A Research Proposal
For
“A comparison between hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination
when using different methods of removing gloves”
留学生Research Proposal代写 The researcher worked on the information collection and literature review over the past few months.
Title of project: A comparison between hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination when using different methods of removing gloves
Abstract 留学生Research Proposal代写
Personal protective equipments (PPE) are recommended to provide optimal protection of cross infection among patients and Healthcare workers (HCW) when care of the infectious person. Gloves are necessarily to use in contact precaution for prevent transmitted infectious bacteria, virus and microorganisms, which spread by direct contact or indirect contact with infected person or contaminated environment. Bacteria and virus can be passed on to a HCW hands through invisible holes in the gloves or by contamination of hands during glove removal. Hence, there might be a chance of contamination and inducing the potential risk of getting infected by contact hands of HCW or their working environment.
This study focuses on the levels or areas of the hand and environmental contamination after doffing gloves. Fifty participants will be invited from an acute hospital to attend the study; each participant should perform a personal or causal doffing gloves method and a CDC removal gloves method after add Fluorescein solution onto their gloved hands. By using of Fluorescein stains as the contaminate of pathogens, testing the levels of contamination on hand and environment. The researcher will investigate and compare hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination when using different methods of doffing gloves. This research study could be helped to understand the infection control measures in order to develop better practice and also enhanced to focus on environmental cleaning.
译文:
概述 留学生Research Proposal代写
建议使用个人防护装备 (PPE) 以在护理感染者时为患者和医护人员 (HCW) 之间的交叉感染提供最佳保护。手套必须用于接触预防,以防止通过直接接触或间接接触感染者或受污染的环境而传播的传染性细菌、病毒和微生物。细菌和病毒可以通过手套上的隐形孔或在摘除手套过程中污染手部而传染给医护人员。因此,可能存在污染的机会,并引发医护人员接触手或其工作环境而被感染的潜在风险。
这项研究的重点是脱下手套后手和环境污染的水平或区域。将邀请 50 名来自急症医院的参与者参加研究;每个参与者在戴手套的手上添加荧光素溶液后,应执行个人或因果脱手套法和 CDC 脱手套法。通过使用荧光素染色剂作为病原体的污染物,测试手上和环境的污染水平。研究人员将调查并比较使用不同脱手套方法时的手部污染率和环境污染程度。这项研究有助于了解感染控制措施,以制定更好的实践,并加强对环境清洁的关注。
Objectives
The objective of the project is to compare the differences of hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination associated with different glove removal methods.
译文:
目标 留学生Research Proposal代写
该项目的目的是比较手部污染率的差异以及与不同手套去除方法相关的环境污染水平。
Research Questions
- What is the hand contamination rate in different glove removal methods?
- What is the difference between the environmental contaminations in different glove removal methods?
- What is the correlation between the hand contamination rate and glove removal methods?
- What is the correlation between the environmental contamination and glove removal methods?
译文:
研究问题 留学生Research Proposal代写
- 不同脱手套方法的手部污染率是多少?
- 不同的手套去除方法对环境污染有什么区别?
- 手部污染率与脱手套方法有什么关系?
- 环境污染与脱手套方法有什么关系?
Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis: There is no difference between the levels and the rate of hand contamination and environment contamination when using different methods for removing gloves. .
Alternate Hypothesis: There is a change between the levels and the rate of hand and environment contamination when using different methods for removing gloves.
译文:
假设 留学生Research Proposal代写
零假设:使用不同的脱手套方法时,手部污染和环境污染的水平和比率没有差异。 .
替代假设:当使用不同的脱手套方法时,手和环境污染的水平和比率会发生变化。
Background
The consequences of bioterrorism and the threat of emerging infectious diseases have become a reality for the frontline healthcare workers (HCW) (Chan 2007; Health Canada 2003; Seto 2003; Stein, Makarawo & Ahmad 2003; World Health Organization [WHO] 2006; WHO 2003). Personal protective equipments (PPE) are recommended to provide optimal protection of cross infection among patients and HCW (Stein et al. 2003; Seto 2003; WHO 2006; WHO 2003). Likewise, many studies have recognized that HCW may contaminate their hands or gloves when touching contaminated environmental surfaces and therefore causing their hands or gloves to become contaminated with a numbers of organisms that are likely to result in cross infection (Boyce 2007; Seto 2003; Doebbeling, Pfaller, Houstion & Wenzel 1988). 留学生Research Proposal代写
In fact, the Glove is one of the PPE items that is commonly used in clinical settings. Gloves are necessarily to use in contact precaution for prevent transmitted infectious bacteria, virus and microorganisms, which spread by direct contact or indirect contact with infected person or contaminated environment (Bhalla, Pultz, Gries, Ray, Eckstein, Aron, Donskey 2004). There are many cases related to Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), Rota Virus, Norwalk Virus and Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies in clinical facilities (Hartstein, Pemry, Houstion, Wenzel 1988; CDC 2006 & Klevens, Edwards, Tenover, McDonald, Horan, Gaynes 2006). Contact Precautions also apply where the presence of excessive wound drainage, fecal incontinence, or other discharges from the body suggest an increased transmission risk (CDC 2006).

