CHAPTER 2
Autism Research代写 his chapter reviews earlier works in the research topic to give the study a firm base. Relevant educational materials
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.0 INTRODUCTION Autism Research代写
This chapter reviews earlier works in the research topic to give the study a firm base. Relevant educational materials consulted include books, journals (both electronic and print), internet sources and working papers where applicable. This chapter will bring scholars and readers up to date with current literature on autism and forms the basis for another goal such as the justification for future research in the area.
2.1 BACKGROUND OF AUTISM Autism Research代写
Organization for Autism Research (2003) traces autism to mid 20th century when the first diagnosed case of autism was discovered by a child psychologist in John Hopkins Hospital. The diagnosis revealed similar disorder in the major developmental human areas namely communication skills, social integration, interaction capacity and interests. Since this discovery, many views have been put forward to address the nature and causes of autism. One of the most accepted view, the behavioural view of autism postulates that the behaviour of an individual is purely the result of the interaction to the environment (Simpson, 2006). Many educational strategies adopted to train students with autism have been based on this view of autism since the future of the learner will largely depend on the behaviour leant.
Cognitive view of autism on the hand holds that people think different and as such,
autistic individual have different understanding of things not only because their they have a disorder but also because its natural for different people to have different points of view and understanding (Organization for Autism Research, 2003). The basis of this autistic view is that, autistic individuals have a different thinking line as opposed to the normal people and have a believe that everybody views all things the way they do.Autism Research代写
Therefore, planning has been made to help the children appreciate other people’s different interviews. Psychoanalytic autistic view is a less appreciated view and has been criticized by many researchers for its lack of evidential value and no subsequent research has conducted to support it. The theory cites the child’s reaction to the immediate psychological environment as the cause of autism. The theory further highlights the mother’s rejection attitude of the child during pregnancy as the sole cause of autism (Howlin, 2000).Autism Research代写
Howlin (2000)
includes environmental autistic view as a more practical and proved view that recognizes genetics as a cause of autism but places the environmental effects around which a child grows as a player in influencing the genes. This view holds that autism disorder can only be best expressed if the victim interacts with the real environment. In the choice of intervention for autism from environmental influence, planning should be adequate to eradicate environmental agents that are likely to cause autism. The last expressed view on the causes of autism is the biological approach which provides the most accepted cause of autism and encompasses both psychological and behavioural views. According to this view, autism is as a result of the biological make up of a child during inception. While deciding on a remedy for such caused autism, biological treatments such as proper diet and medication should be considered.

2.2 THE NATURE AND EFFECTS OF AUTISM Autism Research代写
All parents expect to have perfect children; children with no inabilities and impairments. It’s thus difficult for any parent to accept diagnosis that confirms the kid is suffering from autism (Adams et al, 2004). This is usually a setback to many parents because they want a promising future for all their children thus autism overshadows the very good wishes of the parents to their children. Individuals with autism just like other normal individual have their unique potentials and great care should be taken to ensure that these potentials are exploited. Personal planning comes in hardy when deciding the program to use in educating autistic children with autism because this planning is more likely to identify the specific and unique needs of every child. Autistic individuals are able to prosper and grow and this is where great cautions should be taken to ensure that the developmental process is normal.
Many researchers have revealed that autism has no cure and the only remedy to deal with it is training victims on how to live with the disorder and reduce its effects. However, Adams et al (2004) argues that contrary to many reports from professional bodies and researchers, autism can be treated. He advises that treatments and educational programs for autistic should be sought as early as possible so that the ailment can be contained. Adams et al (2004) in their working paper,
advice for parents of young autistic children, writes:
‘The earlier the appropriate treatment is administered to the autistic individuals, the better for the progress and future for individuals although their progress will be slow but happy and secure life will be guaranteed.’Autism Research代写
Some autistic disorders do not need any medical address but personal training and guidance. The main Autism disorders as pointed out by ADDM Net (2000) include:
- Verbal/nonverbal communication problem and social skills impairment. Those with perfect verbal skills tend to have poor social skills and vice versa. Those with poor verbal skills also have low interests to communicate and interact.
- Uncommon interest and behaviours and not doing what normal individuals are doing.
