Econ331 Midterm 2 Practice question
经济练习题代写 1.Everything else held constant, a decrease in wealth ________. A) increases the demand for stocks B) increases the demand for bonds
Ch5 THE BEHAVIOUR OF INTEREST RATES
1-5
1.Everything else held constant, a decrease in wealth ________.
A) increases the demand for stocks
B) increases the demand for bonds
C) reduces the demand for silver
D) increases the demand for gold
2.Everything else held constant, if the expected return on ABC stock rises from 5 to 10 percent and the expected return on CBS stock is unchanged, then the expected return of holding CBS stock ________ relative to ABC stock and the demand for CBS stock ________.
A) rises; rises
B) rises; falls
C) falls; rises
D) falls; falls
3.The demand curve for bonds has the usual downward slope, indicating that at ________ prices of the bond, everything else equal, the ________ is higher.
A) higher; demand
B) higher; quantity demanded
C) lower; demand
D) lower; quantity demanded
4.The supply curve for bonds has the usual upward slope, indicating that as the price
________, ceteris paribus, the ________ increases.
A) falls; supply
B) falls; quantity supplied
C) rises; supply
D) rises; quantity supplied
5.When the price of a bond is above the equilibrium price, there is an excess ________ bonds and price will ________.
A) demand for; rise
B) demand for; fall
C) supply of; fall
D) supply of; rise
6-10 经济练习题代写
6.When the price of a bond is ________ the equilibrium price, there is an excess demand for bonds and price will ________.
A) above; rise
B) above; fall
C) below; fall
D) below; rise
7.When the interest rate on a bond is ________ the equilibrium interest rate, in the bond market there is excess ________ and the interest rate will ________.
A) above; demand; rise
B) above; demand; fall
C) below; supply; fall
D) above; supply; rise
8.If the price of bonds is set ________ the equilibrium price, the quantity of bonds demanded exceeds the quantity of bonds supplied, a condition called excess ________.
A) above; demand
B) above; supply
C) below; demand
D) below; supply
9.A movement along the bond demand or supply curve occurs when ________changes.
A) bond price
B) income
C) wealth
D) expected return
10.During business cycle expansions when income and wealth are rising, the demand for bonds ________ and the demand curve shifts to the ________, everything else held constant.
A) falls; right
B) falls; left
C) rises; right
D) rises; left
11-15 经济练习题代写
11.Everything else held constant, an increase in the riskiness of bonds relative to alternative assets causes the demand for bonds to ________ and the demand curve to shift to the ________.
A) rise; right
B) rise; left
C) fall; right
D) fall; left
12.Everything else held constant, an increase in the liquidity of bonds results in a ________ in demand for bonds and the demand curve shifts to the ________.
A) rise; right
B) rise; left
C) fall; right
D) fall; left
13.During a recession, the supply of bonds ________ and the supply curve shifts to the ________, everything else held constant.
A) increases; left
B) increases; right
C) decreases; left
D) decreases; right
14.When the inflation rate is expected to increase, the ________ for bonds falls, while the ________ curve shifts to the right, everything else held constant.
A) demand; demand
B) demand; supply
C) supply; demand
D) supply; supply
15.Everything else held constant, during a business cycle expansion, the supply of bonds shifts to the ________ as businesses perceive more profitable investment opportunities, while the demand for bonds shifts to the ________ as a result of the increase in wealth generated by the economic expansion.
A) right; left
B) right; right
C) left; left
D) left; right
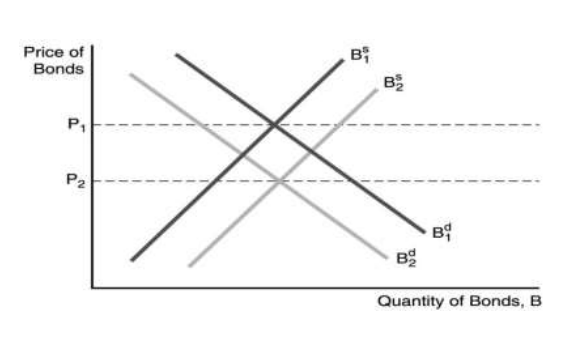
16-20
16.In the figure above, a factor that could cause the supply of bonds to shift to the right is ________.
