深入了解View的绘制流程
1. ViewRoot
ViewRoot是联接WindowManager与DecorView的桥梁,View的全部绘图步骤的三大步走(measure、layout、draw)全是根据ViewRoot进行的。当Activity目标被建立结束后,会将DecorView加上到Window中(Window是对对话框的抽象性,DecorView是一个对话框的顶尖器皿View,其实质是一个FrameLayout),另外会建立ViewRootImpl(ViewRoot的完成类)目标,并将ViewRootImpl与DecorView创建关系。有关ViewRoot,大家只必须了解它是联络GUI智能管理系统和GUI展现系统软件的桥梁。View的绘图步骤从ViewRoot的performTraversals方式逐渐,历经measure、layout、draw三大全过程进行对一个View的绘图工作中。peformTraversal方式內部会启用measure、layout、draw这三个方式,这三个方式內部又各自启用onMeasure、onLayout、onDraw方式。
在onMeasure方式中View会对其全部的子原素实行measure全过程,这时measure全过程就从父器皿”传送”到子原素中,然后子原素会递归的对他的儿子原素开展measure全过程,这般不断进行对全部View树的遍历。onLayout与onDraw全过程的实行步骤与此相近。
measure全过程决策了View的精确测量高宽,这一全过程完毕后,就可以根据getMeasuredHeight和getMeasuredWidth得到View的精确测量宽高了;
layout全过程决策了View在父器皿中的部位和View的最后表明高宽,getTop等方式可获得View的top等四个部位主要参数(View的左上方端点的座标为(left, top), 右下方顶点坐标为(right, bottom)),getWidth和getHeight可得到View的最后表明高宽(width = right – left;height = bottom – top)。
draw全过程决策了View最后表明出去的模样,此全过程进行后,View才会在显示屏上表明出去。
2. MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec为一个32位系统的int值,高2位意味着SpecMode,低30位意味着SpecSize,前面一种指精确测量方式,后面一种指某类精确测量方式下的规格型号尺寸。在一个View的measure全过程中,系统软件会将该View的LayoutParams融合父器皿的“规定”转化成一个MeasureSpec,这一MeasureSpec表明了应当如何精确测量这一View。
(1)三种 SpecMode:
UNSPECIFIED:父器皿不对View作一切规定,一般 用以系统软件內部,表明一种精确测量的情况。
EXACTLY:父器皿早已检验出View所必须的精准尺寸,这类精确测量方式下View的精确测量值便是SpecSize的值。这一SpecMode相匹配于LayoutParams中的match_parent和得出实际尺寸这二种方式。
AT_MOST:父器皿特定了一个能用尺寸即SpecSize,View的尺寸不可以超过此值,能用尺寸在于不一样View的实际完成。这一SpecMode相匹配于LayoutParams中的wrap_content。
(2)针对DecorView,它的MeasureSpec由对话框规格和其本身的LayoutParams一同明确;针对一般View,他的MeasureSpec由父器皿的MeasureSpec和其本身的LayoutParams一同明确。
3. View的实际绘图步骤
(1)measure全过程
a. DecorView的measure全过程
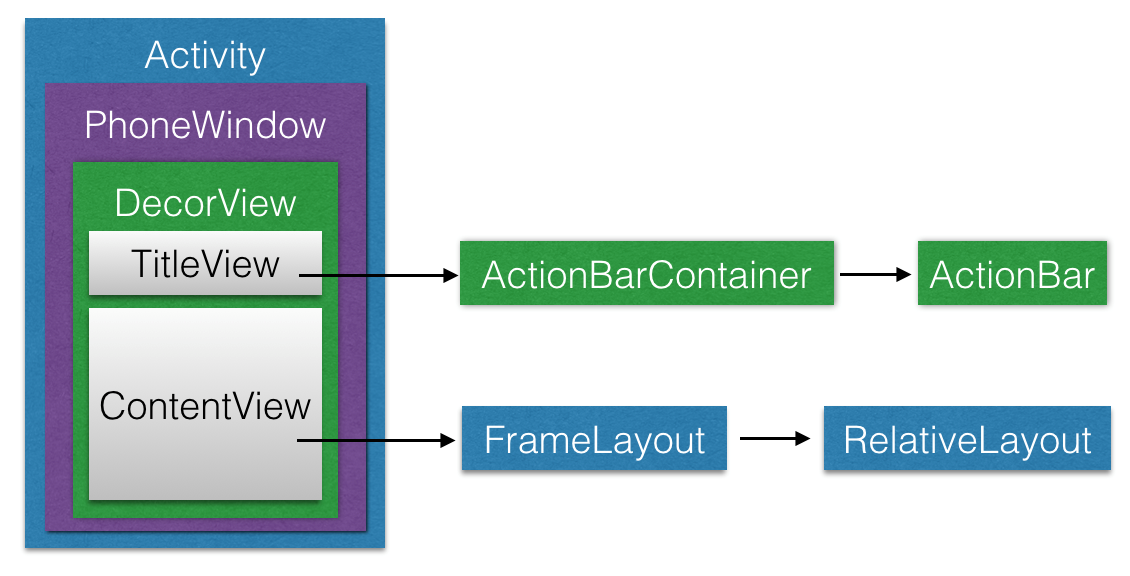
前边大家提及过,DecorView是一个运用对话框的根器皿,它实质上是一个FrameLayout。DecorView有唯一一个子View,它是一个竖直LinearLayout,这一竖直线形布局管理器包括两个子原素,一个是TitleView(ActionBar的器皿),另一个是ContentView(对话框內容的器皿)。有关ContentView,它是一个FrameLayout(android.R.id.content),大家平时用的setContentView便是设定它的子View。如下图中,大家为TilteView中加上了一个ActionBar,为ContentView中加上了一个RelativeLayout(根据setContentView方式)。

前边提及,DecorView的MeasureSpec由对话框的规格和本身的LayoutParams一同决策。在ViewRootImpl的measureHierarchy方式中,完成了建立DecorView的MeasureSpec的全过程,相对的编码精彩片段以下:
