Urban Health Issue
Presented by
Professor
Subject
Date
医学英文论文写作 The expected recommendations include conducting campaigns to create awareness on the side effects of obesity and how to prevent its prevalence.
Synposting
The following sections will be included in the introduction:
- Overview of urban health issues and their effects to the population
- Obesity prevelance in United Kingdom (U.K.) and United States (U.S.)
This section will introduce readers to obesity and its prevelence for the last two centuries in U.K. and U.S. and compared to other regions in the world.
- The objectives of the study
- Thesis statement
译文:
合成
以下部分将包含在简介中:
城市健康问题及其对人口的影响概述
英国 (U.K.) 和美国 (U.S.) 的肥胖症患病率
本节将向读者介绍肥胖及其在过去两个世纪中在英国和美国的流行情况,并与世界其他地区进行比较。
研究目的
论文的声明
Rationale: why obesity is an urban health issue
According to a recent study, national guidlines on peoples’ ideal weight were drawn and the researchers found that overweight people have higher chances of experiencing mortality risk compared to those of normal weight. These studies show that obesity is an urban health issue and people ought to be more aware of its dangers. Main areas in affected with this health issue in london include Westbournene, Queenspark, Harrow road, church street, churchill, North and South of Borough. In U.K. the prevalence of obesity is slightly higher in females (25.6%) than in males(22.6%) and increases with age (Reilly, et al,2003). Figure 1 shows obesity prevelence in U.K. between 1980 and 2010. Figure 2 shows an epidemiological data on obesity prevelence in relation to age.
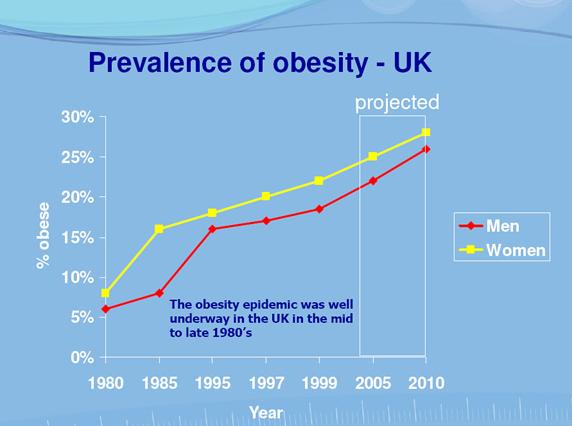
Figure 1: Obesity prevelence in U.K.
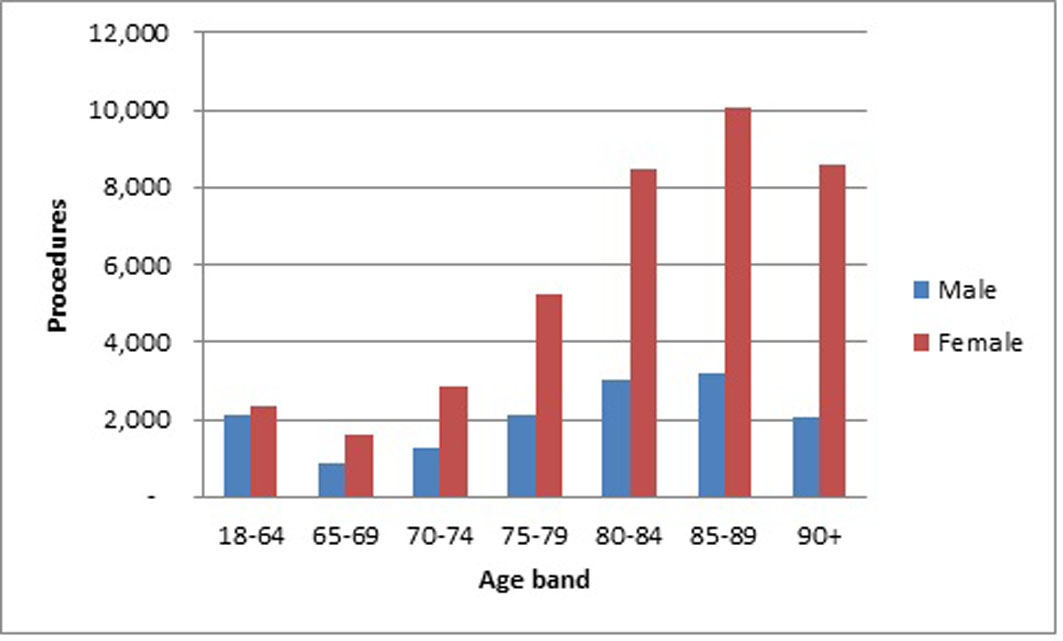
Figure 2: An epidemiological data on obesity prevelence in relation to age
译文:
理由:为什么肥胖是一个城市健康问题
根据最近的一项研究,制定了关于人们理想体重的国家指南,研究人员发现,与正常体重的人相比,超重的人有更高的死亡风险。 这些研究表明,肥胖是一个城市健康问题,人们应该更多地意识到它的危险。 伦敦受此健康问题影响的主要地区包括 Westbournene、Queenspark、Harrow 路、教堂街、丘吉尔、自治市镇的北部和南部。 在英国,女性肥胖患病率 (25.6%) 略高于男性 (22.6%),并且随着年龄的增长而增加 (Reilly, et al, 2003)。 图 1 显示了 1980 年至 2010 年英国的肥胖流行率。图 2 显示了肥胖流行率与年龄相关的流行病学数据。
图 1:英国的肥胖流行率
图 2:肥胖流行率与年龄相关的流行病学数据
The past research shows prevalence of obesity among Westminster dwellers has steadily increased for the past 10 years.