A) a decrease in government budget deficits
B) a decrease in expected inflation
C) a recession
D) a business cycle expansion
17.In the figure above, the price of bonds would fall from P1 to P2 if ________.
A) inflation is expected to increase in the future
B) interest rates are expected to fall in the future
C) the expected return on bonds relative to other assets is expected to increase in the future
D) the riskiness of bonds falls relative to other assets
18.In Keynes’s liquidity preference framework, ________.
A) the demand for bonds must equal the supply of money
B) the demand for money must equal the supply of bonds
C) an excess demand of bonds implies an excess demand for money
D) an excess supply of bonds implies an excess demand for money
19.In Keynes’s liquidity preference framework, if there is excess demand for money, there is ________.
A) excess demand for bonds
B) equilibrium in the bond market
C) excess supply of bonds
D) too much money
20.The bond supply and demand framework is easier to use when analyzing the effects of changes in ________, while the liquidity preference framework provides a simpler analysis of the effects from changes in income, the price level, and the supply of ________.
A) expected inflation; bonds
B) expected inflation; money
C) government budget deficits; bonds
D) government budget deficits; money
21-25 经济练习题代写
21.Keynes assumed that money has ________ rate of return.
A) a positive
B) a negative
C) a zero
D) an increasing
22.In Keynes’s liquidity preference framework, as the expected return on bonds increases (holding everything else unchanged), the expected return on money ________, causing the demand for ________ to fall.
A) falls; bonds
B) falls; money
C) rises; bonds
D) rises; money
23.If there is an excess supply of money ________.
A) individuals sell bonds, causing the interest rate to rise
B) individuals sell bonds, causing the interest rate to fall
C) individuals buy bonds, causing interest rates to fall
D) individuals buy bonds, causing interest rates to rise
24.When the interest rate is above the equilibrium interest rate, there is an excess ________ money and the interest rate will ________.
A) demand for; rise
B) demand for; fall
C) supply of; fall
D) supply of; rise
25.In the Keynesian liquidity preference framework, an increase in the interest rate causes the demand curve for money to ________, everything else held constant.
A) shift right
B) shift left
C) stay where it is
D) invert
26-30 经济练习题代写
26.When real income ________, the demand curve for money shifts to the ________ and the interest rate ________, everything else held constant.
A) falls; right; rises
B) rises; right; rises
C) falls; left; rises
D) rises; left; rises
27.A business cycle expansion increases income, causing money demand to ________ and interest rates to ________, everything else held constant.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
28.A rise in the price level causes the demand for money to ________ and the interest rate to ________, everything else held constant.
A) decrease; decrease
B) decrease; increase
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; increase
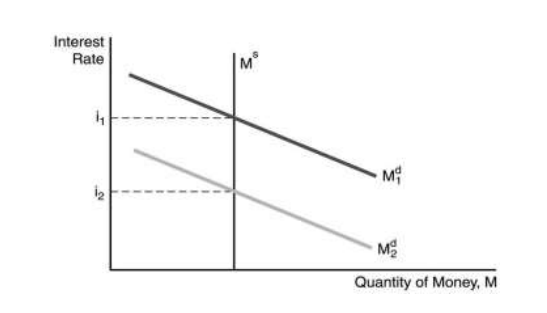
29.In the figure above, one factor not responsible for the decline in the demand for money is ________.
A) a decline the price level
B) a decline in income
C) an increase in income
D) a decline in the expected inflation rate
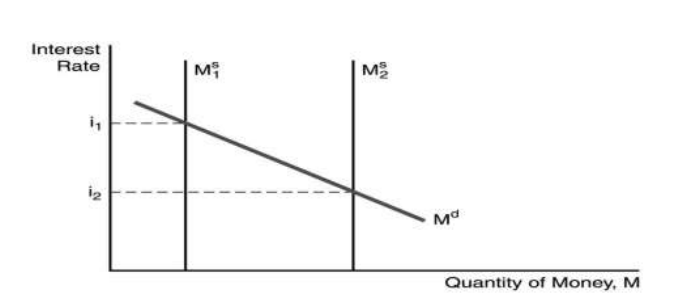
30.In the figure above, the factor responsible for the decline in the interest rate is ________.