However, glove remains an ineffective protection to certain risks of infection (Hartstein, Pemry, Morthland, Lemonte & Pfalller 1995; Thompson, Dwyer, Ussery, Denman, Vacek & Schwartz 1997).
Boyce & Pittet (2002) stated that Bacteria from patients were found on 30% of HCW hands who had worn gloves daily when in contact with a patient. Thus, Bacteria and virus can be passed on to a HCW hands through invisible holes in the gloves or by contamination of hands during glove removal (Boyce 2007; Boyce & Pittet 2002; Thompson et al. 1997; Marples, Towers 1979). Hence, there might be a chance of contamination and inducing the potential risk of getting infected by contact hands of HCW or their working environment. 留学生Research Proposal代写
Consequently, hand hygiene (HH) is the most important way to prevent and control the potential risk of infection transmission (CDC 2006; CDC 2002). Once this is controlled the potential risk of cross infection can be reduced (Infection Control Nurses Association 2002a). Therefore, some infection control measures of reducing the chance of contamination could be realized. Glove is an essential PPE for daily practices of healthcare staff, which is one of risk factors for poor adherence with HH (CDC 2006; CDC 2002). The chance of hand and environmental contamination could be reduced by controlling the method of glove removal. As a result, how to reduce the level of hand and environmental contamination by using of glove has become critical (Tenorio 2001). Besides, Areas which are identified as high levels of environment contamination should have advance daily cleaning procedures.
In view of this, this study focuses on the levels or areas of the hand and environmental contamination after doffing gloves.
An intervention of doff gloves steps from Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will be offered in-between the study by the investigator. All subjects should implement or adjust their glove removal technique according to CDC. The study is able to compare hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination when using different methods of doffing gloves.
译文:
背景 留学生Research Proposal代写
生物恐怖主义的后果和新发传染病的威胁已成为一线医护人员 (HCW) 的现实(Chan 2007;Health Canada 2003;Seto 2003;Stein, Makarawo & Ahmad 2003;世界卫生组织 [WHO] 2006;WHO) 2003)。建议使用个人防护装备 (PPE) 为患者和医护人员之间的交叉感染提供最佳保护(Stein et al. 2003; Seto 2003; WHO 2006; WHO 2003)。同样,许多研究已经认识到,医护人员在接触受污染的环境表面时可能会污染他们的手或手套,从而导致他们的手或手套被许多可能导致交叉感染的生物体污染(Boyce 2007;Seto 2003;Doebbeling , Pfaller, Hostion & Wenzel 1988)。
事实上,手套是临床环境中常用的 PPE 项目之一。手套必须用于接触预防,以防止通过与感染者或受污染环境的直接接触或间接接触传播的传染性细菌、病毒和微生物(Bhalla、Pultz、Gries、Ray、Eckstein、Aron、Donskey 2004)。临床机构中有许多与多重耐药菌 (MDRO)、轮状病毒、诺沃克病毒和结痂(挪威)疥疮相关的病例(Hartstein、Pemry、Houstion、Wenzel 1988;CDC 2006 和 Klevens、Edwards、Tenover、McDonald、Horan ,盖恩斯 2006)。接触预防措施也适用于伤口渗液过多、大便失禁或其他身体排泄物表明传播风险增加的情况 (CDC 2006)。
然而,手套对于某些感染风险仍然无效(HARTSTEIN、PEMRY、MORTHLAND、LEMONTE & PFALLER 1995;THOMPSON、DWYER、USSERY、DENMAN、VACEK & SCHWARTZ 1997)。
Boyce & Pittet (2002) 指出,在每天与患者接触时戴手套的医护人员手上,有 30% 的人发现了来自患者的细菌。因此,细菌和病毒可以通过手套上的隐形孔或通过脱手套过程中的手污染传播到医护人员的手上(Boyce 2007;Boyce & Pittet 2002;Thompson 等人 1997;Marples,Towers 1979)。因此,可能存在污染的机会,并引发医护人员接触手或其工作环境而被感染的潜在风险。
因此,手卫生 (HH) 是预防和控制潜在感染传播风险的最重要方式(CDC 2006;CDC 2002)。一旦这得到控制,交叉感染的潜在风险就可以降低(感染控制护士协会 2002a)。因此,可以实现一些减少感染机会的感染控制措施。手套是医护人员日常工作中必不可少的 PPE,这是 HH 依从性差的风险因素之一(CDC 2006;CDC 2002)。通过控制脱手套的方法,可以减少手和环境污染的机会。因此,如何通过使用手套来降低手和环境污染的程度变得至关重要(Tenorio 2001)。此外,被确定为环境污染程度高的区域应提前进行日常清洁程序。
有鉴于此,本研究重点关注脱下手套后手部和环境污染的水平或区域。
