Reducing Errors in Pathology Laboratoriess: A focus on Laboratory Staff Skills
Name of Student
Institution
医学Medicine代写 There are different kinds of errors that occur in pathology laboratories. The errors occur at different phases of laboratory processes.
Abrtract
There are different kinds of errors that occur in pathology laboratories. The errors occur at different phases of laboratory processes. In some cases, the errors are associated with the laboratory staff. In particular, lack of adequate training among the staff has contributed immensely to the increased number of errors in clinical laboratories recently. The current paper examines how staff contribute to errors in pathology laboratories. Further, the paper examines how enhancing the skills of the laboratory staff can help to reduce the errors. In order to understand how the staff have contributed to the errors recently, the paper gives an overview of the level of training of the of pathology laboratory staff in the US, as well as the UK laboratory system. Lastly, the paper examines the modern systems that have been implemented in the Australian laboratory system top reduce errors.
译文:
摘要 医学Medicine代写
病理实验室会发生不同类型的错误。 错误发生在实验室过程的不同阶段。 在某些情况下,错误与实验室工作人员有关。 尤其是工作人员缺乏足够的培训,这极大地导致了最近临床实验室中错误数量的增加。 当前的论文研究了工作人员如何导致病理实验室的错误。 此外,本文还探讨了提高实验室工作人员的技能如何有助于减少错误。 为了了解工作人员最近如何导致错误,本文概述了美国病理实验室人员的培训水平以及英国实验室系统。 最后,本文检查了澳大利亚实验室系统中已实施的现代系统减少错误。
Introduction
The risks involved in the health profession are not excluded in the pathology laboratories. The risks can pose serious consequences to both the laboratory staffs and the patients. In some cases, they emanate from the wide range of mechanical, chemical, biological and environmental hazards that the laboratories practices involve (Buesa, 2007). However, the risks are also caused by the errors that occur in the laboratories. While some of the errors are caused by lack of adequate knowledge and skills among the medical laboratory personnel, others are caused by ineffective equipments used in the laboratories. There are universal, as well as national regulations that regulate the qualifications for entry into the medical laboratory profession in different countries.
Although the standards in many countries have been improved to address the problem of inadequate training, there is still a gap between the required and the current level of knowledge and skills for the pathology laboratory personnel (Zima, 2010).
In addition, some pathology laboratories have been able to implement the new modern technologies that are more effective in reducing errors. However, others, especially those that are in community hospitals, have not been able to implement them. 医学Medicine代写
The problems have contributed immensely to the numerous cases of errors that occur in clinical laboratories (Zima, 2010). The eventual impact of such errors is poor quality of care that is provided to patients. The current paper presents a review of the errors that occur in the pathology laboratories and strategies for reducing them, through enhancing the knowledge and skills of the laboratory personnel. Prior to addressing the main topic, the paper gives an overview of the certification and training levels of laboratory personnel in the US, as well as the UK laboratory system.
译文:
介绍 医学Medicine代写
病理实验室不排除卫生专业所涉及的风险。这些风险会对实验室工作人员和患者造成严重后果。在某些情况下,它们源自实验室实践涉及的广泛的机械、化学、生物和环境危害(Buesa,2007)。然而,风险也是由实验室中发生的错误造成的。一些错误是由于医学化验人员缺乏足够的知识和技能造成的,另一些错误是由于实验室使用的设备效率低下造成的。不同国家有通用的和国家级的法规来规范进入医学实验室专业的资格。
尽管许多国家/地区的标准已经改进以解决培训不足的问题,但在病理学实验室(2010 个人)所需的知识和技能水平与当前水平之间仍然存在差距。
此外,一些病理实验室已经能够实施更有效地减少错误的现代新技术。然而,其他人,尤其是那些在社区医院的人,却未能实施。
这些问题极大地导致了临床实验室中发生的众多错误案例(Zima,2010)。此类错误的最终影响是提供给患者的护理质量很差。目前的论文回顾了病理实验室中发生的错误以及通过提高实验室人员的知识和技能来减少这些错误的策略。在讨论主题之前,本文概述了美国实验室人员的认证和培训水平,以及英国的实验室系统。
Certification and training of Medical Laboratories Staff
Different countries have different certification requirements for clinical laboratories. In the US, the federal standards require all medical laboratories are certified under the 1988 Laboratory Improvement Amendments Act (CLIA). The certification given depends on the kind and complexity of testing taking place in the laboratory (Walz, 2013). Other bodies that inspect and set regulations to laboratory practices in the US include Commission on Laboratory Accreditation, the Joint Commission and College of American Pathologists (Sciacovelli Let al., 2010). The standards set in CLIA apply in all countries worldwide. CLIA standards define the roles of each laboratory staff and the required qualifications, depending on the level and complexity of responsibility.
