International Trade – Final Exam
国际贸易考试代写 1、Consider a world with a home country H and a foreign country F, both populated by L consumers who can only supply their labor domestically.
1、 国际贸易考试代写
Consider a world with a home country H and a foreign country F, both populated by L consumers who can only supply their labor domestically. Every consumer has one unit of labor and consumes goods indexed by w ∈ [0; 1]. Preferences are such that a consumer with income x facing prices {pw} w∈[0;1] chooses to consume {cw}w∈[0;1] according to
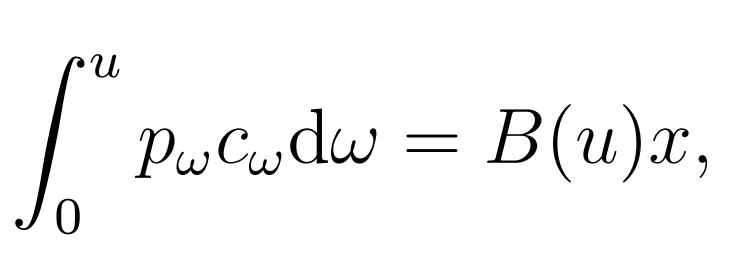
where B(·) is a strictly increasing function with B(0) = 0 and B(1) = 1. Let V (·) be the inverse of B(·), so that b = B(V (b)) for all b ∈ [0,1].
All goods are produced using linear labor-only technologies, with productivities {zw,j}w∈[0,1] in country j ∈{H,F} . The goods are ranked so that A(ω) = zw,H/zw,F is strictly decreasing, and A(0) = ∞ while A(1) = 0. International trade is subject to transportation costs: if one unit of good ! is shipped from country j to the other country, only 1/δj < 1 units arrive.
Write {pw,j}w∈[0,1] for goods prices and ωj for wages in country j, all expressed in some common unit of account.
a. 国际贸易考试代写
Using the fact that there can be no profits and consumers in both countries will buy every good, determine the pw,j in terms of labor productivities, transportation cost parameters, and wages.
b.
Show that the home country produces the goods in [0 , uH) for its domestic market, where uH satisfies wH/wF =δF A(uH). Similarly, show that the foreign country produces the goods in (uF , 1] for its domestic market, where uF must satisfy wH/wF = δF A(uH).
Show that there are goods that are not traded internationally.
c.
State and briefly explain the equilibrium condition for wH/wF and (uH , uF) implied by the fact that labor income in the home country must equal the revenues of home-country producers.
Define bj = the share of country-j consumer expenditures that is imported from abroad.
d.
Explain why uH= V (1 — bH) and uF = V (bF). Use this to eliminate (uH , uF) and wH/wF from the equilibrium conditions given in parts parts b and c. Construct a diagram with bH on the horizontal axis and bF on the vertical axis that shows the resulting equilibrium Explain the shape of these equilibrium conditions.
e.
Showwhat will happen to the wage ratio wH/wF and to the thresholds (uH, uF) when there is a reduction in δF > Prove or disprove: both countvses ms11 gasn espovt mavhets.
2、 国际贸易考试代写
Consider a world with a home country H and a foreign country F, consumption goods 0 and 1, and technologies that use capital and labor. The home country has endowments(KH, JH), and the foreign country has endowments (KF, JF) of capital and labor. The production function for consumption good w ∈ {0,1} is Fw(K , L). These production functions are increasing and concave, and exhibit constant returns to scale. The isoquants of F0 and F1 are smooth and do not hit the axes. Any pair of isoquants for F0 and F1 has one and only one intersection.
Everyone everywhere has identical homothetic preferences. Write pw for the world price of good w ∈ {0,1} and (vj , wj ) for the prices of capital and labor in country j ∈ {H,F}.
a.
Suppose world prices (p0 , p1) are such that country j produces both goods. Construct the Lerner diagram assuming good 0 is the capital intensive good. Explain and
(i) show how you can determine the factor prices (vj ,wj ) from this diagram;
(ii) show how the factor endowments (Kj ,Lj ) are allocated.
b. 国际贸易考试代写
Copy what you need from part a to show what happens to the factor prices (vj ,wj ) in country j when p0 increases.
c.
Copy what you need from part a to show what happens to output (Y0,j , Y1,j) in country j when (i) first Kj goes down and (ii) then Lj increases.
From now on, assume (p0 , p1) are equilibrium prices and that both countries produce both goods. Continue to assume good 0 is the capital intensive good. Assume KH > KF and LH < LF and suppose prices are such that the home country is wealthier than the foreign country.
e.
Construct a diagram that shows the cone of diversification for this economy, the allocation of capital and labor in the two countries, and the factor content of consumption in the two countries. Explain how you are determining the factor content of consumption.
Use the diagram to show which goods the two countries export and import.

更多代写:编程代码 电影代考 英国数学网课代上 波士顿essay代写 北美term paper代写 留学生作业辅导