1 childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
之上编码精彩片段中的childXxxMeasureSpec即是DecorView的MeasureSpec,lp.width和lp.height被系统软件取值为MATCH_PARENT。getRootMeasureSpec的编码以下:
private int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
所述编码中启用了makeMeasureSpec方式来获得measureSpec,而传到的rootDimension主要参数即是lp.width或lp.height,数值MATCH_PARENT,从而必得DecorView的MeasureSpec,在其中SpecMode为EXACTLY,SpecSize为windowSize。
b. 一般View(非ViewGroup)的measure全过程:
非ViewGroup的View的特性是不可以有子原素,因而只需精确测量好本身就可以了。一般View的measure根据measure方式来进行:
1 public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//....
//回调函数onMeasure()方式
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//more
}
一般View的measure方式是由ViewGroup在measureChild方式中启用的(即完成了measure全过程从ViewGroup到子View的传送),ViewGroup启用他的儿子View的measure时即传到了该子View的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec。注意到measure是一个final方式,因而要完成自定的measure全过程,必须重写onMeasure方式:
1 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
setMeasureDimension方式用以设定View的精确测量高宽,如果不重写此方式,默认设置是立即启用getDefaultSize获得规格的:
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
由之上编码得知,一切正常状况下(SpecMode为AT_MOST或EXACTLY),getDefaultSize获得的规格尺寸即是specSize。由之上编码还可了解,立即承继View的自定控制必须重写onMeasure方式并设定wrap_content时的本身尺寸,不然在合理布局中应用wrap_content就等同于应用match_parent的实际效果。实例以下:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, mHeight);
}
}
所述实例编码中的mWidth,mHeight是为wrap_content时设置的默认设置高宽。这一默认设置高宽可依据具体必须自主设定,例如TextView在wrap_content时的默认设置宽高是依据在其中的全部文本的总宽来设置的,进而完成恰好“包囊”文本內容的实际效果。
c. ViewGroup的measure全过程:
ViewGroup必须先进行子View的measure全过程,才可以进行本身的measure全过程,ViewGroup的onMeasure方式依据不一样的布局管理器类(LinearLayout、RelativeLayout这些)有不一样的完成,例如LinearLayout的onMeasure方式编码以下:
1 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOriention == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
measureVertical中精确测量子原素的主要编码以下:
//See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
for (int i = 0; i < count; i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
. . .
//Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or previous children have given a weight,
//then we allow it to use all available space (and we will shrink things later if needed).