A) a decline the price level
B) a decline in income
C) an increase in the money supply
D) a decline in the expected inflation rate
31-33
31.Of the four effects on interest rates from an increase in the money supply, the one that works in the opposite direction of the other three is the ________.
A) liquidity effect
B) income effect
C) price level effect
D) expected inflation effect
32.If the liquidity effect is smaller than the other effects, and the adjustment to expected inflation is immediate, then the ________.
A) interest rate will fall
B) interest rate will rise
C) interest rate will fall immediately below the initial level when the money supply grows
D) interest rate will rise immediately above the initial level when the money supply grows
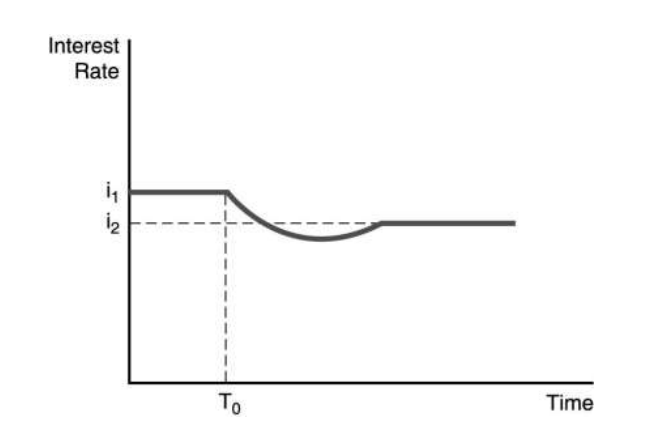
33.The figure above illustrates the effect of an increased rate of money supply growth at time period T0. From the figure, one can conclude that the ________.
A) liquidity effect is smaller than the expected inflation effect and interest rates adjust quickly to changes in expected inflation
B) liquidity effect is larger than the expected inflation effect and interest rates adjust quickly to changes in expected inflation
C) liquidity effect is larger than the expected inflation effect and interest rates adjust slowly to changes in expected inflation
D) liquidity effect is smaller than the expected inflation effect and interest rates adjust slowly to changes in expected inflation
Ch 7. The Stock Market, the Theory of Rational Expectations, and the Efficient Market Hypothesis 经济练习题代写
34-39
34.The value of any investment is found by computing the ________.
A) present value of all coupon payments
B) present value of all future liabilities
C) future value of all dividends
D) value in today’s dollars of all future cash flows

36.Using the one-period valuation model, assuming a year-end dividend of $0.11, an expected sales price of $110, and a required rate of return of 10 percent, the current price of the stock would be ________.
A) $110.11
B) $121.12
C) $100.10
D) $100.11
37.Using the Gordon growth model, a stock’s price will increase if ________.
A) the dividend growth rate increases
B) the growth rate of dividends falls
C) the required rate of return on equity rises
D) the expected sales price rises
38.Using the Gordon growth formula, if D1 is $1.00, ke is 10 percent or 0.10, and g is 5 percent or 0.05, then the current stock price is ________.
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $40
39.In the Gordon Growth Model, the growth rate is assumed to be ________ the required return on equity.
A) greater than
B) equal to
C) less than
D) proportional to
40-44 经济练习题代写
40.A change in perceived risk of a stock changes ________.
A) the expected dividend growth rate
B) the expected sales price
C) the required rate of return
D) the current dividend
41.A stock’s price will fall if there is ________.
A) a decrease in perceived risk
B) an increase in the required rate of return
C) an increase in the future sales price
D) current dividends are high
42.A monetary expansion ________ stock prices due to a decrease in the ________ and an increase in the ________, everything else held constant.
A) reduces; future sales price; expected rate of return
B) reduces; current dividend; expected rate of return
C) increases; required rate of return; future sales price
D) increases; required rate of return; dividend growth rate
43.The subprime financial crisis lead to a decline in stock prices because ________.
A) of a lowered expected dividend growth rate
B) of a lowered required return on investment in equity
C) higher expected future stock prices
D) higher current dividends
44.Economists have focused more attention on the formation of expectations in recent years. This increase in interest can probably best be explained by the recognition that ________.