研究人员将在研究之间提供来自疾病控制和预防中心 (CDC) 的脱下手套步骤的干预。所有受试者都应根据 CDC 实施或调整他们的手套去除技术。该研究能够比较使用不同脱手套方法时的手部污染率和环境污染水平。
Subjects
A convenience sample of fifty frontline HCW of an acute hospital will be invited to attend the study, including nursing staff, healthcare assistants and doctors. According to Portney & Watkins (2000) mentioned in the paired t test table that the power is set at 0.8 (beta is 0.2) and the adopted alpha level is at 0.05 with medium effect size. Because of this power being set at 0.8 the probability of rejecting a null hypothesis is false. Historically, the range value of power set to 0.8, Beta 0.2; and alpha 0.05 has been used for calculating the sample size that is needed to achieve the power for an experiment.
Besides, analysis of PASS 2008 under the Group-Sequential Logrank Tests , the total sample size of numbers is also calculated to 50 (appendix 1). Thus, 50 subjects will be collected in this study. Ethics approval should be applied before the study, and the experimental protocol should be approved by the Human Subject Ethics Sub-committee of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Besides, each subject was informed of the purpose and a procedure of the study as well as written consent was obtained beforehand. All participations were voluntary and subjects could withdraw at any time without any reason. Confidentiality and anonymity were also assured
译文:
科目 留学生Research Proposal代写
将邀请 50 名急症医院一线医护人员的便利样本参加这项研究,包括护理人员、医疗助理和医生。根据配对 t 检验表中提到的 Portney & Watkins (2000),功效设置为 0.8(β 为 0.2),采用的 alpha 水平为 0.05,具有中等效应大小。由于此幂设置为 0.8,拒绝原假设的概率为假。历史上,power的范围值设置为0.8,Beta 0.2;并且 alpha 0.05 已用于计算实现实验功效所需的样本量。
此外,在 Group-Sequential Logrank Tests 下对 PASS 2008 的分析,数字的总样本量也计算为 50(附录 1)。因此,本研究将收集 50 名受试者。研究前应申请伦理批准,实验方案须经香港理工大学人类受试者伦理小组委员会批准。此外,每个受试者都事先被告知研究的目的和程序以及书面同意。所有的参与都是自愿的,受试者可以随时退出,没有任何理由。保密性和匿名性也得到保证
Fluorescein solution and UV lamp
Fluorescein is a type of organic dye, in yellow colour and is safe to use as topical, oral, intravenous and retinal (Ford 1996). Many studies like to use Fluorescein stain to represent the contaminate of pathogens (Zamora, Murdoch, Simchison & Day 2006; Li, Wong, Chung, Gohel & Leung 2008; Li, Wong, Chung, Guo, Hi, Guan, Yao L, Song, Newton 2006; Wong, Chung, Chan, Ching, Lam, Chow, Seto 2004).
Adverse reactions of Fluorescein includes nausea, vomiting, skin rash, acute hypotension, anaphylactoid reaction and cardiac arrest but report rates vary from 1% – 6% (Fineschi, Monasterolo, Rosi & Turillazzi 1999). Accordingly, a Fluorescein skin test is done on the inner part of the forearm on each subject before the study to make sure there is no allergic reaction. In this study, a Fluorescein solution is dilated from 0.5cc of a 25% solution in 100 cc of sterile water as a contaminate and then 5 cc of the Fluorescein solution is sprayed on each gloved palm (total 10cc are given both palms). Subjects will then be instructed to close both palms together with friction application for ten seconds. 留学生Research Proposal代写
Fluorescein solution and ultra violet (UV) light detectable paste combine to form surrogate contamination. UV lamp is useful to detect the Fluorescein stain as it allows the invisible stained patch to become visible. The UV lamp machine might be checked and tested before the study takes place; same brand of machine is preferable from the start to the end of the study. This can prevent various results under distinct UV power. All participants need to be assessed with an UV lamp before donning the protective clothing in order to ensure that no Fluorescein is present.