- Mental retardation and other associated neural disorders such as constant anxiety, stress and depression.Autism Research代写
The effects of autism differ from individual to individual but generally,
autism leads to delays in acquiring social, communications skills and behavioural skills. Lack of speech is the most common effect of autism but other victims have less speech. Those autistic individuals with normal speech usually have severe behavioural and social impairments. When autism is not treated, the victim usually end up not learning normal social and communication skills as well as developing inappropriate behavioural patterns and to some extends inabilities to talk. Autism develops during pregnancy though it’s usually realized once the child has been born and shows different characteristics from that of a normal newborn. Other children develop autism in their first year of birth, a fact that has received critics from many researchers on grounds that the impairment is only realized late.Autism Research代写
Before 1990, many cases of autism were reported at birth compared to lesser cases reported one year and above after birth. However, the years after 1990 have seen a reverse in the situation with many cases being reported many children became autistic between their first and second year of birth possibly due to environmental insult exposure between these two years of birth.
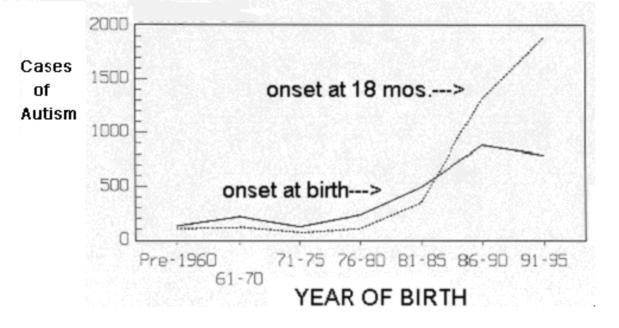
Moxon and Gates (2001) quote genetics as the major player in causing autism.
Evidently, if one identical twin is diagnosed with autistic disorder, the other twin is often affected too but this is the opposite when it comes to fraternal twins. Research further indicates that, if the parents have autism, then the probability of their kids developing the ailment is very high. Scientific evidence has tried to bring several environmental factors that lead to development of autistic disorder.Autism Research代写
Many vaccinations that children receive in their early life usually lead to weakening of the immune system because many parents report that their kids were perfect when the vaccines were being administered. The MMR vaccine in measles vaccines and thimerosal preservatives has been quoted as the major vaccines that contribute to development of autism. Gut problems which eventually leads to loss of speech have been caused by unlimited use of oral antibiotics which has increased accumulation of mercury in the bodies of the mothers which has transferred to the bodies of the unborn. Inadequate minerals to the mothers during pregnancy that are needed for the growth of mental and body mechanisms of the child lead to deficiency of the same minerals to the unborn bodies.Autism Research代写
The prevalence of autism is more reported in the western world which indicates increasing number of individuals diagnosed with autistic disorders each year.
According to California Centralized Reporting System, cases of autism are rapidly increasing rising from 1 case per every 2,500 individuals in 1970 to 1 per 285 individuals in 1999. Autism represents over 45% of all developmental disorders all over the world. These increased cases have been arguable caused by increased diagnosis of many individuals especially children at birth.Autism Research代写
There are many conditions that are associated with people suffering from autism but only a few have been brought into full documentation. Mental disorder is the first and most severe effect of autism. An estimation of over 80% of individuals suffering from autism has grown mental retardation. Another notable condition of autism is growth of seizures in early childhood and adolescence. These seizures may include low level of concentration, continued starring and confusion. Autistic children also suffer from rest and sleep problems because of another severe effect which is constant constipation and diarrhoea. Sensory insensitiveness has also been noted as another condition that affects individual suffering from autism. These individuals display abnormal sensitivities to common sensatory mechanisms like smell, touch, sight, sound and taste.
2.3 EDUCATIONAL APPROACHES TO AUTISMAutism Research代写
The objective of this research as quoted earlier is to establish the availability of personal planning in the education of autistic students., from the above causes and effects of autism, many researchers, psychologists and scholars have provided several solutions to autism disorders. The educational programming as a solution for students with autism should be guided by the many accepted principles. First, the needs and abilities of the autistic that are under the training program should be constantly reviewed, monitored and evaluated. The autistic children should be allowed, encouraged and involved in the education curriculum that is used by the other able students.Autism Research代写
This should include other co-curriculum activities such as sports, seminars, debates etc. additionally, the trainers and teachers should know that all the components in the training program work together and some components can’t work alone. Parents, relatives, peers and friends involvement in the training program of the autistic children is fundamental and should be maintained throughout the program because this program requires a great degree team work, assistance, guidance and collaboration. Most importantly, both the autistic children staff and to some extend the parents and guardians should have continuous access to all resources that are needed in this training program.Autism Research代写
Educational remedies coupled with behavioural measures have proved to be the most effective strategies to improve the lives of autistic individuals. This is achieved by equal participation of all people around the autistic people especially the parents, teachers, siblings and friends. To ensure success of the approaches taken to contain autistic disorder, Prince-Hughes (2003) outlines several factors that must be considered before implementing any intervention method to the children with autism.