A) expectations influence the behavior of participants in the economy and thus have a major impact on economic activity
B) expectations influence only a few individuals, have little impact on the overall economy, but can have important effects on a few markets
C) expectations influence many individuals, have little impact on the overall economy, but can have distributional effects
D) models that ignore expectations have little predictive power, even in the short run
45-49 经济练习题代写
45.If expectations of the future inflation rate are formed solely on the basis of a weighted average of past inflation rates, then economics would say that expectation formation is ________.
A) irrational
B) rational
C) adaptive
D) reasonable
46.If during the past decade the average rate of monetary growth has been 5 percent and the average inflation rate has been 5 percent, everything else held constant, when the Bank of Canada announces that the new rate of monetary growth will be 10 percent, the adaptive expectation forecast of the inflation rate is ________.
A) 5 percent
B) between 5 and 10 percent
C) 10 percent
D) more than 10 percent
47.The major criticism of the view that expectations are formed adaptively is that ________.
A) this view ignores the fact that people use more information than just past data to form their expectations
B) it is easier to model adaptive expectations than it is to model rational expectations
C) adaptive expectations models have no predictive power
D) people are irrational and therefore never learn from past mistakes
48.In rational expectations theory, the term “optimal forecast” is essentially synonymous with ________.
A) correct forecast
B) the correct guess
C) the actual outcome
D) the best guess
49.An expectation may fail to be rational if ________.
A) relevant information was not available at the time the forecast is made
B) relevant information is available but ignored at the time the forecast is made
C) information changes after the forecast is made
D) information was available to insiders only
50-54 经济练习题代写
50.According to rational expectations theory, forecast errors of expectations ________.
A) are more likely to be negative than positive
B) are more likely to be positive than negative
C) tend to be persistently high or low
D) are unpredictable
51.People have a strong incentive to form rational expectations because ________.
A) they are guaranteed of success in the stock market
B) it is costly not to do so
C) it is costly to do so
D) everyone wants to be rational
52.If market participants notice that a variable behaves differently now than in the past, then, according to rational expectations theory, we can expect market participants to ________.
A) change the way they form expectations about future values of the variable
B) begin to make systematic mistakes
C) no longer pay close attention to movements in this variable
D) give up trying to forecast this variable
53.The theory of rational expectations, when applied to financial markets, is known as ________.
A) monetarism
B) the efficient markets hypothesis
C) the theory of strict liability
D) the theory of impossibility
54.If the optimal forecast of the return on a security exceeds the equilibrium return, then ________.
A) the market is inefficient
B) no unexploited profit opportunities exist
C) the market is in equilibrium
D) the market is myopic
55-57 经济练习题代写
55.The efficient markets hypothesis suggests that if an unexploited profit opportunity arises in an efficient market, ________.
A) it will tend to go unnoticed for some time
B) it will be quickly eliminated
C) financial analysts are your best source of this information
D) prices will reflect the unexploited profit opportunity
56.According to the efficient markets hypothesis, purchasing the reports of financial analysts ________.
A) is likely to increase one’s returns by an average of 10 percent
B) is likely to increase one’s returns by about 3 to 5 percent
C) is not likely to be an effective strategy for increasing financial returns
D) is likely to increase one’s returns by an average of about 2 to 3 percent
57.You have observed that the forecasts of an investment advisor consistently outperform the other reported forecasts. The efficient markets hypothesis says that future forecasts by this advisor ________.
A) may or may not be better than the other forecasts Past performance is no guarantee of the future
B) will always be the best of the group
C) will definitely be worse in the future What goes up must come down
D) will be worse in the near future, but improve over time
58-59 经济练习题代写
58.Sometimes one observes that the price of a company’s stock falls after the announcement of favorable earnings. This phenomenon is ________.
A) clearly inconsistent with the efficient markets hypothesis
B) consistent with the efficient markets hypothesis if the earnings were not as high as
anticipated
C) consistent with the efficient markets hypothesis if the earnings were not as low as anticipated consistent with the efficient markets hypothesis if the favorable earnings were expected
59.You read a story in the newspaper announcing the proposed merger of Dell Computer and Gateway. The merger is expected to greatly increase Gateway’s profitability. If you decide to invest in Gateway stock, you can expect to earn ________.