However, Walz (2013) explains, the qualification requirements set by CLIA are considered inadequate by the laboratory professional community, and are viewed as having contributed to the high number of errors that have been occurring in the pathology laboratories. For instance, the staff qualification requirements set in CLIA standards for the moderate and high class laboratories are a high school diploma and additional training in the required field. The problem prompted the 2005 task force of the American Society for the Clinical Laboratory Sciences that explored the educational levels and the requirements of the laboratory staffs. The task force’s position paper was adopted in 2009. In response, the laboratory professional community has responded by setting their own qualification standards for different staff members working in medical laboratories. 医学Medicine代写
Despite the intervention of the laboratory professional community, the current standards set for laboratory workers such as laboratory attendants, assistants/technicians, medical technologists and consultants are still low.
As Walz (2013) explains, the low level of standards has contributed to low level of training among the different staff members working in medical laboratories. For instance, the pathology laboratory technicians are required to attend training programs offered by different organizations in the US and seek certification through agencies such as American Medical Technologists and National Credentialing Agency for Laboratory Personnel.
However, the level of training is not well regulated, and the technicians may qualify after attending training programs for just seven months. As a result, they do not receive adequate training to enable them handle complex tests in clinical laboratories (Walz, 2013). The problem has contributed immensely to the increased number of errors in the pathology laboratories. Figure 1.0 in the presents the laboratory error rate identified by the American College of Pathologists.
译文:
医学实验室工作人员的认证和培训
不同国家对临床实验室有不同的认证要求。在美国,联邦标准要求所有医学实验室都根据 1988 年实验室改进修正案 (CLIA) 进行认证。所提供的认证取决于实验室进行的测试的种类和复杂性(Walz,2013 年)。在美国检查和制定实验室实践法规的其他机构包括实验室认证委员会、联合委员会和美国病理学家学院 (Sciacovelli Let al., 2010)。 CLIA 中设定的标准适用于全球所有国家。 CLIA 标准根据职责的级别和复杂性定义了每个实验室工作人员的角色和所需的资格。
然而,Walz (2013) 解释说,实验室专业团体认为 CLIA 设定的资格要求是不够的,并且被认为是导致病理实验室发生大量错误的原因。例如,CLIA 标准中为中等和高级实验室设定的员工资格要求是高中文凭和所需领域的额外培训。这个问题促使美国临床实验室科学学会 2005 年的工作组探索了实验室人员的教育水平和要求。工作组的立场文件于 2009 年获得通过。 作为回应,实验室专业界对此做出了回应,为在医学实验室工作的不同工作人员制定了自己的资格标准。
尽管实验室专业社区进行了干预,但目前为实验室工作人员(如实验室服务员、助理/技术人员、医疗技术人员和顾问)制定的标准仍然存在。
正如 Walz (2013) 解释的那样,低水平的标准导致在医学实验室工作的不同工作人员之间的培训水平低。例如,病理实验室技术人员必须参加美国不同组织提供的培训计划,并通过美国医疗技术专家和国家实验室人员资格认证机构等机构寻求认证。
但是,培训水平并没有得到很好的规范,技术人员在参加培训项目仅仅七个月后就可能获得资格。因此,他们没有接受足够的培训来处理临床实验室中的复杂测试(Walz,2013)。这个问题极大地导致了病理实验室中错误数量的增加。图 1.0 显示了美国病理学家学会确定的实验室错误率。
Evaluation of the UK Laboratory System
In the UK, the Clinical Pathology Accreditation (CPA-UK) recognizes that a laboratory is an entity that should be held legally responsible (CPA-UK, 2007). In line with this, all the laboratories are required to operate as per the regulations of the CPA that govern laboratory operations. The law thus requires all personnel working in a medical laboratory to have adequate training, authority and resources in order to carry out their duties effectively. In addition, the law requires arrangements to be made to shield the laboratory from internal, external and financial pressures that may compromise results (CPA-UK, 2007). Further, the laboratories are required to make arrangements that would ensure that clients do not lose confidence in the services they provide.