He presents these factors as a general procedure for any intervention program:
- A complete evaluation of every child’s needs to gain insightful data may help in devising the best treatment method. Prince-Hughes points out that constant review should be done to each child that will be included in the intervention program so that any change of behaviour and skill is noted.
- Evaluation should be followed by goals determination, that is, the expected result of the treatment process that will be used. More attention should be given to long term goals because they will determine the child’s destiny.Autism Research代写
- Once the goals have been established, the actual implementation of the selected strategy follows. This is simply putting appropriate measures to achieve the set goals.
- The last step is re-evaluation of the strategy that has been put into work. This involves establishing how the plan is working. For instance, whether the condition of child is improving or if the plan is a progressing according to the identified goals. If a fault is detected in one of the steps, then cycle starts again (pp 16-17).
However, Prince-Hughes proposition of the steps and factors that should be considered when planning an intervention for an individual with autism falls short of important components in any intervention program such as the resources and parties involved in the program. Lundine and Smith (2006) in their title, Career training and personal planning for students with autism spectrum disorders,
provide several remedies for this disorder:
a)Applied behavioural analysis (ABA) is the most successful method to train and educate autistic individuals. It’s a personal program that involves only the trainer and the autistic individual. In this case, therapists are able to plan for an education program depending on the personal interest of the individual. Professional therapists spend between 20 and 40 hours every week training autistic individuals the basic skills they need to improve their lives. This method has been used to teach autistic children how to talk and it’s most effective when applied during the first five years after birth when the kids do not need much of the outside environment. Parents have been therapists to their own autistic kids through undergoing ABA training.Autism Research代写
b)Sensory assimilation has been applied to autistic individuals who have sensory problem i.e. hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to stimulus. This method usually focuses on normalizing the individual senses particularly the motion, touch and joints. This is more of a behavioural solution to autism but also includes adequate planning for every autistic child to establish the effects of autism to child’s sensory system so that an effective intervention program can be devised.
c)Communication psychotherapy
is a treatment that is usually integrated with other home or school programs for it to be effective. A minimum of two week should be preserved to affect this therapy. Sign language is also used to reinforce the pronunciation of words. Many institutions of learning have incorporated programs of using visual elements to train deaf and autistic children.Autism Research代写
d.Developing friendships is another behavioural strategy but mostly used in an educational setting. Many schools encourage autistic pupils and other typical pupils to interact freely. Autistic individuals have been encouraged and helped to make friends with peers. This has greatly improved their social and communication skills thus ensuring interaction with the real world.Autism Research代写
Social forums like school clubs, sporting activities and other activities of shared interests have created relevant environment for autistic individuals to develop important social skills and developing a sense of belonging to the society. Friends social therapists and psychological professionals can be very helpful for the social life the autistic individuals. These supportive teams will help the autistic individuals fight stress, depression and other psychological disturbances. Physical social networks are also highly recommended for autistic individuals. In these networks, autistic individuals can find mentors and role models who able to give a suitable coaching to their lives.
2.4 ALTERNATIVE INTERVENTION METHODSAutism Research代写
Different welfare associations have decided to come up with other autistic intervention methods that have not been addressed in the classroom and school environment (Glennon, 2001). Some of these intervention autistic supplements include:
2.4.1After school educational programs
These are programs that are offered during school breaks especially weekends and end term holidays. These programs are only applied to those children who are likely to lose some skills during the breaks thus a need to keep the children abreast with the learnt skills (Lawrence et al, pp 18). These programs have been used to train young affected kids and those children whose autistic effect has grown to a greater extend. Such programs might include social skills and communications programs and like other strategies, they should also be based on individual needs of the children.
2.4.2Structured time and active engagement in activities
The National Research council Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism (2001) states that training of autistic individuals dictates that each moment be accounted for thus there should be no or minimal unstructured time for the children. This time should be fully engaging to the children depending on their concentration. Young children who are likely to have limited attention to tasks should have a short schedules for each task while those autistic children who can function better should be allocated a longer schedule per task (Alberta Children Services, 2002). The scheduled time for the children should be highly engaging the children in learning activities. However, the daily schedule for each student should be dependent on the individual capability and strength of the child.Autism Research代写
2.4.3Community and home training
This training is more focused on imparting social and behavioural skills. Such skills include how the children should behave in different situation and this involves taking the children to these different situations and teaching them what is required of them. For instance, the parents can decide to take their autistic child to a hospital, church, a market, a store etc and then training the children on how to behave on such situations. This child will be able to understand the skills if trained in an environment where the skills are needed (Lawrence et al, pp 22).