译文:
荧光素溶液和紫外灯
荧光素是一种有机染料,呈黄色,可安全用作局部、口服、静脉注射和视网膜(Ford 1996)。许多研究喜欢用荧光素染色来代表病原体的污染(Zamora, Murdoch, Simchison & Day 2006; Li, Wong, Chung, Gohel & Leung 2008; Li, Wong, Chung, Guo, Hi, Guan, Yao L, Song , Newton 2006; Wong, Chung, Chan, Ching, Lam, Chow, Seto 2004)。
荧光素的不良反应包括恶心、呕吐、皮疹、急性低血压、过敏样反应和心脏骤停,但报告率从 1% 到 6% 不等(Fineschi、Monasterolo、Rosi 和 Turillazzi 1999)。因此,在研究之前,会在每个受试者的前臂内侧进行荧光素皮肤测试,以确保没有过敏反应。在这项研究中,荧光素溶液是从 100 毫升无菌水中 0.5 毫升的 25% 溶液中作为污染物膨胀的,然后将 5 毫升的荧光素溶液喷在每只戴手套的手掌上(两手掌共喷洒 10 毫升)。然后将指示受试者将双手掌合在一起并施加摩擦十秒钟。
荧光素溶液和紫外线 (UV) 光可检测糊状物结合形成替代污染。紫外线灯可用于检测荧光素染色,因为它可以让不可见的染色斑块变得可见。在研究开始之前,可能会检查和测试紫外线灯机;从学习开始到结束,最好使用相同品牌的机器。这可以防止在不同的紫外线功率下出现各种结果。在穿上防护服之前,所有参与者都需要用紫外线灯进行评估,以确保不存在荧光素。
Gloves
Latex disposable gloves will be selected in the test as it is a common material used by Hong Kong Hospital Authority. There are three general sizes: small, medium and Large. Disposable gloves are designed as a single-use medical tool which has invisible perforations that cannot provide complete protection against hand contamination (CDC 2002; Infection Control Nurses Association 2002b; Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency 2006). Each subject might be required to exam the integrity of the glove and double checked by the investigator before applying the Fluorescein solution. No leakage of gloves is allowed as it may affect the contaminated Fluorescein patch.
译文:
手套 留学生Research Proposal代写
由于乳胶手套是香港医院管理局常用的材料,因此测试将选择乳胶一次性手套。 共有三种尺寸:小号、中号和大号。 一次性手套被设计为一次性医疗工具,具有隐形穿孔,不能完全防止手部污染(CDC 2002;感染控制护士协会 2002b;药品和保健品监管局 2006)。 在应用荧光素溶液之前,每个受试者可能需要检查手套的完整性并由研究人员进行双重检查。 不允许手套泄漏,因为它可能会影响受污染的荧光素贴片。
Preliminary test
A preliminary test to practise the method of photographing under the UV lamp in the dim or dark room will be done before the study. The preliminary test should check the successful results of Fluorescein patch shown on the photos and also estimate the number of sample size. 10% of total subjects are invited to attend in this test, and all of the experiment setting as well as equipments will be the same as the research study.
译文:
初步测试
在研究之前将进行初步测试,以练习在昏暗或黑暗的房间中在紫外线灯下拍摄的方法。 初步测试应检查照片上显示的荧光素贴片的成功结果,并估计样本数量。 本次测试邀请10%的被试参加,所有的实验设置和设备将与研究相同。
Experimental Protocol
This trial is an intervention study of experimental designs that allocates and compares the contamination level between subjects as well as carries out the intervention of CDC off gloves’ steps. The study is using a convenience sample plans collected from an acute hospital in Hong Kong; all subjects are frontline HCW who are working in clinical settings and familiar with using gloves in daily practices.
The fifty subjects will be invited to a private room that is kept between 22-25°C and at 70% humidity level, which is like their working environment in the hospital. Firstly, they will proceed with a skin test of Fluorescein solution and assess by an UV lamp as mentioned before. Then, they need to wear a suitable size of latex gloves, if there are no complaints or any allergy reactions. A disposable, nonwoven cloth gown will be provided and put on the subject, which enhances to serve as a unique absorption material for the Fluorescein patch and reduces influencing the result.