In 2012, around 65%of UK adults were classified as overweight or obese. More than 25% fell under the obese category. It is predicted that there will be continued increase in overweight and obesity across all age groups. Obesity has always been asociated with negative health implications such as diabetes an d cardiovascular diseases. Many deaths have resulted from cardiovascular diseases over the past few years and as aresult, obesity has become an issue of concern to researchers. According to studies, people who live near parks tend to be more physically active because they are likely to use them more for physicall exercises (Millward 2013).
Acording to Dor, Langwith & Tan, (2010), though obesity is common in all population groups, there exists a variation in the distribution across the UK population. It is more prevalent in areas such as Harrow road and Queenspark. Many features of suburban built environment are associated with decreased physical activity hence higher risks of being obese. Some of these features might include street conectivity that do not allow physical activity.
译文:
过去的研究表明,在过去的 10 年里,西敏斯特居民中肥胖症的患病率稳步上升。
2012 年,大约 65% 的英国成年人被归类为超重或肥胖。超过 25% 的人属于肥胖类别。预计所有年龄组的超重和肥胖人数将持续增加。肥胖一直与负面健康影响有关,例如糖尿病和心血管疾病。在过去几年中,许多死亡是由心血管疾病导致的,因此,肥胖已成为研究人员关注的问题。根据研究,住在公园附近的人往往更活跃,因为他们可能更多地使用公园进行体育锻炼(Millward 2013)。
根据 Dor、Langwith 和 Tan (2010) 的说法,尽管肥胖在所有人群中都很常见,但在英国人群中的分布存在差异。它在哈罗路和皇后公园等地区更为普遍。郊区建筑环境的许多特征与体力活动减少有关,因此肥胖的风险更高。其中一些功能可能包括不允许身体活动的街道连通性。
Determinants of obesity in an urban set up
Obesity is a complex phenomena which involves a wide range of behavioural, societal and biological factors. In 1997, obesity was recognised by a World Health Organization as an epidemic. Economic growth and globalization of food markets were found to be the main determinants of obesity. Other determinants include diet, sedentary lifestyles, higher income and changes in consumer behaviour (Gentile, Panico, et al 2010).
Most people in urban areas consume mainly junk foods, snacking and high sugar containing foods which are high in calorie content. Calories are known to be the determining factors of obesity when consumed in large quantities over a given period of time. When talking of physical activity, data shows that people living in Westminster or other urban areas get less than the recomended daily exercises. This results to lack of cardio-respiratory fitness. It is more common among the adult generation since they dont engage in much physical exercises.