2.4.4Supportive behavioural strategies
The behaviour of individuals is usually manifested through communication. Autistic children may be disadvantaged in manifesting their behaviour if they don’t have speech or if they are frustrated and cannot speak. This strategy therefore involves establishing why autistic children cannot demonstrate their behaviour and what strategy can be used to intervene. The best strategy has been to modify the environment that these children are living in so that they are able to demonstrate their behaviours and learn new behaviours but prevent learning of problem behaviours.Autism Research代写
2.4.5Planning for the future
Glennon (2001) confirms that many schools usually think of the future of the pupils and students after they are through with lower level education. Parents have taken this as their responsibility to think of the future of their children, both normal and disabled children right from the moment the children are born. Parents have developed an integrated system for their children from their childhood through their education to adulthood that guarantees a future stable environment for the children. When devising such futuristic strategies, parents and other supportive individuals should fully understand the aspirations and strengths of every child so that the efforts are put on the right place.
2.4.6Communication support Autism Research代写
Communication support comprise those methods not taught in a school environment and can improve communication skills of autistic children. Use of visual and audio visual system has been used after school to train children how to speak and how to perceive things. For instance, autistic children who can speak can be trained on how to use visual communication so that when they are annoyed and frustrated and want to express something then they can use visual communication. Communication is therefore very important and parents should not assume that their children are getting communication training in their schools. It’s believed that lack of proper communication leads to development of problem behaviours and a sense of isolation.
2.4.7Social skills interventions
Many schools give social skills training to disable children a priority. However, in a school situation where the children only interact with other children and teachers may not present a better environment to practice those social skills. Parents therefore have established this gap and have embarked on home training on how to use and improve the learnt social skills. Many studies have shown that social skills are best taught in context.Autism Research代写
2.4.8Professional support
Parents and guardians have been providing all the portfolio of their affected children to the trainers and professionals so that these professionals can come up with the best strategies depending on the individual needs of the children. Parents should also ask for assistance of all other adults that are directly or indirectly involved with the children at school.
The combination of the above methods has been proved to work in the cases where they have been implemented. However, the challenge is experienced when autistic children are about to graduate to adulthood. Cameto and Wagner (2003) views the intervention process for autistic children as one complex process that needs prior planning once the disorder has been diagnosed. This process involves all the people that in one way or the other influence the life of the autistic child (Malian and Nevin, 2002).Autism Research代写
Transition process is not uniform and is most influenced by the age and maturity of the children. Many professionals recommend that transition planning be started at the age 14 years. The needs, capabilities and weaknesses must be captured in the any transition program. The goals of the program should be well stated and should be compatible with the abilities and strengths of the students. The plan should also take in to consideration the environment in which the autistic individual is living and the future environment of the individual (Malian and Nevin, 2002).
The role of autistic children in the transition plan should be provided.
Since most of the transition planning happens when children are about to complete their secondary education, these autistic children should be allowed to contribute to the transition plan through guidance of their parents and guardians. The students can contribute to their future careers, residential locations and social choices (Cameto, Levine and Wagner 2004).
Thus, according to the Autism Society of North Carolina (2008), the process of transition of autistic individual can be said to be a pre-arranged set of activities that are involved in a complete and desired movement from a school environment to more complex post school activities especially job environment and career development. This is an all inclusive process and involves many parties which include parents, autistic individual, trainers and coaches, peer and guidance counsellors, transition specialists, professional counsellors, employers, friends and relatives.Autism Research代写
Many researchers have concluded that the above methods have been successfully used to address the major effects of autism which include; difficulties in understanding and responding to both verbal and abstract information, difficulties in expressing own thoughts, needs and ideas either verbally or non-verbally. Other difficulties that have been addressed are; highly repetitive and unusual language, centralizing attention to oneself while regulating the same to the external environment, giving a general view to all people and things, long time in shifting from one physical or mental activity, demonstrating unusual sensory expressions and problems in simple problem solving, decision making and organization. A major problem has been poor social skills such that the child has difficulties when interacting with friends of similar age, younger and adults. The child also demonstrates slow and difficulties in understanding basic social norms and provides unusual responses to such norms.
