历迭代器获取各个元素。
// 假设set是HashSet工具
for(Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
iterator.hasNext(); ) {
iterator.next();
}
3.2 通过for-each遍历HashSet
第一步:按照toArray()获取HashSet的元素荟萃对应的数组。
第二步:遍历数组,获取各个元素。
// 假设set是HashSet工具,而且set中元素是String范例
String[] arr = (String[])set.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
HashSet的遍历测试措施如下:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*
* @desc 先容HashSet遍历要领
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class HashSetIteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 新建HashSet
HashSet set = new HashSet();
// 添加元素 到HashSet中
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
set.add(""+i);
// 通过Iterator遍历HashSet
iteratorHashSet(set) ;
// 通过for-each遍历HashSet
foreachHashSet(set);
}
/*
* 通过Iterator遍历HashSet。推荐方法
*/
private static void iteratorHashSet(HashSet set) {
for(Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
iterator.hasNext(); ) {
System.out.printf("iterator : %s\n", iterator.next());
}
}
/*
* 通过for-each遍历HashSet。不推荐!此要领需要先将Set转换为数组
*/
private static void foreachHashSet(HashSet set) {
String[] arr = (String[])set.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
}
}
第4部门 HashSet示例
#p#分页标题#e#
下面我们通过实例进修如何利用HashSet
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*
* @desc HashSet常用API的利用。
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// HashSet常用API
testHashSetAPIs() ;
}
/*
* HashSet除了iterator()和add()之外的其它常用API
*/
private static void testHashSetAPIs() {
// 新建HashSet
HashSet set = new HashSet();
// 将元素添加到Set中
set.add("a");
set.add("b");
set.add("c");
set.add("d");
set.add("e");
// 打印HashSet的实际巨细
System.out.printf("size : %d\n", set.size());
// 判定HashSet是否包括某个值
System.out.printf("HashSet contains a :%s\n", set.contains("a"));
System.out.printf("HashSet contains g :%s\n", set.contains("g"));
// 删除HashSet中的“e”
set.remove("e");
// 将Set转换为数组
String[] arr = (String[])set.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.printf("for each : %s\n", str);
// 新建一个包括b、c、f的HashSet
HashSet otherset = new HashSet();
otherset.add("b");
otherset.add("c");
otherset.add("f");
// 克隆一个removeset,内容和set一模一样
HashSet removeset = (HashSet)set.clone();
// 删除“removeset中,属于otherSet的元素”
removeset.removeAll(otherset);
// 打印removeset
System.out.printf("removeset : %s\n", removeset);
// 克隆一个retainset,内容和set一模一样
HashSet retainset = (HashSet)set.clone();
// 保存“retainset中,属于otherSet的元素”
retainset.retainAll(otherset);
// 打印retainset
System.out.printf("retainset : %s\n", retainset);
// 遍历HashSet
for(Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
iterator.hasNext(); )
System.out.printf("iterator : %s\n", iterator.next());
// 清空HashSet
set.clear();
// 输出HashSet是否为空
System.out.printf("%s\n", set.isEmpty()?"set is empty":"set is not empty");
}
}