The UK laboratories have a quality policy statement that identifies their scope of practice, standards, intention, commitment to good professional practice, commitment to legislation and a commitment to the welfare and safety of all the staff members, clients and visitors.
In terms of personnel, the UK laboratories are headed by a laboratory director, just like in the US. The director is required to have consultative, educational, administrative and scientific skills. The policy also requires laboratories to have enough personnel to prevent errors that may occur as a result of work overload due to staff shortage. Adherence to the set policies and standards can help to reduce errors in the laboratories. 医学Medicine代写
However, medical laboratories in the UK face shortages of personnel in some areas. For instance, the number of trained medical technologists in clinical laboratories in the UK has been reducing over the last one decade. The problem has also been experienced recently in the US. The problem has been caused by a low level of entry into the profession and a high level exit. The fundamental causes of the problem are the lack of attractive remuneration and too much pressure, among others. Addressing such problems can help to attract more candidates into the profession and hence, face out the problem of shortage. Eventually, the move can help to reduce the number of errors occurring in the laboratory as a result of overload.
译文:
英国实验室系统评估 医学Medicine代写
在英国,临床病理学认证 (CPA-UK) 承认实验室是应该承担法律责任的实体 (CPA-UK, 2007)。根据这一点,所有实验室都必须按照管理实验室操作的 CPA 的规定进行操作。因此,法律要求在医学实验室工作的所有人员都接受足够的培训、权力和资源,以便有效地履行职责。此外,法律要求做出安排以保护实验室免受可能影响结果的内部、外部和财务压力(CPA-UK,2007)。此外,实验室需要做出安排,以确保客户不会对他们提供的服务失去信心。
英国实验室有一份质量政策声明,其中确定了他们的实践范围、标准、意图、对良好职业行为的承诺、对立法的承诺以及对所有员工和 CSITOR 的福利和安全的承诺。
在人员方面,英国实验室和美国一样,由实验室主任领导。主任必须具备咨询、教育、行政和科学技能。该政策还要求实验室有足够的人员,以防止由于人员短缺而导致工作超负荷而可能发生的错误。遵守既定的政策和标准有助于减少实验室中的错误。
然而,英国的医学实验室在某些领域面临着人员短缺的问题。例如,在过去十年中,英国临床实验室中训练有素的医疗技术人员的数量一直在减少。最近在美国也遇到了这个问题。问题是进入这个行业的门槛低,退出的门槛高。问题的根本原因是缺乏有吸引力的薪酬和压力过大等。解决这些问题有助于吸引更多候选人进入该行业,从而解决人才短缺的问题。最终,此举有助于减少实验室因过载而发生的错误数量。
Laboratory Errors and Quality Enhancement
Karkalousos and Evangeloupos (2011) categorize errors depending on the stage of the testing process they occur. In other words, errors can occur in the pre-analytic stage, analytic stage or post-analytic stage (Karkalousos & Evangeloupos, 2011). The pre-analytical stage includes the procedures that are carried out before the analysis of the samples of the patients. Pre-Analytical errors include inappropriate specimen, the wrong anticoagulant, improper conservation method, mistakes in patient identification and inappropriate preparation of the patient (Karkalousos & Evangeloupos, 2011). 医学Medicine代写
The analytical errors occur during the analysis stage. According to Karkalousos and Evangeloupos (2011), most of the errors that occur in the analytical stage are caused by laboratory personnel. Examples of analytical errors include expired reagents, sampling system failure, analyzer failure and a timed-out calibration system (Karkalousos & Evangeloupos, 2011). The post-analytical errors include wrong matching, loss of results and wrong copy of results. Figure 2.0 in the appendix presents the rates and types of errors that occur in the three laboratory testing phases. The errors have significant implications because they affect the reproducibility, precision, accuracy and repeatability of results. Figure 3.0 presents some effects of laboratory errors on patient care.

Some laboratories have installed automated analyzers in an attempt to reduce errors or to generate credible laboratory results.
The automated analyzers are capable of producing multiple results in a short time. As Karkalousos and Evangeloupos (2011) explain, this has been enabled through the incorporation of technology of robotics, computer science and analytical chemistry. However, as Karkalousos and Evangeloupos (2011) explain, statistical quality control is a bit difficult to monitor due to the large number of samples that are taken for testing. In addition, the wide range of varying diagnosis tests conducted in laboratories makes it difficult to use automated analyzers without making errors. As such, automated analyzers are hardly effective in reducing errors in laboratories.