A) above average returns since you will share in the higher profits
B) above average returns since your stock price will definitely appreciate as higher profits are earned
C) below average returns since computer makers have low profit rates
D) a normal return since stock prices adjust to reflect expected changes in profitability almost immediately
60-64 经济练习题代写
60.A situation when an asset price differs from its fundamental value is ________.
A) a random walk
B) an inflation
C) a deflation
D) a bubble
61.________ is the field of study that applies concepts from social sciences such as psychology and sociology to help understand the behavior of securities prices.
A) Behavioral finance
B) Strategical finance
C) Methodical finance
D) Procedural finance
62. ________ means people are more unhappy when they suffer losses than they are happy when they achieve gains.
A) Loss fundamentals
B) Loss aversion
C) Loss leader
D) Loss cycle
63.Psychologists have found that people tend to be ________ in their own judgments.
A) underconfident
B) overconfident
C) indecisive
D) insecure
Ch 14 CENTRAL BANKS AND THE BANK OF CANADA 经济练习题代写
64-68
64.Unemployment rates in Canada after the Great Depression rose close to ________.
A) 20 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 30 percent
D) 10 percent
65.Bank of Canada started operations in ________.
A) 1935
B) 1925
C) 1915
D) 1945
66.The Great Depression ________.
A) was of fundamental importance in the creation of the Bank of Montreal
B) contributed to significant changes in government policy
C) involved the largest increase in the level of economic activity in the history of Canada
D) contributed to significant changes in foreign affairs policy
67.Which of the following are entities of the Bank of Canada?
A) The Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI)
B) The Governing Council
C) The Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC)
D) The Federal Reserve
68.All of the following have served as Bank of Canada governors except for ________.
A) Roy Romanow
B) David Dodge
C) Gordon Thiessen
D) John Crow
69-73 经济练习题代写
69.Which of the following is an element of the Bank of Canada?
A) The Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI)
B) The Governing Council
C) The Board of Directors
D) B and C only
70.The Board of Directors appoints the governor of the Bank of Canada for a renewable term of ________ years.
A) seven
B) five
C) eight
D) six
71.The Bank of Canada quarterly Monetary Policy Report is published every ________, ________, ________ and ________.
A) January; April; July; October
B) February; May; August; November
C) March; June; September; December
D) January; February; August; December
72.Foreign exchange reserves are held by ________.
A) the federal government
B) the department of finance
C) the Ministry of Central Banking
D) individual provinces and territories
73.The benefit of the Ban k of Canada’s role as the lender-of-last-resort include ________.
A) easing liquidity problems of any financial institution
B) deterring bank runs and panics
C) reducing the monetary base to increase liquidity
D) A and B only
74-78 经济练习题代写
74.Which of the following functions are not performed by the Bank of Canada?
A) Cheque clearing
B) Conducting economic research
C) Setting interest rates payable on time deposits
D) Issuing new currency
75.In its role as the federal government’s fiscal agent, the Bank of Canada provides debt management services for the federal government such as ________.
A) advising on provincial government borrowings
B) managing new debt offerings by the federal government
C) servicing the federal government’s outstanding debt
D) B and C only.
76.Which of the following functions are not performed by the Bank of Canada in its role as the federal government’s fiscal agent?
A) Advising on federal government borrowings
B) Managing new debt offerings by the federal government
C) Setting interest rates payable on time deposits
D) Servicing the federal government’s outstanding debt
77.Because of its unique power to ________ base money, the Bank of Canada can ease the liquidity problems of ________.
A) create; financial institutions
B) create; provincial governments
C) save; financial institutions
D) save; provincial governments
78.Canada’s national payments system currently clears and settles payments and transactions, at a volume that is currently ________ times our annual GDP.
A) 15
B) 10
C) 5
D) 2
79-83 经济练习题代写
79.The Bank of Canada’s goal of low inflation is closely tied to ________.
A) economic growth
B) price volatility
C) low interest rates
D) growth in the money supply
80.The responsibility of monetary policy in Canada was given by the 1967 Bank of Canada Act to the ________.