All subjects should stand on the measured point of the room that has designated footprints on the floor. The designated area is marked with USA shoes sizes 5 to 7 footprints. The study of environment contamination will be measured 2 feet from three sides of the subject (front, left and right). A rubbish bin will also be placed near the front wall for discarding the removed gloves.
The 2 feet distance is according to the gown down area setting in this hospital.
A total of 10 cc Fluorescein solution will be applied to each subject’s gloved palms and the subject is instructed to close both palms together with friction application for ten seconds afterwards. Then, the subject is allowed to doff the gloves off by casual or personal style. Photos will be taken of all the contaminated areas including bare hands, gown, rubber bin cover and walls under the UV lamp lighting in the dark.
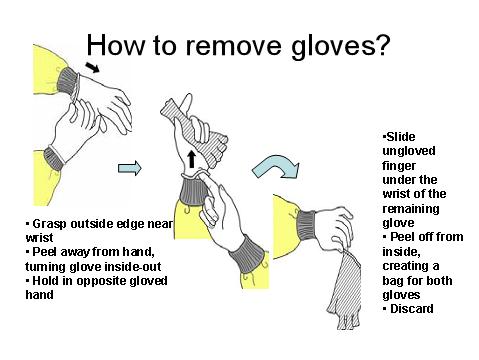
A snack plus a bottle of distilled water will be offered after hand hygiene and a 30 minutes rest. During the resting time, the writer will present a video and demonstration of CDC’s recommended guidelines and methods on how to remove gloves. A demonstration of the CDC gloves removal method (figure 1) should be done by all the subjects after the break. Off gloves method of CDC is divided into 6 steps: 1. outside of gloves is contaminated; 2. grasp outside of glove with opposite gloved hand, peel off; 3. hold removed glove in gloved hand; 4. slide fingers of ungloved hand under remaining glove at wrist; 5. peel glove off over first glove & 6. discard gloves in waste container (CDC, 2003).
The implementations of CDC doff gloves method will be tested in Fluorscein solution when the subjects have passed the instructors pre-test of the CDC demonstration. A check list to record the important points of removing steps in CDC instructions might be acknowledged and verified (appendix 2). Subjects need to follow the instructions that eliminate any bias. Another set of photos will be taken afterwards. The work flow of paired Fluorsecein test is pointed out in figure 2.
译文:
实验方案
该试验是一项实验设计的干预研究,它分配和比较受试者之间的污染水平,并执行 CDC 脱手套步骤的干预。该研究使用从香港一家急症医院收集的便利样本计划;所有受试者都是在临床环境中工作并熟悉在日常实践中使用手套的一线医护人员。
五十名受试者将被邀请到一个保持在 22-25°C 和 70% 湿度水平的私人房间,就像他们在医院的工作环境一样。首先,他们将进行荧光素溶液的皮肤测试,并使用前面提到的紫外线灯进行评估。然后,如果没有投诉或任何过敏反应,他们需要戴上合适尺寸的乳胶手套。将提供一次性无纺布长袍并穿上受试者,增强作为荧光素贴片的独特吸收材料的作用,并减少对结果的影响。
所有受试者应站在房间的测量点上,该点在地板上有指定的脚印。指定区域标有美国鞋码 5 至 7 号脚印。环境污染的研究将在距离对象三侧(前、左和右)2 英尺处进行测量。前墙附近还将放置一个垃圾桶,用于丢弃取下的手套。
2 英尺的距离是根据这家医院的睡衣区设置而定的。
总共 10 cc 荧光素溶液将应用于每个受试者戴手套的手掌,然后指示受试者将双手掌合在一起并摩擦应用十秒钟。然后,受试者可以随意或个人风格脱下手套。将在黑暗中在紫外线灯照明下拍摄所有污染区域,包括裸手、长袍、橡胶箱盖和墙壁。
完成手卫生并休息 30 分钟后,将提供小吃和一瓶蒸馏水。在休息时间,作者将展示 CDC 推荐的如何脱手套的指南和方法的视频和演示。休息后,所有受试者都应演示 CDC 手套去除方法(图 1)。 CDC的脱手套方法分为6个步骤:1.手套外面被污染; 2. 用戴手套的另一只手抓住手套外面,剥开; 3. 戴手套的手拿着摘下的手套; 4. 将未戴手套的手的手指滑到手腕处剩余的手套下; 5. 在第一只手套上脱下手套 & 6. 将手套丢弃在废物容器中 (CDC, 2003)。
当受试者通过 CDC 演示的讲师预测试后,CDC 脱下手套方法的实施将在荧光素溶液中进行测试。记录 CDC 说明中删除步骤的要点的核对表可能会得到确认和验证(附录 2)。受试者需要遵循消除任何偏见的说明。之后将拍摄另一组照片。配对荧光素试验的工作流程如图2所示。
Contamination
According to Zamora et al. (2006) study, the contamination stain will be measured in a Fluorescent patch size. A size larger than 1 square centimetre (cm²) is counted as a large patch (LP) and one smaller than 1 cm² is counted as a small patch (SP). Moreover, Squares of 30cm x 30cm will be marked on the white cloth which place on the walls of examination room that facilitating the calculation of Fluorescein patches on the photos. The Fluorescent patches might indicate the level of contamination.