A study conducted by Layfield and Anderson (2010) revealed that 75% of the errors, in a study of a span of 18 months, involved wrong patient labelling. 24% of the errors involved the site that was being labelled. Layfield and Anderson (2010) note that, even though many laboratories have focused on the errors described by the Institute of Medicine’s report of 1999, specimen labelling errors have not been adequately addressed.
译文:
实验室错误和质量提升
Karkalousos 和 Evangeloupos (2011) 根据错误发生的测试过程的阶段对错误进行分类。换句话说,错误可能发生在分析前阶段、分析阶段或分析后阶段 (Karkalousos & Evangeloupos, 2011)。分析前阶段包括在分析患者样本之前执行的程序。分析前错误包括样本不当、抗凝剂错误、保存方法不当、患者识别错误和患者准备不当(Karkalousos & Evangeloupos,2011)。
分析错误发生在分析阶段。根据 Karkalousos 和 Evangeloupos (2011) 的说法,分析阶段发生的大部分错误都是由实验室人员造成的。分析错误的例子包括试剂过期、采样系统故障、分析仪故障和校准系统超时 (Karkalousos & Evangeloupos, 2011)。分析后错误包括错误匹配、结果丢失和结果复制错误。附录中的图 2.0 显示了三个实验室测试阶段中发生的错误率和类型。误差具有重大意义,因为它们会影响结果的再现性、精密度、准确度和可重复性。图 3.0 显示了实验室错误对患者护理的一些影响。
一些实验室已经安装了自动分析仪,以尝试减少错误或生成可靠的实验室结果。
自动分析仪能够在短时间内产生多个结果。正如 Karkalousos 和 Evangeloupos (2011) 解释的那样,这是通过结合机器人技术、计算机科学和分析化学来实现的。然而,正如 Karkalousos 和 Evangeloupos (2011) 解释的那样,由于需要大量样本进行测试,因此统计质量控制有点难以监控。此外,实验室中进行的各种不同的诊断测试使得使用自动分析仪而不会出错变得困难。因此,自动化分析仪在减少实验室错误方面几乎没有效果。
Layfield 和 Anderson (2010) 进行的一项研究表明,在一项为期 18 个月的研究中,75% 的错误涉及错误的患者标签。 24% 的错误涉及被标记的网站。 Layfield 和 Anderson (2010) 指出,尽管许多实验室已经将注意力集中在医学研究所 1999 年报告中描述的错误上,但样本标签错误并未得到充分解决。
According to Layfield and Anderson (2010), the identification errors are also prevalent in the laboratories, and only a few studies have documented them.
The errors lead to a significant harm and inconveniences in patient care. Some of the techniques used to identify labelling errors have often under-estimated the frequency of occurrence of errors, making it difficult to record all the errors that occur in the laboratories (Layfield & Anderson, 2010). However, the pathologists, laboratory staff and clinicians are in a better position to identify labelling and other types of errors. Since expertise is needed in such detection, inadequate skills among the laboratory personnel are likely to increase the frequency of errors in the laboratories.
According to Hammerling (2012), the difficulties in translating new knowledge to practice and implementing new technology are among the factors inhibiting effective reduction of errors in medical laboratories.
Numerous researchers have made recommendations on how to reduce errors in medical laboratories. However, lack of adequate knowledge and training among the laboratory staffs makes it difficult to achieve the improvements. Precisely, many staff members in the medical laboratories are hardly updated with the new knowledge and ways of implementing the advanced, more effective equipments. 医学Medicine代写
In addition, some medical laboratories have not been able to acquire a modern, effective equipments. As such, Hammerling (2012) suggests that the incorporation of new technology in the medical laboratory can help to reduce the errors. In addition, Hammerling (2012) suggests that adequate skills among laboratory staff members can help to reduce documentation errors. Dintzis et al. (2011) highlights the importance of communication in reducing cases of errors in medical laboratories. According to Dintzis et al. (2011), effective communication between laboratory staff members and other health professionals such as doctors and nurses can help to determine the sources of errors as early as possible and to take the necessary action to avoid them. Lippi and Plebani (2009) also highlights the importance of reporting cases of errors in order to establish ways of rectification.