2.5 THE RATIONALE FOR INTERVENTION
Children living with autism require special attention and specific services according to the unique needs of each child (United States Accountability Office, 2005). Depending on the kind of disorder, an appropriate therapy is administered. For instance, speech therapy is administered to individuals with speech autistic disorder. Cameto and Wagner (2003) points out several needs expressed by all autistic individuals irrespective of the intensity of the disorder.Autism Research代写
These include:
- Behavioural intervention
- Professional training and support,
- Support in living arrangements for old victims,
- Occupational therapy
- Physical therapy,
- Social relation support and assistance,
- Communication services and therapy,
- Vision services,
- Mobility training,
- Mental health care,
- Audiology training among other needs
The educational objectives for the students diagnosed with autism have been tailored towards meeting the above needs and they included but not limited to the following training skills:
a)Communication skills which covers both verbal and non verbal skills development. Use of symbols and signs as a form of non verbal communication should be encouraged for the victims whose verbal strength has been completely affected.
b)Social and interaction skills which involve how the individual will relate and interact to the environment. These objectives should be geared towards creating the impression that the victim is living in the real world and should as such try to understand and relate to the environment. Social skills also include learning the appropriate and conventional societal skills, that is, the best code of conduct.
c)Physical skills which involve learning several motor skills like walking, playing, performing simple home and school tasks etc.Autism Research代写
d)Cognitive skills should be developed so that the child can achieve the required academic skills and continue building and engaging mind
e)Problem solving and decisional skills should also be a lead objective when designing an educational strategy to educate autistic individuals. Such skills will help children perform important task like organizing, controlling and coordinating their activities thus learning to be independent.
(Schall et al, 2006)
Therefore, the goals and aspirations of the autistic child should not be seen as any different from those of a typical child. The goals are the same and like the other normal children, an autistic kid can achieve high level personal, occupational and social success thus all parties involved in the program should promote the development of a character that will make the child more responsible in future. (Alberta Children Services, 2002)Autism Research代写
Autistic individuals, like other people have rights to participate and develop their skills especially though securing job opportunities. Therefore, in personal planning for education of individuals with autism, their penetration into the job market should be considered (Lundine & Smith, 2006). Unconscious learning through socializing, peer influence and interaction, has been quoted by many academicians as one of the best and influential strategy that can be used to train individuals with autistic disorder (Simpson, 2005 Willis, 2006). Children should be prepared for their future lives as early as possible through deciding the best careers for each child depending on the strengths, weaknesses and interests ( Mackenzie,2008)
Treatment and education of autistic children asks for so much in terms of financial and time resources.Autism Research代写
This has had effects to those parents who cannot afford finances to take their children to special school and to pay for therapists and professional counsellors (Willis, 2006). Many parents and anti-autism social associations have sought financial and professional assistance from the government and social welfare organizations to ensure that autistic children have a perfect and consolidated transition to adulthood.
The process of training and educating autistic individuals is highly productive when started at early childhood as it saves many resources that could otherwise be used once the process is started at a later age. Children at early ages are more likely to respond to training more easily than aged individuals (McClannahan et al. 2002). The children will develop better understanding of their environment, enhance their social and communication skills and develop required career and personal planning for their future (Quill, 1995). Planning, training and educating autistic individuals is a complex and long shared responsibility and doesn’t only include instilling the individual the required skills and knowledge but also training them how to use and perfect the skills so that they can be of help in their future lives (Moxon and Gates2001).Autism Research代写
According to Simpson (2007),
many professional bodies and individuals have identified and used correct training, education and treatment methods that present a good chance of producing best results for individual diagnosed with Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Autistic individuals require effective measures because they are always prone to and suffer from contentious treatments. These are treatments that may have no basis but promise restoring the normalcy to the affected individuals leading to counter reaction because they have no clinical or theoretical foundation.