译文:
污染 留学生Research Proposal代写
根据萨莫拉等人的说法。 (2006) 研究,污染污渍将在荧光斑块大小中进行测量。 尺寸大于 1 平方厘米 (cm²) 的算作大补丁 (LP),小于 1 cm² 的算作小补丁 (SP)。 此外,30cm x 30cm 的正方形将被标记在放置在考试室墙壁上的白布上,以方便计算照片上的荧光斑块。 荧光贴片可能表明污染程度。
Data analysis
This study describes the relation of the environment contamination formed by removing contaminated gloves and determines the difference between the levels of surrounding contamination after being introduced to an intervention of doffing gloves from CDC. However, the study also provides evidence to the impact of removing glove intervention in the current infection control practice. The data is analyzed by using SPSS 15.0 for windows, which calculates paired t test as the data is assumed to have normal distribution. Paired t test simply compares the two sets of data and identifies the results.
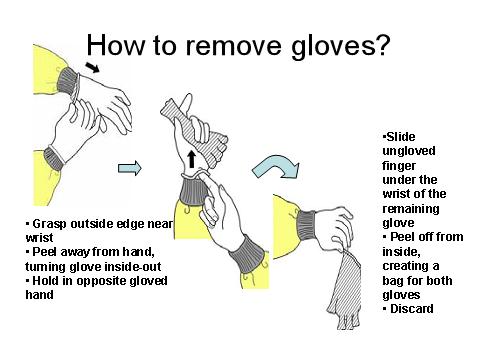
Figure 1. CDC recommendation on off gloves.
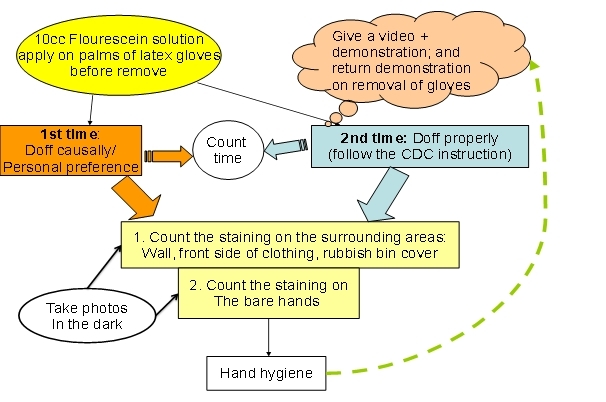
Figure 2. The work flow of paired Fluorscein test. Photos take in the dim lighting or dark room.
译文:
数据分析 留学生Research Proposal代写
本研究描述了脱下受污染手套所形成的环境污染的关系,并确定了在引入 CDC 脱下手套干预后周围污染水平之间的差异。 然而,该研究还提供了证据,证明在当前的感染控制实践中去除手套干预的影响。 使用 SPSS 15.0 for windows 对数据进行分析,由于假设数据具有正态分布,因此计算配对 t 检验。 配对 t 检验只是比较两组数据并确定结果。
图 1. CDC 建议戴上脱手套。
图 2. 配对荧光素测试的工作流程。 照片在昏暗的灯光或黑暗的房间里拍摄。
Time Planning
The researcher worked on the information collection and literature review over the past few months. For the recent month, finalizing the experimental setup was the most important issue and anticipating of the ethic approval from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University as well as reviewing the literature and gathering information. In the coming month, research volunteer (HCW) recruitment should start while the research topic and experimental setup is finalized. Furthermore, the preliminary test should be proceeded. Data collection procedures in the following three to six month, and commence the data analysis afterwards. The most effective way is to review the schedule periodically. Every semester a progress report of the research need to be submitted and a dissertation should be submitted at the end of semester four.