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
if (oldHeight != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
lp.height = oldHeight;
}
final int childLength = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength childHeight lp.topMargin lp.bottomMargin getNextLocationOffset(child));
}
由所述编码能够了解,在measureVertical方式时会对每一个LinearLayout中的子原素开展解析xml并根据measureChildBeforeLayout方式对每一个子原素实行measure全过程。在measureChildBeforeLayout方式內部会启用子原素的measure方式,那样会先后让每一个子原素进到measure全过程。mTotalLength表明LinearLayout在垂直方位上的规格,每进行一个子原素的measure全过程,它的值也会相对提升。精确测量完子原素后,LinearLayout会精确测量本身的尺寸。measureVertical中精确测量LinearLayout本身的关键编码以下:
//Add in our padding.
mTotalLength = mPaddingTop mPaddingBottom;
int heightSize = mTotalLength;
//Check against our minimum height
heightSize = Math.max(heightSize, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
//Reconcile our calculated size with the heightMeasureSpec
int heightSizeAndState = resolveSizeAndState(heightSize, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
heightSize = heightSizeAndState & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
. . .
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState), heightSizeAndState);
对竖直的LinearLayout而言,它在水平方向的精确测量全过程与一般View的measure全过程一样,在垂直方位的measure全过程以下:若该竖直LinearLayout的layout_height为match_parent或实际标值,它的measure全过程与一般View一样;若该竖直LinearLayout的layout_height为wrap_content,则它垂直方位的高宽比为全部子原素占有的高宽比之和,但不可以超出父器皿的能用室内空间尺寸,最后高宽比也要充分考虑其垂直方位的padding,有关的编码以下:
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (speczMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
ViewGroup关键根据其measureChildren方式进行他的儿子View的measure全过程,上边竖直LinearLayout中启用的measureChildBeforeLayout能够看作是measureChildren的一个“变异”,measureChildren方式编码以下:
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
在其中,measureChild方式进行对联View的measure全过程:
1 protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
留意在这儿,在实行child.measure方式前,就早已根据getChildMeasureSpec获得了子View的MeasureSpec。getChildMeasureSpec依据子View的LayoutParams和父器皿的MeasureSpec来决策子View的MeasureSpec,getChildMeasureSpec的编码以下:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//这儿传到的spec为ViewGroup的MeasureSpec
//specMode和specSize即为父器皿的MeasureSpec
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//padding为父器皿中已应用的室内空间尺寸,size为父器皿能用室内空间尺寸
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//子View要想和父器皿一样大
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//子View想自身决策它的尺寸,但不可以比父器皿大
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
//Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
之上涵数的工作中全过程可小结以下:
a. 当childLayoutParams特定为实际的大钟头:若parentSpecMode为EXACTLY,则childSpecMode为EXACTLY,childSpecSize为childSize(layout_width和layout_height中特定的实际尺寸);若parentSpecMode为AT_MOST,则childSpecMode和childSpecSize各自为EXACTLY和childSize。
b. 当childLayoutParams为match_parent时:若parentSpecMode为EXACTLY,则childSpecMode和childSpecSize各自为EXACTLY和parentSize(父器皿中能用的尺寸);若parentSpecMode为AT_MOST,则childSpecMode和childSpecSize各自为AT_MOST和parentSize。
c. 当childLayoutParams为wrap_content时:若parentSpecMode为EXACTLY,则childSpecMode和childSpecSize各自为AT_MOST和parentSize;若parentSpecMode为AT_MOST,则childSpecMode和childSpecSize各自为AT_MOST和parentSize。
也有一点必须留意的是,View的measure全过程和Activity生命期的回调函数方式并不是同歩的,也就是不可以确保在某一生命期的回调函数方式中measure全过程早已实行结束。
(2)layout全过程
layout全过程用于明确View在父器皿中的部位,因而是由父器皿获得子View的部位主要参数后,启用child.layout方式并传到已获得的部位主要参数,进而进行对联View的layout。当ViewGroup的部位被明确后,它在onLayout中会解析xml全部子原素并启用其layout方式,在layout方式中子原素的onLayout又会被启用。layout方式明确先View自身的部位,再启用onLayout方式明确全部子原素的部位。layout方式以下:
1 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
2 ……
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : set(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
9 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy =
(ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>) li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
18 }
19 }
20 }
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAGS3_IS_LAID_OUT;
}
layout方式的大概步骤:最先根据setFrame方式设置View的四个部位主要参数,即用传出的l、t、r、b四个主要参数复位mLeft、mTop、mRight、mBottom这四个值,进而明确了该View在父器皿中的部位。若部位发生改变就启用onLayout方式,onLayout方式在View类中为空,由于对联原素合理布局的工作中仅有器皿View才必须做。在ViewGroup中,onLayout是一个抽象方法,由于针对不一样的布局管理器类,对联原素的合理布局方法是不一样的。例如,LinearLayout的onLayout方式以下:
1 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOriention == VERTIVAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
之上编码会依据LinearLayout的orientation为水准或竖直启用相对的涵数来进行合理布局全过程,这儿以layoutVertical为例子剖析一下竖直线形布局管理器的合理布局全过程,layoutVertical的关键编码以下:
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
. . .