Sedentary lifestyles- alot of time is spent watching television, videos or using computers, studying and other sedentary hobies. High level of screen time is usually associated with greate risks of being obese. However, this should not be confused with lack of physical exercise. Most urban dwellers earn high incomes. This comes with prestige and bad consumption habits which lead to obesity (Segel 2011).
译文:
城市环境中肥胖的决定因素
肥胖是一种复杂的现象,涉及广泛的行为、社会和生物学因素。 1997年,肥胖被世界卫生组织认定为流行病。经济增长和食品市场全球化被认为是肥胖的主要决定因素。其他决定因素包括饮食、久坐不动的生活方式、更高的收入和消费者行为的变化(Gentile、Panico 等,2010 年)。
城市地区的大多数人主要消费垃圾食品、零食和高热量的高糖食品。众所周知,卡路里是在给定时间内大量食用时肥胖的决定因素。在谈到体育锻炼时,数据显示居住在威斯敏斯特或其他城市地区的人们获得的日常锻炼量少于推荐的日常锻炼量。这导致缺乏心肺健康。这在成年人中更为常见,因为他们不进行太多的体育锻炼。久坐的生活方式——大量时间花在看电视、视频或使用电脑、学习和其他久坐的爱好上。高水平的屏幕时间通常与肥胖的风险增加有关。然而,这不应与缺乏体育锻炼相混淆。大多数城市居民的收入很高。这伴随着导致肥胖的声望和不良消费习惯(Segel 2011)。
Consequences of obesity
Obesity, just like other diseases, has an impact on communities, nations and even individuals. Some of these effects include heart and stroke diseases, diabetes and cancer. Heart disease and stroke are the major consequences of obesity, and are the major causes of death and disability for both men and women in the Western World. Obese people are more likely to have high blood pressure. This a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, than people who are not overweight. high blood levels of cholesterol and blood fats can also lead to heart disease and often are linked to being overweight (Public Health England 2013).
Diabetes-Obesity
Acording to Bray (2004), diabetes- obesity is usually associated with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes in the Western World. Type 2 diabetes lowers the ability of the body to control blood sugar. This results to early death, heart disease, kidney disease, stroke, and blindness. Type 2 diabetes can be reduced by increase of physical activity.
Cancer
Different types of cancer are brought by obesity. these include cancer of the uterus, gallbladder, cervix, ovary, breast, and colon. This is mostly common in women who are overweight. Overweight men are also have greater chances of getting cancer of the colon and prostate. This is caused by the extra weight and excess fats. Excess weight also leads to premature wear and tear of the joints. There are changes (osteoarthritis) of the knee and hip joints which limits mobility. According to research, Arthritis has been reported to be common in obese women (Pergola, G. D., & Silvestris 2013).
According to (Danaei, et al 2009), the health care costs of obesity in the U.K were estimated to be as high as $170 billion in 2007. This includes amount of money spent directly on medical care and prescription drugs related to obesity. Other costs associated with obesity include cost of lost days of work, insurance premiums, lower income and wages linked to obesity-related complications. Obese employees miss more days from work as a result of short-term complications brought by obesity. Employers on the other hand pay higher life insurance premiums.