译文:
根据莱菲尔德和安德森 (2010) 的说法,鉴定错误在实验室中也很普遍,只有少数研究记录了这些错误。
这些错误会给患者护理带来重大伤害和不便。一些用于识别标签错误的技术往往低估了错误发生的频率,因此很难记录实验室中发生的所有错误 (Layfield & Anderson, 2010)。然而,病理学家、实验室工作人员和临床医生可以更好地识别标签和其他类型的错误。由于此类检测需要专业知识,实验室人员技能不足可能会增加实验室出错的频率。
根据 Hammerling (2012) 的说法,将新知识转化为实践和实施新技术的困难是阻碍医学实验室有效减少错误的因素之一。
许多研究人员就如何减少医学实验室中的错误提出了建议。然而,实验室工作人员缺乏足够的知识和培训,难以实现改进。确切地说,医学实验室的许多工作人员几乎没有了解使用先进、更有效设备的新知识和方法。
此外,一些医学实验室还没有能够获得现代化、有效的设备。因此,Hammerling (2012) 建议将新技术纳入医学实验室有助于减少错误。此外,Hammerling (2012) 建议实验室工作人员具备足够的技能有助于减少文档错误。丁齐斯等人。 (2011) 强调了沟通在减少医学实验室错误案例方面的重要性。根据 Dintzis 等人的说法。 (2011),实验室工作人员与其他卫生专业人员(如医生和护士)之间的有效沟通有助于尽早确定错误的来源并采取必要的措施来避免这些错误。 Lippi 和 Plebani (2009) 还强调了报告错误案例以建立纠正方法的重要性。
Modern Systems to Reduce Errors
The modern methods of laboratory error reduction have been applied at the pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical stages of specimen processing in the laboratories (Plebani, 2006). However, the pre- and post-analytical stages have been found to be more prone to errors than the analysis phases. The main cause of the problem is that some phases are not in direct control of the laboratory personnel. Continuous monitoring and educational initiatives have highly contributed to the reduction of the errors in the laboratories. Plebani (2006) asserts that between 1999 and 2000, inter-laboratory Q-Tracks improvement programs showed that errors reduced from 7.4 to 3 percent due to continuous monitoring and educational initiatives. Interdepartmental cooperation has also been identified as a measure that has contributed to the reduction of laboratory errors (Plebani, 2006). 医学Medicine代写
The automated analyzers used in the pre-analytical stage have also helped to reduce laboratory errors. The hazards and errors at this stage have further been reduced through the introduction of analytical robotic workstations that are automated (Plebani, 2006). The automatic workstations have helped to reduce errors of labelling, sorting, routing and pour-off. The analytical stage errors have also been significantly reduced through technological advancement and standardization (Plebani, 2006). For example, a high level of accuracy has been achieved in the testing of blood products for infectious agents. Plebani (2006) observes that nucleic acid testing has reduced contamination rates in blood testing from 1 in 100 units to 1 in 1.8 million units. However, interference with immunoassays has led to serious errors.
According to Lippi, Plebani & Šimundić (2010), efforts tailored to reduce medical laboratory errors have been successful in improving patient care in many cases.
Lippi et al. (2010) propose the need to to address the fundamental causes of the errors, rather than individuals. In addition, Lippi et al. (2010) highlight the importance of implementing effective modern technology and supporting decision-making processes in reducing cases of clinical laboratory errors.
According to Da Rin (2009), accountability should also be improved using performance and outcome measures. Da Rin (2009), cite heterogeneity in the definition of laboratory errors as hindrance to good, standardized method of reducing laboratory errors. Da Rin (2009), also emphasizes that the increase in the reduction of laboratory errors has a connection to the lack of adequate training of medical laboratory personnel. In addition, Da Rin (2009), proposes that rules should be adopted to define the allowable errors in order to reduce the errors that arise due to quackery. Proficiency testing programs and external assessment schemes have been found to be effective in reducing laboratory errors. These schemes have also been effective in detecting the sources of errors. According to Da Rin (2009), team working and departmental corporation can also help to reduce laboratory errors.