The first step to identifying the best practice to use in restoring the normalcy of autistic individuals is evaluating the suitability of already used methods on students and individuals with ASD. The evaluation should be based on specific individuals who have specific problems and needs. Since the new methods are being developed, the next step will be to evaluate likely future practices and compare them with the already existing practices and come up with a harmonized practice that will take less time and cost and produce the best results.Autism Research代写
Simpson and colleagues (2005) highlight several considerations when deciding the practice or treatment to use for any autistic individual:
- Anticipated results and effects
- Professionalism of the people expected to apply the treatment to victims
- The best time and conditions when the practice is likely to be more productive
- Risks that may result due to implementation of a given methods and how such risks can be maintained
- The costs involved in terms of financial resources and time
- The procedures to evaluate the success or failure of the implemented strategy
However,
he argues that, there is no one universally accepted method that has been accepted to be the only effective to train individuals with autism but there are many strategies that can form a basis for treating autistic individuals. Schall et al (2006) notes that, despite many effective measures taken by parents and professional bodies to ensure a complete transition of autistic children to a promising future, many autistic individual have been unable to get employment opportunities. Howlin (2000) supports this argument by the fact that even those seemingly able autistic individuals continue to fully depend on their guardians because only few chances are available. This shows a fault in many methods that are used to train autistic children to live up to their future lives especially through securing employment opportunities.Autism Research代写
Previous research has revealed much on the nature, causes and treatment of autism. Many researchers have dwelled much on behavioural and psychological remedies which only help in improving social life of affected individuals. The other areas of individual lives that have direct impact on their welfare and future like education have received minimal academic concentration. There is therefore a research gap in establishing educational intervention and remedies to autism disorders. This research seeks to fill this gap in establishing the availability of appropriate planning that can enhance the education o autistic children.
REFERENCES Autism Research代写
Adams B. et al. 2004. Advice for Parents of Young Autistic Children: a Working Paper.
Arizona: Arizona State University ADDM Net. 2002. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorders in Multiple Areas of United States.
Available at www.cdc.gov/mmwr/mmwrss accessed on 1st October 2010.
Alberta Children Services. 2002. A system Care for Children with Autism: Expert Panel Report available at www.child.gov.ab.ca/whatwedo/disabilities/pdf/autism_expert_report.pdf accessed on 11th October 2010.
Cameto,R, Levine, P & Wagner, M. 2004. Transitional Planning for Students with Disabilities in Journal of National Longitudinal Transition Study SRI International November pp2-89.
Cameto,R & Wagner, M. 2003. Vocational Education Courses and Services available at www.nlts2.org/pdfs/goschool_ch7.pdf accessed on 11th October 2010.
Howlin, P. 2000. Outcome in Adult Life for more Able Individuals with Autism or Asperger Syndrome. Autism, vol 4, pp 63-83.
Howlin, P. et al. 2004. Adult outcomes for children with Autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, vol 45, pp212-229.
Gerhardt. P. 2007. Effective Transition Planning for Learners with Autism Spectrum Disorde Approaching Adulthood, Journal for Vocational Special Needs Education pp 33-42 vol 29.
Lundine, V., & Smith, C. 2006. Career Training and Personal Planning for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers
Malian, I & Nevin, A. 2002. Review of Self-Deternmination Literature : Implications for Practitioners. Remedial and special education, vol 23(2) pp 68-74
McClannahan, L, MacDuff, G, & Krantz, P. 2002. Behaviour Analysis and Intervention for Adults with Autism. Behavior Modification, vol 26(1), pp 9-26
Moxon, L, & Gates, D. 2001. Children with Autism: Supporting the Transition to Adulthood. Educational and Child Psychology, vol 18 issue 2
National Research council Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism, 2001. Educating Children with Autism. Washington DC : National Academic Press.Autism Research代写
Organization for Autism Research and Danya International Inc. 2003. Life Journey through Autism : A Parents Guide to Research. Arlington: OAR
Quill, K. 1995. Children with Autism: Strategies to Enhance Communication and Socialization. New York. Delmar.
Schall, C. et al, P. 2006. Applications for Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorders. In P. Wehman (Ed.), Life Beyond the Classroom: Transition Strategies for Young People with Disabilities, Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes Publishing.
Simpson, R. 2005. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Interventions & Treatments for Children & Youth. Washington. Corrwin Press, Sage Publications Ltd.Autism Research代写
Simpson, R. 2007. Effective Practices for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders, Journal For Vocational Special Needs Education pp 33-42 vol 29 number 2.
United States Accountability Office. 2005. Special Education: Children with Autism.
Washington: GAO Willis, C. 2006. Teaching Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. New York: Gryphon House, Inc.

其他代写:考试助攻 计算机代写 java代写 algorithm代写 assembly代写 function代写paper代写 金融经济统计代写 web代写 编程代写 report代写 algorithm代写 数学代写 finance代写 [r代写 essay代写

