STAT3017/7017 Final Project
Big Data Statistics – Final Project
统计代写价格 We will now consider the detection- of-correlations problem which is concerned with detecting unusual correlations in observations.
Total of 100 Marks
This is a research-led project that is working off very recent research papers so I encourage you to start this project as soon as possible for a number of reasons: (1) To ensure you are not caught by a large amount of work at the end of the semester; (2) To spot any issues in the project and inform me (typos, difficulties, etc) so that I can adjust the project accordingly. If you spot something that seems incorrect or unclear, please check the ‘Last updated’ date at the bottom of this page to ensure you have the latest version and inform me of the typo, unclear question, etc. so I can fix it (if it has not already been fixed).
Sample correlation matrices
Question 1 [50 marks] 统计代写价格
Let x1,. .. , xn be a sequence of independent random vectors from a p-dimensional normal distri- bution Np(µ, ⌃) with mean vector µ and p ⇥ p covariance matrix ⌃ = (oij ). The corresponding (population) correlation matrix Rn = (rij ) is defined by
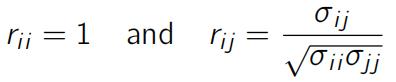
for all 1 i 6= j p. Given a random sample x1,. .., xn, we construct the n ⇥ p data matrix X = (xij ) = (x1,. .., xn)0 then the Pearson correlation coefficient betweeen (x1i,. .., xni )0 and (x1j,. .., xnj )0 is given by
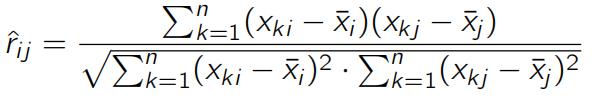
where ![]() The sample correlation matrix is defined as
The sample correlation matrix is defined as ![]() From a data analysis point-of-view, the advantage of working with sample correlation matrices (instead of sample covariance matrices) is that they are invariant under scaling and shifting. Over the last 15 years a number of interesting results have been obtained about sample correlation matrices Rˆn in the high–dimensional regime where p, n !1 such that p/n ! y < 1. These results are mostly in the case where the (population) correlation matrix Rn = I.
From a data analysis point-of-view, the advantage of working with sample correlation matrices (instead of sample covariance matrices) is that they are invariant under scaling and shifting. Over the last 15 years a number of interesting results have been obtained about sample correlation matrices Rˆn in the high–dimensional regime where p, n !1 such that p/n ! y < 1. These results are mostly in the case where the (population) correlation matrix Rn = I.
(a)Showthat (in the case Rn = I) the limiting spectral distribution of the eigenvalues of Rˆn is Marcenko-Pastur. How do p and n relate to the parameters of this distribution?

(b)Showthat (in the case Rn = I) the largest entry of Rˆn given by
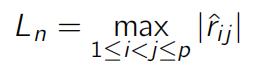
satisfies
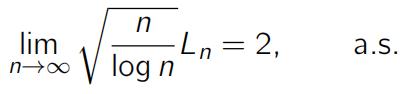
and the limiting cumulative distribution function is
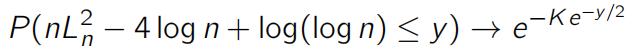
as n → ∞. What is the parameter K equal to? See [I].
(c)Showthat (in the case Rn = I) the largest eigenvalue of Rˆn satisfies the Tracy-Widom law; see [G].
(d)Showthat (in the case Rn = I) the quantity log |Rˆn| satisfies a CLT; see [E] and [D]. Check what happens to the CLT when Rn has an AR1 structure.
(e)Showthat the quantity log |Rˆn| satisfies the CLT from [A] in the following cases:
(i) Rn = I;(ii) Rn has a compound symmetry structure (all entries of Rn are equal to ↵ 2 [0, 1/2) except the diagonal which contains 1’s) and do this using the result of Corollary 1 of [A]; (iii) Rnhas an AR1 structure; (iv) Rn is a banded correlation matrix. 统计代写价格
(f)In the context of hypothesis testing: (i) explain why it is good to understand the power of the test; (ii) give an counterexample of what could go wrong if you don’t consider the power; (iii) using your counterexample and a simulation study to show why the results of [A] are useful.