译文:
减少错误的现代系统 医学Medicine代写
减少实验室误差的现代方法已应用于实验室样本处理的分析前、分析和分析后阶段(Plebani,2006 年)。然而,已经发现分析前和分析后阶段比分析阶段更容易出错。问题的主要原因是某些阶段不受实验室人员的直接控制。持续的监测和教育举措对减少实验室中的错误做出了重大贡献。 Plebani (2006) 声称,1999 年至 2000 年间,实验室间 Q-Tracks 改进计划表明,由于持续的监测和教育举措,错误率从 7.4% 减少到 3%。部门间合作也被确定为有助于减少实验室错误的措施(Plebani,2006 年)。
在分析前阶段使用的自动分析仪也有助于减少实验室错误。通过引入自动化的分析机器人工作站,这一阶段的危险和错误进一步减少(Plebani,2006)。自动工作站有助于减少标签、分类、路由和倾倒方面的错误。通过技术进步和标准化,分析阶段的误差也显着减少(Plebani,2006)。例如,在血液制品的传染性检测中已经达到了很高的准确度。 Plebani (2006) 观察到核酸检测已将血液检测的污染率从 100 个单位中的 1 个降低到 180 万个单位中的一个。然而,对免疫测定的干扰导致了严重的错误。
根据 LIPPI、PLEBANI 和 ŠIMUNDIĆ (2010) 的说法,在许多情况下,为减少医学实验室错误而做出的努力在改善患者护理方面取得了成功。
里皮等人。 (2010) 提出需要解决错误的根本原因,而不是个人。此外,Lippi 等人。 (2010) 强调了实施有效的现代技术和支持决策过程在减少临床实验室错误案例方面的重要性。
根据 Da Rin (2009) 的说法,还应该使用绩效和结果衡量标准来改进问责制。 Da Rin (2009) 引用实验室错误定义中的异质性作为减少实验室错误的良好标准化方法的障碍。 Da Rin (2009) 还强调,实验室错误减少的增加与医学实验室人员缺乏足够的培训有关。此外,Da Rin (2009) 建议应采用规则来定义允许的错误,以减少因骗术而产生的错误。已发现能力验证计划和外部评估计划可有效减少实验室错误。这些方案在检测错误来源方面也很有效。根据 Da Rin (2009) 的说法,团队合作和部门合作也有助于减少实验室错误。
Reducing Errors in Australia and Canada and Successful examples
In Australia, several strategies have been adopted to reduce laboratory errors. Rin (2009) observes that a comprehensive five-step interrelated plan has been devised to reduce errors in Australian laboratories. These steps include developing written procedures that are clear, enhancing healthcare professional training, monitoring laboratory indicators, automating laboratory functions, and improving communication among the healthcare providers, and also between the care providers and the patients. 医学Medicine代写
In Australia, the automation of pre-analytic workstations in the prevention of errors is an example of a successful intervention. According to Rin (2009), the incorporation of automated robotic workstations has greatly reduced the human errors that occurred through human processing. In addition, the automated workstations improved the handling of specimens. The introduction of workstations was also been accompanied by the setting of specific quality goals to ensure that errors in the laboratories are reduced.
A case of success in reducing laboratory errors has also been documented in regard to San Bassanio hospital.
Some of the steps that the management implemented to improve the reduction of laboratory errors are mentioned here. The management installed a wireless network in the hospitals to enhance easy access to images and medical records (Rin, 2009). Other clinical applications have also been employed to ensure that recording of patient data is easily done, even at the bedside. Secondly, computerized order entry systems with highly effective laptops were introduced (Rin, 2009). The improvement has enabled the laboratory personnel to carry out tests and radiology at the patient’s bedside. 医学Medicine代写
Requesting of tests can be done online, hence reducing the errors that result from documentation. Also, automated sample-labelling systems have been introduced in order to reduce labelling errors. The systems are also accompanied by test tube kits that contain the spaces that the laboratory staff should just fill. Another improvement is the introduction of barcode ID wristbands for both the outpatients and inpatients.
The barcode has enabled the system succeed in the reduction of identification errors (Rin, 2009). The other improvement procedure in the reduction of errors is the standardization of collection procedures. Rin (2009) suggests that nurses should receive training in order to make this implementation process a success. Finally, the system has been enhanced through the incorporation of wireless internet to enhance communication between the different departments of the hospital that depend on the laboratory. Leape (2009) asserts that Canada has also recorded progress in incorporating these measures to ensure patient safety.