A preliminary work schedule:
| Year
Task |
2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||
| 9 ~ 12 | 1 ~ 4 | 5 ~ 8 | 9 ~ 12 | |||||||||||||
| Critical thinking of project title | ||||||||||||||||
| Information collection | ||||||||||||||||
| Literature review | ||||||||||||||||
| Equipment collection | ||||||||||||||||
| Subjects recruitment | ||||||||||||||||
| Preliminary test | ||||||||||||||||
| Finalize experimental setup | ||||||||||||||||
| Data analysis | ||||||||||||||||
| Reporting | ||||||||||||||||
| Review | ||||||||||||||||
Budget 留学生Research Proposal代写
| Dollar
Items |
Year 1 (HK $) | Year 2 (HK $) |
| Research materials:
Gloves, gowns, cloth, Fluorescein |
N/A | 2500 |
Equipments:UV lamp, lamp bulb |
N/A | 500 |
| Stationary:
Paper, copies fee, pens |
N/A | 500 |
| Totals | N/A | 3500 |
译文:
时间规划
在过去的几个月里,研究人员致力于信息收集和文献综述。最近一个月,完成实验设置是最重要的问题,期待香港理工大学的伦理批准以及查阅文献和收集信息。在接下来的一个月里,研究志愿者 (HCW) 招募应该开始,同时研究主题和实验设置最终确定。此外,还应进行初步测试。在接下来的三到六个月内完成数据收集程序,然后开始数据分析。最有效的方法是定期检查时间表。每学期需要提交研究进展报告,并在第四学期末提交论文。
初步工作计划:
| Year
Task |
2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||
| 9 ~ 12 | 1 ~ 4 | 5 ~ 8 | 9 ~ 12 | |||||||||||||
| Critical thinking of project title | ||||||||||||||||
| Information collection | ||||||||||||||||
| Literature review 留学生Research Proposal代写 | ||||||||||||||||
| Equipment collection | ||||||||||||||||
| Subjects recruitment | ||||||||||||||||
| Preliminary test | ||||||||||||||||
| Finalize experimental setup | ||||||||||||||||
| Data analysis | ||||||||||||||||
| Reporting | ||||||||||||||||
| Review | ||||||||||||||||
预算
| Dollar
Items |
Year 1 (HK $) | Year 2 (HK $) |
| Research materials:
Gloves, gowns, cloth, Fluorescein |
N/A | 2500 |
Equipments:UV lamp, lamp bulb |
N/A | 500 |
| Stationary:
Paper, copies fee, pens |
N/A | 500 |
| Totals | N/A | 3500 |
References: 留学生Research Proposal代写
Bhalla A, Pultz N J, Gries DM, Ray AJ, Eckstein E C, Aron DC, Donskey CJ. 2004. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol, 25:164-167.
Boyce JM. 2007. Environmental contamination makes an important contribution to hospital infection. J Hosp Infect, 65:50-54.
Chan P. 2007. Influenza-Asian Focus. Asia-Pacific Advisory Committee on Influenza, 2(3):3.
[CDC] US Centers for Disease Control. 2002. Guideline for Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Setting. Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report, 51:1-56. [CDC] US Centers for Disease Control. 2003. Donning Personal Protective Equipment [Online]. Accessed on December 5, 2008. URL: http:// www.cdc.gov /ncidod/dhq/pdf/ppe/ppeposter148.pdf [CDC] US Centers for Disease Control. 2006. MDRO Guideline for Management of Multidrug-resistant Organisms in Healthcare Setting [Online]. Accessed on January 10, 2008. URL: http:// www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dhqp/gl_isolation_ contact.htmlDoebbeling BN, Pfaller MA, Houstion AK, Wenzel RP. 1988. Removal of nosocomial pathogens from the contaminated glove: implications for glove reuse and hand washing. Ann Intern Med,109:194-198. 留学生Research Proposal代写
Fineschi V, Monasterolo G, Rosi R, Turillazzi E. 1999. “Fatal anaphylactic shock during a fluorescein angiography”.Forensic Sci Int, 100(1-2):137-142.
Hartstein AI, Pemry MA, Morthland VH, Lemonte AM, Pfalller AM. 1995. Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a hospital and an intensive care unit. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 16(7):405-411.