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i ) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop = measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
. . .
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
childTop = mDividerHeight;
}
childTop = lp.topMargin;
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop getLocationOffset(child), childWidth, childHeight);
childTop = childHeight lp.bottomMargin getNextLocationOffset(child);
i = getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
}
}
之上编码中,LinearLayout会解析xml它的全部子View,并启用setChildFrame方式设定子View的部位,编码中的childTop意味着当今子View的top部位主要参数。setChildFrame方式的编码以下:
1 private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
child.layout(left, top, left width, top height);
}
换句话说,在父器皿(这儿为LinearLayout)完成了对联原素部位主要参数(top、left、right、bottom)的获得后,会启用子原素的layout方式,并把获得到的子原素部位主要参数传到,进而进行对联原素的layout全过程。子原素在自身的layout方式中,也会先进行对自身的合理布局(明确四个部位主要参数),再启用onLayout方式进行对他的儿子View的合理布局,那样layout全过程就顺着View树一层层传了下来。
layout全过程进行后,便能够根据getWidth和getHeight方式获得View的最后表明高宽,这俩方式源代码以下:
1 public final int getWidth() {
return mRight – mLeft;
}
1 public final int getHeight() {
return mBottom – mTop;
}
从而便能够了解,根据getMeasuredWidth/getMeasuredHeight方式获得的精确测量高宽与根据getWidth/getHeight方式获得的最后表明高宽的差别:即最后表明宽高是根据View的部位主要参数做差获得的,一切正常状况下应当与精确测量高宽相同。但如果我们重写View的layout方式以下:
1 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.layout(l, t, r, b, r 100, b 100);
}
那样便会造成最后表明高宽比精确测量宽又高又大100。(除非是你很确立的了解自身要想做什么,不然不应该那样做)
(3)draw全过程
关键分成下列六步:
a. 绘图情况;
b. 假如要主视图表明渐变色框,这儿会做一些准备工作;
c.
绘图主视图自身,即启用onDraw()涵数。在View中onDraw()是个空涵数,换句话说实际的主视图都需要override该涵数来完成自身的表明,而针对ViewGroup则不用完成该涵数,由于做为器皿是“沒有內容“的,其包括了好几个子view,而子view早已完成了自身的绘图方式,因而只必须告知子view绘图自身就可以了,也就是下边的dispatchDraw()方式;
d.
绘图子主视图,即dispatchDraw()涵数。在View中它是个空涵数,实际的主视图不用完成该方式,它是专业为容器类提前准备的,也就是容器类务必完成该方式;
e. 假如必须, 逐渐绘图渐变色框;
f. 绘图下拉列表;
draw方式的编码以下:
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & DIRTY_MASK) == DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
//step 2 & 5
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
// we're done...
return;
}
}
}
View的draw全过程的传送根据diapatchDraw来完成,dispatchDraw会解析xml启用全部子View的draw方式,那样draw事情就一层层传了下来。重写View的onDraw方式能够订制View绘图出去的模样,比如完成一些独特的图型和动漫。
View有一个名叫setWillNotDraw的方式,若一个View不用绘图一切內容,可根据这一方式将相对标识设成true,系统软件会开展相对提升。ViewGroup默认设置打开这一标识,View默认设置不打开。
之上就是我学习培训View的绘图步骤后的简易小结,许多地区描述的还不够清楚精确,如有什么问题热烈欢迎大伙儿在发表评论一起探讨 🙂