译文:
肥胖的后果
肥胖与其他疾病一样,对社区、国家甚至个人都有影响。其中一些影响包括心脏病和中风疾病、糖尿病和癌症。心脏病和中风是肥胖的主要后果,也是西方世界男性和女性死亡和残疾的主要原因。肥胖的人更容易患高血压。与不超重的人相比,这是心脏病和中风的主要危险因素。高胆固醇和血脂水平也会导致心脏病,并且通常与超重有关(Public Health England 2013)。
糖尿病-肥胖症
根据 Bray (2004) 的说法,糖尿病 – 肥胖通常与 2 型糖尿病相关。2 型糖尿病是西方世界最常见的糖尿病类型。 2 型糖尿病会降低身体控制血糖的能力。这会导致早逝、心脏病、肾病、中风和失明。 2 型糖尿病可以通过增加体力活动来减少。
癌症
肥胖会带来不同类型的癌症。这些包括子宫癌、胆囊癌、宫颈癌、卵巢癌、乳腺癌和结肠癌。这在超重的女性中最常见。超重的男性也有更大的机会患上结肠癌和前列腺癌。这是由额外的体重和多余的脂肪引起的。超重还会导致关节过早磨损。膝关节和髋关节的变化(骨关节炎)会限制活动能力。根据研究,据报道关节炎在肥胖女性中很常见(Pergola, G. D., & Silvestris 2013)。
根据 (Danaei, et al 2009),2007 年英国肥胖症的医疗保健费用估计高达 1700 亿美元。这包括直接花费在与肥胖症相关的医疗保健和处方药上的金额。与肥胖相关的其他成本包括误工天数、保险费、收入下降和与肥胖相关并发症相关的工资。由于肥胖带来的短期并发症,肥胖员工会错过更多的工作天数。另一方面,雇主支付更高的人寿保险费。
Policies, preventions and awareness
Regular physical exercises can serve as a better way of preventing obesity. Proper exercise leads to burning of excess calories which cause obesity. Healthy eating habits should be adopted. Foods with high sugar content and excess snacking should be avoided. More fruits and vegetables should be taken. People should be made aware of the health implications of obesity country-wide. This can be done through the mass media and other forms of massage transmission that can reach a larger population at once. Screen time i.e. time spent watching television and using computers should be minimized. (Colditz, 2008).
Personal interventions should be encouraged. This refers to what individuals can do to mitigate this health problem.
An example is vaccination of communicable diseases. Incentives should play a bigger part in encouraging healthy eating and physical exercises. Many legislative proposals can be put in place such as fitness bonuses on tax returns, incentives for weight reduction.
Building standards for public buildings should be encouraged. Buildings with multiple stairs are a good opportunity for people to exercise. Codes could require that the stairs be designed in such a way so as to encourage their use. Nutrition support should also be given to older generation. National strategies to promote and increase consumption of fruits and vegetables and reduce consumption of saturated fats should be formulated. A written policy document which is concerned with nutrition should be drawn up and made available to the whole public. Schools should also chip in by coming up with health and nutrition education programs. This should be a national rule which all schools and colleges should adhere to. The government needs to come up with a legislation requiring labeling of nutritional values of all food stuffs sold. Information such as ingredients and corresponding energy intake should be included.
译文:
政策、预防和意识
定期体育锻炼可以作为预防肥胖的更好方法。适当的运动会燃烧多余的卡路里,从而导致肥胖。应养成健康的饮食习惯。应避免含糖量高的食物和过多的零食。应该多吃水果和蔬菜。应该让人们意识到肥胖对全国范围内的健康影响。这可以通过大众媒体和其他形式的按摩传播来实现,这些传播方式可以同时覆盖更多的人群。屏幕时间,即花在看电视和使用电脑上的时间应该最小化。 (科尔迪茨,2008 年)。
应该鼓励个人干预。这指的是个人可以做些什么来减轻这一健康问题。
一个例子是传染病的疫苗接种。激励措施应该在鼓励健康饮食和体育锻炼方面发挥更大的作用。许多立法提案都可以落实到位,例如纳税申报表上的健身奖金、减轻体重的激励措施。
应鼓励公共建筑的建筑标准。多楼梯的建筑是人们锻炼身体的好机会。法规可能要求楼梯的设计方式以鼓励其使用。还应给予老一辈营养支持。应制定促进和增加水果和蔬菜消费以及减少饱和脂肪消费的国家战略。应起草一份与营养有关的书面政策文件,并向全体公众提供。学校还应该通过提出健康和营养教育计划来参与进来。这应该是所有学校和学院都应该遵守的国家规则。政府需要制定一项立法,要求对所有出售的食品的营养价值进行标签。应包括成分和相应的能量摄入等信息。
Recommendation
The expected recommendations include conducting campaigns to create awareness on the side effects of obesity and how to prevent its prevalence. Secondly, the study will provide a recommendation to the urban dwellers on the type of diet they should take and the amount of weight one is expected to have. Finally, a recommendation to the government and health centers to introduce medical support at low cost for obese people.