译文:
减少澳大利亚和加拿大的错误和成功的例子
在澳大利亚,已经采用了几种策略来减少实验室错误。 Rin (2009) 观察到已经制定了一个综合的五步相关计划来减少澳大利亚实验室的错误。这些步骤包括制定明确的书面程序、加强医疗保健专业培训、监控实验室指标、自动化实验室功能以及改善医疗保健提供者之间以及护理提供者与患者之间的沟通。
在澳大利亚,预分析工作站在预防错误方面的自动化是成功干预的一个例子。根据 Rin (2009) 的说法,自动化机器人工作站的加入大大减少了通过人工处理发生的人为错误。此外,自动化工作站改进了样品的处理。工作站的引入还伴随着特定质量目标的设定,以确保减少实验室中的错误。
SAN BASSANIO 医院还记录了一个成功减少实验室错误的案例。
这里提到了管理层为减少实验室错误而实施的一些步骤。管理层在医院中安装了无线网络,以方便访问图像和医疗记录(Rin,2009 年)。其他临床应用也已被采用,以确保即使在床边也能轻松完成患者数据的记录。其次,引入了具有高效笔记本电脑的计算机化订单输入系统(Rin,2009)。改进使实验室人员能够在患者床边进行测试和放射学检查。
测试请求可以在线完成,从而减少文档导致的错误。此外,还引入了自动样本标记系统以减少标记错误。该系统还配有试管套件,其中包含实验室工作人员应该填充的空间。另一项改进是为门诊和住院患者引入了条形码 ID 腕带。
条形码使系统成功地减少了识别错误(Rin,2009)。减少错误的另一个改进程序是收集程序的标准化。 Rin (2009) 建议护士应该接受培训,以使这个实施过程取得成功。最后,通过结合无线互联网增强了系统,以增强依赖实验室的医院不同部门之间的通信。 Leape (2009) 声称加拿大在纳入这些措施以确保患者安全方面也取得了进展。
Conclusion
In conclusion, the review has found that laboratory errors are prevalent and that they are facilitated by defects in the equipment and mistakes by the laboratory staffs. Many of the errors are as a result of adequate training and shortage of laboratory staff members. The paper has also established that laboratory directors and the pathologists are not satisfied with the training system for the laboratory staff.
With the demand for the application of new technology and knowledge in medical laboratories, it warrants that laboratory staffs receive high level education. A comparison of literature shows that training of laboratory staffs has a direct bearing on the reduction of errors in the laboratories. In regard to reduction of errors using modern techniques, some laboratories in the United States, Australia, UK and Canada have adopted new technologies to effect the same. They include the incorporation of workstations, wireless network, automated labelling and standardization of collection procedures. Most of the studies consulted agree that training is an important aspect in reducing medical laboratory errors. More academic studies need to be conducted in this crucial area in order to ascertain the role of adequate skills in reducing laboratory errors.
译文:
结论 医学Medicine代写
综上所述,检讨发现实验室错误普遍存在,并且是由设备缺陷和实验室工作人员的错误促成的。许多错误是由于培训充分和实验室人员短缺造成的。该论文还表明,实验室主任和病理学家对实验室工作人员的培训体系并不满意。
随着新技术和新知识在医学实验室中应用的需求,实验室工作人员接受高水平教育成为了保障。文献比较表明,实验室人员的培训对减少实验室错误有直接的影响。在使用现代技术减少错误方面,美国、澳大利亚、英国和加拿大的一些实验室已经采用了新技术来实现这一点。它们包括工作站的结合、无线网络、自动标记和收集程序的标准化。所咨询的大多数研究都同意,培训是减少医学实验室错误的一个重要方面。需要在这个关键领域进行更多的学术研究,以确定足够的技能在减少实验室错误方面的作用。
References 医学Medicine代写
Bonini, P., Plebani, M., Cerrotti, F., & Rubolli, F. (2002). Errors in Laboratory medicine. Clinical Chemistry, 48(5), 691-698.
Clinical Pathologies Accreditation (CPA-UK). (2007). Standards for the medical laboratory. Rutland Park, UK: Author.
Da Rin G. (2009). Pre-analytical workstations: A tool for reducing laboratory errors. Clin Chim
Acta, 404, 68–74
Dintzis, M. S., Stetsenko, Y. G., Sitlani, M. C., Grownoski, M. A., Astion, M. L., & Galagher, H. T. (2011). Communicating pathology and laboratory errors: Anatomic pathologists and laboratory medical directors’ attitudes and experiences. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 135(5), 760-765.
Hammerling, J. A. (2012). A Review of Medical Errors in Laboratory Diagnostics and Where
We Are Today. LabMedicine, 43, 41-44. 医学Medicine代写
Karkaousos, P., & Evangeloupos, A. (2011). Quality control in clinical laboratories. In InTech, Applications and Experiences of Quality Control. (PP. 321-360). Shanghai: Springer
Layfield, J. L., & Anderson, M. G. (2010). Specimen labelling errors in surgical pathology: An 18-month experience. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 134(3), 466-470.
Leape, L. L. (2009). Errors in medicine. Clinica Chimica Acta, 404 (1), 2-5.