A) government
B) Bank of Canada
C) provincial governments
D) parliament
81.Instrument independence is the ability of ________ to set monetary policy ________.
A) the central bank; goals
B) Parliament; goals
C) Parliament; instruments
D) the central bank; instruments
82.Goal independence is the ability of ________ to set monetary policy ________.
A) the central bank; goals
B) Congress; goals
C) Congress; instruments
D) the central bank; instruments
83.Under the current “joint responsibility system,” ________.
A) in the event of a serious policy conflict the minister of finance can issue a directive that the Bank of Canada must follow
B) the government accepts full responsibility for monetary policy
C) the Bank of Canada does not have considerable autonomy in the conduct of day-to-day monetary policy
D) A and B only.
84-85 经济练习题代写
84.The case for Bank of Canada independence includes the idea that ________.
A) a politically insulated Bank of Canada would be more concerned with long-run objectives and thus be a defender of a sound dollar and a stable price level
B) a Bank of Canada under the control of the government might make the so-called political business cycle more pronounced
C) the principal-agent problem is perhaps worse for the Bank than for politicians since the former does not answer to the voters on election day
D) A and B only.
85.Which of the following statements concerning an independent central bank are true?
A) Politicians may prefer an independent central bank, as it can be used as a “whipping boy” or “scapegoat” for poor economic performance.
B) Politicians in a democratic society may be shortsighted because of their desire to win reelection; thus, the political process may generate a political business cycle, in which just before an election expansionary policies are pursued to lower unemployment and interest rates.
C) Putting the Bank of Canada under control of the government may place too much pressure on the Bank to finance federal budget deficits, thereby imparting an inflationary bias to monetary policy.
D) All of the above are true statements.
86-87 经济练习题代写
86.Advocates of Bank of Canada independence fear that subjecting the Bank to direct
government control would ________.
A) impart an anti-inflationary bias to monetary policy
B) force monetary authorities to sacrifice the long-run objective of price stability
C) make the so-called political business cycle even more pronounced
D) B and C only.
87.Supporters of the current system of Bank of Canada independence believe that a less autonomous Bank would ________.
A) adopt a short-run bias toward policymaking
B) pursue overly expansionary monetary policies
C) be more likely to create a political business cycle
D) do each of the above
88-90 经济练习题代写
88.Politicians in a democratic society may be shortsighted because of their desire to win reelection; thus, the political process can ________.
A) impart an inflationary bias to monetary policy
B) impart a deflationary bias to monetary policy
C) generate a political business cycle, in which just before an election expansionary policies are pursued to lower unemployment and interest rates
D) cause A and C only
89.The theory of bureaucratic behaviour suggests that the objective of a bureaucracy is to maximize ________.
A) the public’s welfare
B) profits
C) its own welfare
D) conflict with the executive and legislative branches of government
90.The theory of bureaucratic behaviour suggests that the Bank of Canada will fight ________.
A) to preserve the public’s welfare
B) to maximize profits
C) minimize its own welfare
D) to preserve autonomy
91-93 经济练习题代写
91.The Maastricht Treaty which established the European Central Bank, defined price stability as an inflation rate equal to ________.
A) It did not specify exactly.
B) 0 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 2 percent
92.Regarding central bank independence, ________.
A) the Fed is more independent than the European Central Bank
B) the European Central Bank is more independent than the Fed
C) the trend in industrialized nations has been to reduce central bank independence
D) the Bank of England has the longest tradition of independence of any central bank in the world
93.Which of the following statements about central bank structure and independence are true?
A) In recent years, with the exception of the Bank of England and the Bank of Japan, most countries have reduced the independence of their central banks, subjecting them to greater democratic control.
B) Before the Bank of England was granted greater independence, the Federal Reserve was the most independent of the world’s central banks.
C) Both theory and experience suggest that more independent central banks produce better monetary policy.
D) While the European Central Bank is independent, it is not as independent as the Federal Reserve.

更多代写:计算机加拿大代修网课 托福代考 英国环境经济学代上网课 美国Essay代写费用 加拿大毕业论文代写 代写留学生essay