译文:
推荐
预期的建议包括开展运动以提高人们对肥胖副作用以及如何预防其流行的认识。 其次,该研究将为城市居民提供关于他们应该采取的饮食类型和预期体重的建议。 最后,建议政府和健康中心为肥胖人群提供低成本的医疗支持。
Conclusion
Obesity is a general health problem that affects all age groups and as a result, all parties should take participation in reducing and preventing its effects. The ministry of health, together with ministry of agriculture should come up with proper administrative structure responsible for the implementation of the above policies.
译文:
结论
肥胖是影响所有年龄组的普遍健康问题,因此,所有各方都应参与减少和预防其影响。 卫生部会同农业部应制定适当的行政结构,负责实施上述政策。
References list
BRAY, G. A. 2004). “Medical consequences of obesity,” Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 89(6), 1-32.
CAWLEY, J. MEYERHOEFER, C. (2012). “The medical care costs of obesity, an instrumental variables approach,” Journal of Health Economics, 31(1), 219-300
COLDITZ G. W. & WANG, Y. C. (2008). Economic costs of obesity, Obesity Epidemiology, New York: Oxford University Press.
DANAE, G., DING, E. L., Mozaffarian, D., et al. (2009). The preventable causes of death in the United States, comparative risk assessment of dietary, lifestyle, and metabolic risk factors,
COLDITZ G. A. (2009). Economic costs of obesity. Retrieved from:
DAY, K. & ALFONZO, M, (2009). Overweight and obesity in urban centers. New York:
DOR, A. F., LANGWITH, C., & TAN, E. (2010). A heavy burden, The individual costs of being overweight and obese in the United States, The George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services Department of Health Policy.
FINKELSTEIN, E. A., TROGDON, J. G., COHEN, J. W. & DIETZ, W. (2009). Annual medical spending attributable to obesity: Prayer-and-service specific estimates. Project HOPE-The People-to-People Health Foundation, Inc. retrieved from:
http://dhss.alaska.gov/ahcc/Documents/meetings/200908/pdf/obesity.pdf
GENTILE, M., PANICO, S., RUBBA, F., MATTIELLO, A., CHIODINI, P., JOSSA, F., ET AL. (2010). “Obesity, overweight, and weight gain over adult life are main determinants of elevated hs-CRP in a cohort of Mediterranean women, “European Journal of Clinical Nutrition,64(8), 873-878.
MILLWARD, D. J. (2013). Energy balance and obesity: a UK perspective on the gluttony v. sloth debate. Nutrition Research Reviews, 26(02), 89-109.
PANEL, NHLBI OBESITY EDUCATION INITIATIVE EXPERT. (1998). Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. Bethesda (MD): National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
PERGOLA, G. D., & SILVESTRIS, F. (2013). Obesity as a Major Risk Factor for Cancer. Journal of Obesity, 2013. Retrieved November 18, 2013, from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/291546
PUBLIC HEALTH ENGLAND. (2013, November 14). Home :: Public Health England Obesity Knowledge and Intelligence team. Home :: Public Health England Obesity Knowledge and Intelligence team. Retrieved March 8, 2014, from:
http://www.noo.org.uk/
REILLY, J., METHVEN, E., McDOWELL, Z., HACKING, B., ALEXANDER, D., STEWART, L & KELNAR, C. (2003). “Health consequences of obesity,” Archives of disease in childhood, 88(9), 748-752.
RUSELL, P., LOPEZ, H. & PATRICIA, (2004). Obesity, physical activity and urban environment. USA: Environmental Health: A Global Access Science Source
SEGEL, C. M. (2011). Childhood obesity risk factors, health effects, and prevention. New York: Nova Science.
TROGDON, J. G., FINKELSTEIN, E. A., HYLANDS, T., DELLEA, P. S., KAMAL-BAHL, S. J. (2008). “Indirect costs of obesity, a review of the current literature.” Obesity Review, 9(5), 489-500.
WANG, C. Y., MCPHERSON, K., MARSH, T., GORTMAKER, S., & BROWN, M. (2011). “Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK,” The Lancet, 378(9793), 525-527
ZAMBONI, M. G, ET AL. (2005). “Health consequences of obesity in the elderly, a review of four unresolved questions.” International journal of obesity, 29(9), 55-71

更多代写:计算机作业代写 GMAT考试代考 英国建筑业会计Essay代写 英国Essay代写费用 英国金融学论文代写 雅思保分助考