Lippi, G. & Plebani, M. (2009). The importance of incident reporting in laboratory diagnostics. Scand J Clin Lab Invest, 69, 811–813
Lippi, G., Plebani, M. & Šimundić, A. M. (2010). Quality in laboratory diagnostics: From
theory to practice. Biochem Med, 20, 126–130
Plebani, M. (2006). Errors in clinical laboratories or errors in clinical medicine? Clin Chem Lab Medicine, 44 (6), 750-759.
Rin, D. G. (2009). Pre-analytical workstations: A tool for reducing laboratory errors. Clinica Chinica Acta, 404 (2009), 68-74.
Sciacovelli Let al. (2010). The role of the external quality assessment. Biochem Med, 20, 160
164
Silverstein, M. D. (2003). An approach to medical errors and patient safety in laboratory services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Walz, S. E. (2013). Education and training in laboratory medicine in the United States. JIFCC,
24(1), 1-3.
Wefuan, K. F. (2011). The path to improving the quality of laboratory documentation: A case study from Cameroon. A Masters Thesis presented at the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Troms.
Zima, T. (2010). Accreditation in clinical laboratories. Biochemia Medica, 20 92), 215–220.
Appendix 医学Medicine代写
Figure 1.0 Laboratory error rate identified by the American College of Pathologists
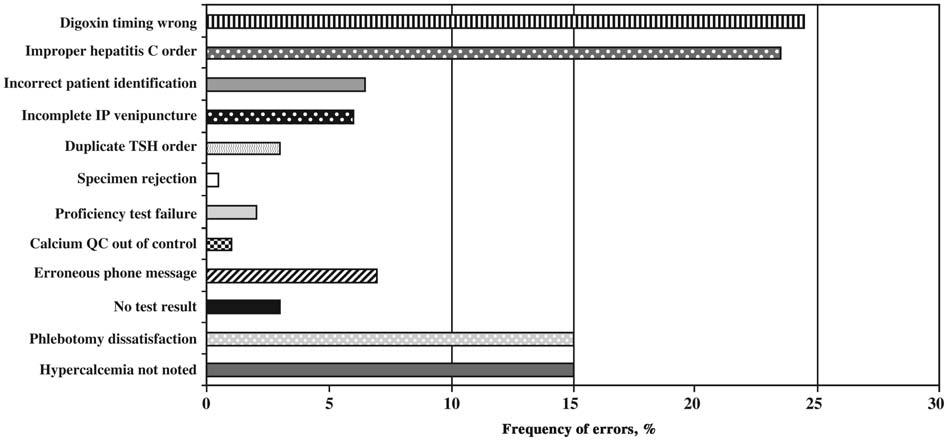
Source: Plebani (2006)
Figure 2.0 The rates and types of errors in the three stages of the laboratory process.
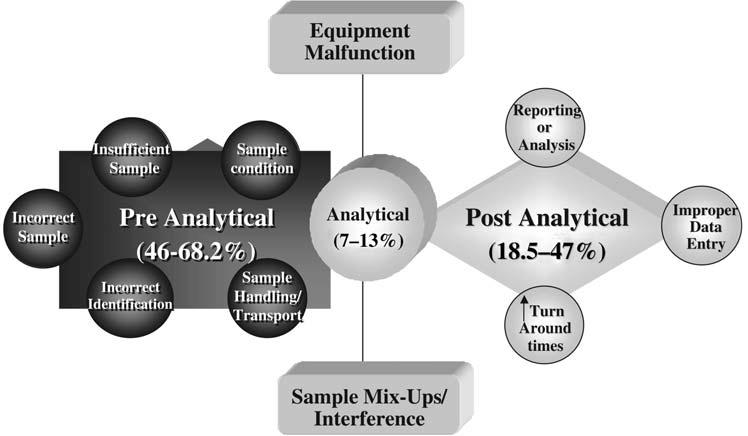
Source: Plebani (2006)
The effect of laboratory errors on patient care.
| Numberof | Effect on | Riskof | |
| errors | patientcare | inappropriate care | |
| • RossandBoone(70) | 336 | 30 | 7 |
| • Nuttinget al.(71) | 180 | 27 | 12 |
| • PlebaniandCarraro(11) | 189 | 26 | 6.4 |
Source: Plebani (2006)

更多代写:美国CS代写 加拿大quiz代考 加拿大代写essay 加拿大留学生Essay怎么写 加拿大高中论文代写 雅思机考作弊