Health Canada. 2003. Cluster of severe acute respiratory syndrome cases among protected health care workers – Toronto. Can Commun Dis Rep, 29:93-7.
Infection Control Nurses Association. 2002a. Protective Clothing: Principles and Guidance. Fitwise, Bathgate.
Infection Control Nurses Association. 2002b. Hand Decontamination Guidelines. Fitwise, Bathgate.
Klevens RM, Edwards JR, Tenover FC, McDonald LC, Horan T, Gaynes R. 2006. Clin Infect Dis, 42:389-391.
Li Y, Guo YP, Wong KCT, Chung WYJ, Gohel MDI, Leung HMP. 2008. Transmission of communicable respiratory infections and facemasks. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 1:17-27.
Li Y, Wong TKS, Chung JWY, Guo YP, Hi JY, Guan YT, Yao L, Song QW, Newton E. 2006. In-vivo protective performance of N95 respirator and surgical facemask. Am J Ind Med, 49:1056-1065. 留学生Research Proposal代写
Marples RR, Towers AG. 1979. A laboratory model for the investigation of contact transfer of micro-organisms. J Hyg (Lond), 82:237–48.
Medicines and healthcare products Regulatory Agency. 2006. DB 2006 Single-use Medical Devices: Implications and Consequences of Reuse. Retrieved December 4, 2008, from www.m hra.gov.uk/home/idcplg?
Portney LG & Watkins MP. 2002. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Tenorio AR, Badri SM, Sahgal NB. 2001. Effectiveness of gloves in the prevention of hand carriage of vancomycin-resistant enterococcus species by health care workers after patient care. Clinical infectious Diseases, 32(5):825-829.
Thompson BL, Dwyer DM, Ussery Xt, Denman S, Vacek P, Schwartz B. 1997. Handwashing and glove use in a long-term care facility. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 18(2):97-103.
Seto WH, Tsang D, Yung RWH, et al. 2003. Effectiveness of Precautions against droplets and contact in prevention of nosocomial transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Lancet, 361:1519-20.
Stein AD, Makarawo TP, Ahmad MFR. 2003. A survey of doctors’ and nurses’ knowledge, and complicance with infection control guidelines in Birmingham teaching hospitals. Journal of Hospital Infection, 54 (1):68-73.
[WHO] World Health Organization. 2003. Hospital infection control guidance for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). 24 April. Geneva, Swizerland: WHO. [WHO] World Health Organization. 2006. Avian influenza: Current situation. 24 August. Geneva, Swizerland: WHO. 留学生Research Proposal代写Wong TKS, Chung JWY, Chan WF, Ching PTY, Lam CHS, Chow CB, Seto WH. 2004. Effective personal protective clothing (PPC) for healthcare workers attending patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Am J Infect Control, 32:90-96.
Zamora JE, Murdoch J, Simchison B, Day AG. 2006. Contamination: a comparison of 2 personal protective systems.CMAJ,175(3):249-254.

Appendix 1. Total sample size calculation by PASS 2008.
Check List of CDC Recommended Doff gloves steps
Please þ when the steps are achieved.
- Fingersshould not touch the skin of your wrist when grasping the outside edge of the opposite gloved hand (step 1) ¨
- Removed glove should be held in the ungloved hand (step 3) ¨
- The ungloved finger should slide under the gloved wrist without touching
outer surface of the glove (step 4) ¨
- One glove should be packed inside the opposite glove when both
gloves are removed ¨
CDC recommendation on off gloves (CDC, 2003)
Appendix 2. Checklist of CDC Recommended Doff gloves steps.
| CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN RESEARCH
Title of Project: A comparison between hand contamination rates and the levels of environmental contamination when using different methods of removing gloves |
| I _______________________ hereby consent to participate in the captioned research conducted by________________.
I understand that information obtained from this research may be used in future research and published. However, my right to privacy will be retained, i.e. my personal details will not be revealed. 留学生Research Proposal代写 The procedure as set out in the attached information sheet has been fully explained. I understand the benefit and risks involved; I understand that my participation is voluntary. I acknowledge that I have the right to question any part of the procedure and can withdraw at any time without penalty of any kind. |
Name of participant
Signature of participant
Name of Parent or Guardian (if applicable)
Signature of Parent of Guardian (if applicable)
Name of researcher LAI Yuen Fun Joanna
Date

更多代写:信息技术作业代写 gre代写 英国统计代上网课 留学生课程论文代写 英国管理学casestudy代写 英国本科留学生代考