In the above questions (a)-(e): (i) assume that we are in the high-dimensional regime; (ii) ensure that you check the result for at least at three different values of yn = p/n; (iii) answers can be argued through appropriate simulation studies and plots.
The detection-of-correlations problem
Question 2 [50 marks] 统计代写价格
Anomaly detection is extremely important in data science. We will now consider the detection- of-correlations problem which is concerned with detecting unusual correlations in observations. Humans are often very good at this task. For example, given a single time series or image, we can usually spot some unusual correlations (see Figures 1 & 2 in [B]). However, getting an algorithm to achieve this can sometimes be quite hard.
(a)Westart by setting up a first test Suppose we are observing a time series X1, X2,. .. , Xn.
Under the null hypothesis, the Xi ’s are i.i.d. standard normal random variables. The alternate is that the time series contains an anomaly in the form of temporal correlations over an (unknown)interval S = {i + 1,. .., i + p} of, say, known length p< n. Here, i 2 {0, 1,. .., n – p} is thus unknown. We want to generate realisations of this time series where the anomalous region S is such that (Xi+1,. .. , Xi+p) ⇠ (Yi+1,. .., Yi+p) where (Yi : i 2 Z) is an autoregressive process of order h (ARh) with zero mean and unit variance, that is,
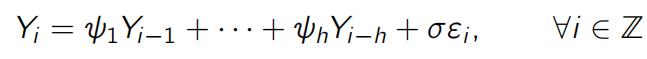
where (εi : i ∈ Z) are i.i.d. standard normal random variables and 1,. .. , h 2 R are the coefficients of the process. Write a code that generates realisations of this time series with(and without) anomalies. See [B] Section 1.3 for further details and Figure 1. Generate and plot three examples of realisations: (i) without anomalies; (ii) a realisation where n = 500,S = {201,. .., 250}, h = 1, and | 1| > 0 but chosen so you can only faintly see the anomaly.(iii) a realisation where n = 500, S = {201,. .. , 250}, h = 1, and | 1| > 0 but chosen so you can clearly see the anomaly. Clearly indicate your choices of Ψ 1 in your plots for (ii) and (iii).
(b)Consider the previous question using a change point analysis approach (e.g., see §2 p3631 of [B] and possibly [H]).
Clearly write up how your chosen approach works(ideally 1/2 page, 1 page max.) [10 points] then implement the approach and comment how well it works on the three cases generated in (a) [10 points].
(c)Setup your second (image) test case in the form of Section 1.4 of [B]. Generate three example figures: (i) without an anomaly; (ii) a very faint anomaly; (iii) the case seen on the rightin Figure 2 of [B]. Use the example dimensions given in Figure 2. 统计代写价格
(d)Considerthe approaches in [B] or [C], choose one and describe how it works (ideally 1/2 page max.) [5 points]; Implement this approach (identifying the bounding box of an anomalous region is sufficient) and check the performance on your three test cases generated in (c) [10 points]; Can you comment on the limitations of detection (e.g., how large/strong does the anomaly have to be)?
References 统计代写价格
[A]Jiang (2019). Determinant of sample correlation matrix with application. Annals ofProbability.
[B]Arias-Castro, Bubeck, Lugosi, and Verzelen (2018).Detecting Markov random fields hidden in white
Bernoulli.
[C]Arias-Castro, Bubeck, and Lugosi (2015). Detecting positive correlations in a multivariate sample.Bernoulli.
[D]Jiang and Qi (2015). Likelihood ratio tests for high-dimensional normal distributions. Scandanavian Journal of Statistics.
[E]Jiang and Yang (2013). Central limit theorems for classical likelihood ratio tests for high-dimensional normal distributions. Annals ofStatistics. 统计代写价格
[F]Jiang, Jiang, and Yang (2012).Likelihood ratio tests for covariance matrices of high-dimensional normal distributions.
Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference.
[G]Bao,Pan and Zhou (2012). Tracy-Widom law for the extreme eigenvalues of sample correlation
Electronic Journal of Probability. 统计代写价格
[H]Bodnar, Bodnar, and Okhrin (2009). Surveillance of the covariance matrix based on the properties of the singular Wishart distribution. Computational Statistics and DataAnalysis.
[I]Jiang (2004). The asymptotic distributions of the largest entries of sample correlation matrices. Annals of Applied Probability.

